|
|
This chapter discusses the initial configuration of the Catalyst 5000 series switch and describes how you configure such functions as IP addressing and SNMP management. An IP address must be assigned if you need to use Telnet to connect to the switch or use SNMP network management for the switch. Up to eight simultaneous Telnet sessions are possible. If your Telnet station or SNMP network management workstation is on a different network from the switch, a static routing table entry must also be added to the routing table. Use the set ip route command to set the static routing table entry.
The Catalyst 5000 features you can customize have default values that will most likely suit your environment, and you will probably not need to change them. The default values of these features are set as follows:
The sections listed below describe how to initially configure the Catalyst 5000 series switch:
You configure the switch through the command line using three basic types of commands: set, show, and clear. Use the set commands to establish switch parameters. After each set command, use the show command to verify that you have entered the correct values and configured the switch correctly. If you make errors, use the set or clear command to overwrite or erase the parameter.
For a list of available commands, type set help, show help, or clear help. To display the command usage, type the command and the word help, as the following example shows:
Console> (enable) set spantree hello help
Usage: set spantree hello <interval> [vlan]
(interval = 1..10, vlan = 1..1000)
Before you begin your configuration, you will need the following information:
Establishing the Console Port Connection
After installing and connecting the switch, perform the following steps to start up and access the switch.
| Task | Command |
|---|---|
| Turn ON the power to the switch and the console terminal. The information shown in Figure 5-1 appears on the screen. | None |
| Access the console port using the console terminal. | None |
| At the Enter password prompt, press Return. | None |
| Enter privileged mode. | enable |
| At the Enter password prompt, press Return. | None |
Figure 5-1 : Initial Bootup Example
ATE0 ATS0=1 Catalyst 5000 Power Up Diagnostics Init NVRAM Log LED Test ROM CHKSUM DUAL PORT RAM r/w RAM r/w RAM address test Byte/Word Enable test RAM r/w 55aa RAM r/w aa55 EARL test BOOTROM Version 1.4, Dated Dec 5 1995 16:49:40 BOOT date: 00/00/00 BOOT time: 03:18:57 SIMM RAM address test SIMM Ram r/w 55aa SIMM Ram r/w aa55 Start to Uncompress Image ... IP address for Catalyst not configured BOOTP will commence after the ports are online Ports are coming online ... Cisco Systems Console Enter password: Thu Mar 21 1996 03:20:41 Module 1 is online Enter Password: Thu Mar 21 1996 03:20:41 Module 2 is online Enter Password: Sending RARP request with address 00:40:0b:6c:2b:ff Sending bootp request with address: 00:40:0b:6c:2b:ff Sending RARP request with address 00:40:0b:6c:2b:ff Sending bootp request with address: 00:40:0b:6c:2b:ff Sending RARP request with address 00:40:0b:6c:2b:ff Sending bootp request with address: 00:40:0b:6c:2b:ff Sending RARP request with address 00:40:0b:6c:2b:ff Sending bootp request with address: 00:40:0b:6c:2b:ff Sending RARP request with address 00:40:0b:6c:2b:ff Sending bootp request with address: 00:40:0b:6c:2b:ff Sending RARP request with address 00:40:0b:6c:2b:ff Sending bootp request with address: 00:40:0b:6c:2b:ff Sending RARP request with address 00:40:0b:6c:2b:ff Sending bootp request with address: 00:40:0b:6c:2b:ff Sending RARP request with address 00:40:0b:6c:2b:ff Sending bootp request with address: 00:40:0b:6c:2b:ff Sending RARP request with address 00:40:0b:6c:2b:ff Sending bootp request with address: 00:40:0b:6c:2b:ff Sending RARP request with address 00:40:0b:6c:2b:ff Sending bootp request with address: 00:40:0b:6c:2b:ff Console> Console> enable Enter password: Console> (enable)
Setting the System Information
Although not required, several system parameters should be set as part of the initial system setup. To set the system parameters, perform the following steps in privileged mode:
| Task | Command |
|---|---|
| Set the system contact. | set system contact contact_string |
| Set the system location string. | set system location location_string |
| Set the system name. | set system name name_string |
| Set the system clock. | set time day_of_week mm/dd/yy hh:mm:ss |
| Set the system prompt. | set prompt prompt_string |
| Set password protection for accessing the command line in normal mode. | set password |
| Set password protection for accessing the command line in privileged mode. | set enablepass |
