
Table of Contents
Troubleshooting the Installation
Troubleshooting the Installation
Your Cisco 7206 router went through extensive testing before leaving the factory. However, if you encounter problems starting the router, use the information in this chapter to help isolate the cause of the problems. This chapter contains the following sections:
The procedures in this chapter assume that you are troubleshooting the initial system startup, and that the Cisco 7206 is in the original factory configuration. If you have removed or replaced components or changed any default settings, the recommendations in this chapter might not apply. Make sure to review the safety warnings listed in the appendix "Translated Safety Warnings" before using the troubleshooting procedures in this chapter.
If you are unable to easily solve the problem, contact a customer service representative for assistance and further instructions. Provide the representative with the following information:
- Date you received the router
- Chassis serial number
- Type of software and release number
- Brief description of the problem you are having
- Brief explanation of the steps you have taken to isolate and resolve the problem
- Maintenance agreement or warranty information
Figure 5-1 shows the general troubleshooting strategy described in this chapter. Refer to this chart, as necessary, to follow the steps to isolate problems to a specific subsystem; then resolve the problem if possible.
Figure 5-1 : Troubleshooting Strategy for Startup Problems
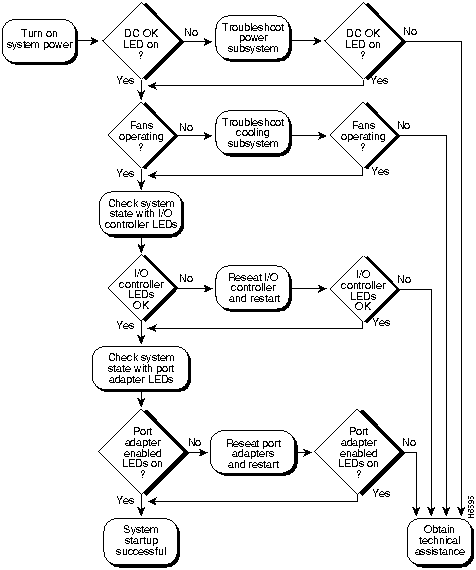
Troubleshooting Overview
This section describes the troubleshooting methods used in this chapter and describes how the Cisco 7206 is divided into subsystems for more efficient problem solving.
Problem Solving with Subsystems
The key to solving problems with the system is isolating the problem to a specific subsystem. The first step in solving startup problems is to compare what the system is doing to what it should be doing. Because a startup problem is usually caused by a single component, it is more efficient to first isolate the problem to a subsystem rather than troubleshoot each component in the system. For these troubleshooting procedures, consider the following subsystems:
- Power subsystem---This subsystem comprises the power supplies, the external power cable, and the midplane.
- Cooling subsystem---The chassis fan tray is the single component in this subsystem. The fans should be operating whenever system power is on. Replace the fan tray if you determine a fan is not functioning properly.
- Processor subsystem---This subsystem includes the I/O controller, network processing engine, and all port adapters. The system memory and management functions reside on the I/O controller and the network processing engine, and the enabled LED on each port adapter indicates if the port adapter is initialized. A port adapter that is partially installed in the midplane can cause the system to hang and crash.
The following sections will help you isolate a problem to one of these subsystems and direct you to the appropriate troubleshooting section.
Identifying Startup Problems
Startup problems are commonly due to the source power or to a board (network processing engine, I/O controller, or port adapter) that is dislodged from the midplane. Although an overtemperature condition is unlikely at initial startup, the environmental monitoring functions are included in this chapter because they also monitor internal voltages.
When you start up the Cisco 7206 for the first time, you should observe the startup sequence described in the section "Starting the Cisco 7206" in the chapter "Installing the Cisco 7206." This section contains a more detailed description of the normal startup sequence and describes the steps to take if the system does not perform that sequence as expected.
With the exception of the fan tray and network processing engine, LEDs indicate all system states in the startup sequence. By checking the state of the LEDs, you can determine when and where the system failed in the startup sequence. Use the following descriptions to isolate the problem to a subsystem, then proceed to the appropriate sections to try to resolve the problem.
When you start up the system by turning on the power supply switch, the following should occur:
- You should immediately hear the fans operating. If not, proceed to the section "Troubleshooting the Cooling Subsystem" later in this chapter. If you determine that the power supply is functioning normally and that a fan is faulty, contact a customer service representative. If a fan does not function properly at initial startup, there are no installation adjustments that you should make.
- The power supply's green power OK LED (at the rear of the chassis) should come on immediately when you place the power supply switch in the on (|) position, and remain on during normal system operation.
- If the green Power OK LED does not come on, proceed to the section "Troubleshooting the Power Subsystem."
- The LEDs on the I/O controller should come on as follows:
- The IO power OK LED comes on immediately and indicates that the I/O controller is receiving DC power from the router midplane. This LED comes on during a successful router boot and remains on during normal operation of the router.
- If this LED remains off when starting the router, either there is a problem with the power supply (it is damaged or not connected to the router midplane), or the network processing engine or the I/O controller are not connected to the router midplane. Proceed to the section "Troubleshooting the I/O Controller, " later in this chapter.
- The enabled LED comes on after the IO power OK LED and indicates that the network processing engine and the I/O controller are enabled for operation by the system; however, it does not mean that the Fast Ethernet port on the I/O controller is functional or enabled. This LED comes on during a successful router boot and remains on during normal operation of the router.
- If this LED remains off when starting the router, it is probably a problem with the network processing engine or the I/O controller (they are damaged or not connected to the router midplane). Proceed to the section "Troubleshooting the I/O Controller," later in this chapter.
- The FE enabled LED comes on after the enabled LED and indicates that the Fast Ethernet port on the I/O controller is initialized and enabled for operation by the system. This LED comes on during a successful router boot and remains on during normal operation of the router.
- If this LED remains off when starting the router, it is probably a problem with the Fast Ethernet port on the I/O controller. Proceed to the section "Troubleshooting the I/O Controller," later in this chapter.
- The FE link LED comes on when only when the Fast Ethernet port on the I/O controller is receiving a carrier signal from the network. This LED remains off during normal operation of the router unless there is an incoming carrier signal, and does not indicate startup problems.
- The slot 1 and slot 2 LEDs come after the enabled LED and indicate which PCMCIA slot is in use. During a successful router boot, these LEDs come on and remain on if a Flash memory card is present in the slot. These LEDs also blink when either slot is being accessed by the system. These LEDs do not indicate startup problems.
- The enabled LED on each port adapter comes on when the network processing engine completes its initialization of the port adapter for operation. The enabled LED indicates that the port adapter is receiving power and has been recognized by the network processing engine; it does not indicate the state of the individual interfaces on the port adapters. If an enabled LED fails to come on, proceed to the section "Troubleshooting the Port Adapters," later in this chapter.
- When all LEDs come on to indicate that the system has booted successfully, the initial system banner should be displayed on the console screen. If it is not displayed, refer to the section "Console and Auxiliary Port Connection Equipment" in the chapter "Installing the Cisco 7206" to verify that the terminal is set correctly and that it is properly connected to the I/O controller's console port.
Troubleshooting the Power Subsystem
Check the following to help isolate a problem with the power subsystem:
- On the first power supply, is the power OK LED on?
- If yes, the power source is good, and the power supply is functional.
- If no, make sure the power cable is connected at both ends.
- If the power OK LED remains off, and the power switch is set correctly, suspect the power source or the power cable. Turn the switch off, connect the power cable to another power source, if available, and turn the switch back on. If the LED comes on, the problem is the first power source.
- If the power OK LED fails to come on after you connect the power supply to a new power source, replace the power cord, and turn the switch back on. If the AC power (or input power) LED then comes on, return the first power cable for replacement.
- If the LED still fails to come on when the power supply is connected to a different power source with a new power cable, the power supply is probably faulty. If a second power supply is available, install it in the other power supply bay and contact a service representative for further instructions.
- Is the power OK LED on for the second (redundant) power supply?
If you are unable to resolve the problem or you determine that either a power supply or chassis connector is faulty, contact a service representative for instructions.