To set the interface type, perform the following steps in privileged mode:
| Task | Command |
|---|---|
| If you are using a local network connection to the console port, set the logical port sc0. Assign the Catalyst 5000 IP address to a VLAN. See Figure 5-2 for an example. | set interface sc0 up
set interface sc0 ip_address [netmask [broadcast]] set interface sc0 vlan_num ip_address |
| If you are using a SLIP connection to the console port, set the slip port sl0. Figure 5-2 for an example. | set interface sl0 up
set interface slip_address dest_address |
| Configure static routes. For example, you need to configure static routes if your Telnet station or SNMP network management workstation is on a different network from the switch. | set ip route destination gateway [metric] |
| Configure a default route, if desired. See Figure 5-2 for an example. | set ip route default gateway metric |
| Check the status of the configuration of the switch. See Figure 5-3 for an example. | show interface |
| Display the route table entries of the configuration. See Figure 5-4 for an example. | show ip route |
Figure 5-2 : set interface and set ip route Commands Example
Console> (enable) set interface sc0 up Interface sc0 administratively up. Console> (enable) set interface sc0 192.200.11.44 255.255.255.0 \ 192.200.11.255 Interface sc0 IP address and netmask set. Console> (enable) set interface sl0 up Interface sl0 administratively up. Console> (enable) set interface sl0 192.200.10.45 192.200.10.103 Interface sl0 SLIP and destination address set. Console> (enable) set interface sc0 5 1 Interface sc0 vlan set. Console> (enable) set ip route default 192.122.173.42 Route added.
Figure 5-3 : show interface Command Examples
The default configuration is as follows:
Console> (enable) show interface
sl0: flags=10<DOWN,POINTOPOINT>
vlan1 inet 0.0.0.0 netmask 0.0.0.0 broadcast 0.0.0.0
sc0: flags=863<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING>
inet 0.0.0.0 netmask 0.0.0.0 broadcast 0.0.0.0
Console> (enable)
After the set interface command has been executed, the show interface command shows the following configuration:
Console> (enable) show interface
sl0: flags=10<DOWN,POINTOPOINT>
inet 192.200.10.45 netmask 192.200.10.103 broadcast 192.200.10.103
sc0: flags=863<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING>
inet 192.200.11.44 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.200.11.255
Console> (enable)
Figure 5-4 : show route Command Example
Console> (enable) show ip route Redirect -------- enabled Destination Gateway Flags Use Interface --------------- --------------- ------ ---------- --------- default 192.22.74.102 UG 59444 sc0 192.22.74.0 192.22.74.223 U 5 sc0 Console> (enable)
Configuring SLIP on the Console Port
To configure the console port for SLIP, perform the following steps:
| Task | Command |
|---|---|
| Access the switch from a remote host with Telnet. | None |
| Set the IP address of the console port. | set interface slip_address dest_address |
| Enable the SLIP for the console port. | slip attach |
IP address information can be set using BOOTP protocol. You can configure a BOOTP server with the MAC and IP addresses of the switch. When the switch boots, it automatically retrieves the IP address from the BOOTP server.
The switch performs a BOOTP request only if the current IP address is set to 0.0.0.0. (This is the default for a new switch or a switch that has had its configuration file cleared using the clear config all command.)
To configure a workstation as a BOOTP server, you must determine the MAC address of the switch and add that MAC address to the BOOTP configuration file on the server. The following steps provide an example of creating a BOOTP server on a Sun workstation:
Figure 5-5 : show module Command Example
Figure 5-6 : BOOTP Tab File on a Sun Workstation Example
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP), an application-layer protocol, facilitates the exchange of management information bases (MIBs) between network devices. SNMP community strings authenticate access to the MIB and function as embedded "passwords." For an SNMP message to be processed, the community string must match one of following three community-string modes configured in the switch:
The switch sends a trap to the receiver (such as an SNMP manager or workstation) under the following conditions:
The set snmp trap command enters the IP address of the receiving station into the trap receiver table, which can hold up to ten addresses. When you enter addresses in the table, you must specify the community string that will appear in the trap message. You can control whether or not the switch issues a trap by using the set snmp trap enable or set snmp trap disable command.