Troubleshooting the Processor Subsystem
The processor subsystem comprises the I/O controller, network processing engine, and all port adapters. The I/O controller and network processing engine are required system components. The system cannot operate unless the I/O controller and network processing engine are installed properly; however, the system can operate without any port adapters installed as long as none are in partial contact with the midplane pins. A port adapter that is partially connected to the midplane will send incomplete signals to the processor, which will fault the PCI bus and cause the system to hang. Therefore, first ensure that the I/O controller and the network processing engine are installed properly and the system software has initialized successfully. Then, if necessary, you can troubleshoot individual port adapters.
Troubleshooting the I/O Controller
These procedures assume that the I/O controller, network processing engine, and router itself are in the original factory configuration, and that you have not made changes to your configuration file.
If the I/O controller LEDs do not go on as expected (refer to the section "Identifying Startup Problems" in this chapter), check the following items to help isolate the problem.
- Do all of the I/O controller LEDs remain off when the system power switch is turned on?
- If the LEDs stay off, first refer to the sections "Troubleshooting the Power Subsystem" and "Troubleshooting the Cooling Subsystem" in this chapter to ensure that both the fans and the power supply are functioning properly.
- If the power supply and fans appear operational but none of the I/O controller LEDs are on, suspect that an improperly connected I/O controller or port adapter has hung the system. Tighten all captive installation screws, and then restart the system.
- With the power supply turned off, reseat the I/O controller in its slot and restart the router.
- Is the I/O controller enabled LED on?
- If yes, the system software has initialized successfully, and the system is operational.
- If the enabled LED remains off, the system detected a processor hardware failure. (This LED should be on in normal operation.) Contact a service representative for instructions.
Troubleshooting the Network Processing Engine
These procedures assume that the I/O controller, network processing engine, and router itself are in the original factory configuration, and that you have not made changes to your configuration file.
If the I/O controller enabled LED does not go on as expected, make sure the power to the router is turned off, reseat the network processing engine in its slot, and restart the router.
If the enabled LED remains off, the system detected a processor hardware failure. (This LED should be on in normal operation.) Contact a service representative for instructions.
Troubleshooting the Port Adapters
Check the following to help isolate a problem with the port adapters:
- Are all port adapter enabled LEDs on?
- If yes, the system is operational.
- Are any port adapter enabled LEDs off?
- If the enabled LED on an individual port adapter is off, suspect that the port adapter has pulled away from the midplane. Reseat the port adapter in its slot (you do not have to turn off the system power when removing or replacing port adapters). After the system reinitializes the interfaces, the enabled LED on the port adapter should go on.
- If the enabled LED remains off, the system detected a processor hardware failure. (This LED should be on in normal operation.) Contact a service representative for instructions.
Troubleshooting the Cooling Subsystem
Check the following to help isolate a problem with the cooling system:
- When you start up the system, do the fans start operating?
- To determine if the fans are operating, listen for them. In noisy environments, place your hand on the left side of the chassis (when viewing the chassis from the front) to feel for air being forced out the vents.
- If yes, the power to the fan tray is good.
- If no, there is a problem with the fan tray or power. Refer to the section "Troubleshooting the Power Subsystem" in this chapter.
- The following message, if displayed, indicates that the system has detected an overtemperature condition or out-of-tolerance power inside the chassis.
Queued messages:
%ENVM-1-SHUTDOWN: Environmental Monitor initiated shutdown
- If an environmental shutdown results from an out-of-tolerance power condition, the power OK LED will go off and the system shuts down. (Refer to the section "Troubleshooting the Power Subsystem" in this chapter.) Although an overtemperature condition is unlikely at initial startup, ensure that heated exhaust air from other equipment is not entering the router's inlet vent, and that there is sufficient clearance around the sides of the chassis to allow cooling air to flow. Refer to the section "Preventive Site Configuration: Maintaining Normal Operation" in the chapter "Preparing for Installation" for preventive site configurations.
- The above message could also indicate a faulty component or temperature sensor. Before the system shuts down, use the show environment or show environment table command to display the internal chassis environment. (Refer to the section "Functional Overview" in the chapter "Product Overview" for descriptions of the show environment and show environment table commands.)
If you experience trouble with the startup that is not resolved with these procedures, contact a service representative for assistance and further instructions.
Copyright 1988-1996 © Cisco Systems Inc.