To configure the switch to be managed using an SNMP network management workstation, perform the following steps:
Figure 5-7 : set snmp Command Example
Figure 5-8 : show snmp Command Example
Setting Up Remote Monitoring (RMON)
To configure the switch for remote monitoring (RMON perform the following steps:
Figure 5-9 : set snmp rmon Command Example
Figure 5-10 : show snmp Command Example
VLANs allow ports on the same or different switches to be grouped so that traffic is confined to members of that group only. This feature restricts broadcast, unicast, and multicast traffic (flooding) to only ports included in a certain VLAN. You can set up VLANs for an entire management domain from a single Catalyst 5000 series switch. A maximum of 250 VLANs can be active at any time.
Setting up VLANs for a management domain requires two tasks, as follows:
Creating VLANs in a Management Domain
The set vtp and set vlan commands use Virtual Trunk Protocol (VTP) to set up VLANs across an entire management domain. The default configuration has all switched Ethernet ports and Ethernet repeater ports grouped as VLAN 1.
By default, Catalyst 5000 switches are in a no-management domain state. They remain in this state until they are configured with a management domain or receive an advertisement for a domain. If a switch receives an advertisement, it inherits the management domain name and configuration revision number; it ignores advertisements with a different management domain or a smaller configuration revision number and checks all received advertisements with the same domain for consistency. While a Catalyst 5000 series switch is in the no-management domain state it is a VTP server that learns from received advertisements.
The set vtp command sets up the management domain. It establishes a management domain name, VLAN trunk protocol mode of operation (server, client, or transparent), interval between VLAN advertisements, and password value. There is no default domain name (the value is set to null). The default advertisement interval is five minutes. The default VLAN trunk protocol mode of operation is set to server.
By default, management domains are set to non-secure mode without a password. Adding a password sets the management domain to secure mode. A password must be configured on each Catalyst 5000 series switch in the management domain to use secure mode.
The set vlan command uses the following parameters to create a VLAN in the management domain:
The Catalyst 5000 uses the security association identifier (SAID) parameter of the set vlan command to identify each VLAN.The default SAID for VLAN 1 is 100001, for VLAN 2 is 100002, for VLAN 3 is 100003, and so on. The default maximum transmission unit (mtu) is 1,500 bytes. The default state is active on an 802.10 trunk.
When translating from one VLAN type (Ethernet, FDDI, Token Ring, FDDI NET, or TR NET) to another, the Catalyst 5000 series switch requires a different VLAN number for each media type.
To create a VLAN across a networking domain, perform the following steps in privileged mode:
Figure 5-11 : set vtp Command Example
Figure 5-12 : show vtp domain Command Example
Figure 5-13 : set vlan Command Example
Figure 5-14 : VLAN Configuration Across a Management Domain
Figure 5-15 : show vlan Command Display Sample
Grouping Switch Ports to VLANs
A VLAN that is created in a management domain remains unused until it is mapped to Catalyst 5000 switch ports. The set vlan command maps VLANs to ports.
The default configuration has all Ethernet ports on VLAN 1. However, you can enter groups of ports as individual entries, for example, 2/1,3/3,3/4,3/5. You can also use a hyphenated format, for example, 2/1,3/3-5.
To create a VLAN, perform the following steps in privileged mode:
Figure 5-16 : set vlan Command Example
Figure 5-17 : Local VLAN Configuration
Figure 5-18 : show vlan Command Display Sample
Use the set trunk command to configure trunks on ports and to configure the mode for the trunk: on, off, desirable, or auto. To establish a trunk, the port on each Catalyst 5000 series switch must be configured as a trunk port. To establish trunks, perform the following steps in privileged mode:
Figure 5-19 : set trunk Command Example
Figure 5-20 : show trunk Command Display Sample
After you have configured the IP address(es), test for connectivity between the switch and a host. The host can reside anywhere in your network. To test for connectivity, perform the following steps:
For example, to test connectivity from the switch to a workstation with an IP address of 192.34.56.5, enter the command ping 192.34.56.5. If the switch receives a response, the following message is displayed:
Copyright 1988-1996 © Cisco Systems Inc.
![]()
Task
Command
Install the BOOTP server code on the workstation, if it is not already installed.
None
Obtain the first address in the MAC address range for module 1 (the supervisor module). Figure 5-5 shows an example of the show config command output. In this example, the first MAC address shown for module 1 is 00-04-0b-90-b5-00.
show module
Add an entry in the BOOTP configuration file (usually /usr/etc/bootptab) for each Catalyst 5000 series switch. Press Return after each entry to create a blank line between each entry. In the example in Figure 5-6, ht is hardware type, ha is hardware address (use the first address in the MAC address range), sm is the network subnet mask, and ip is IP address.
None
Console> (enable) show module
Mod Module-Name Ports Model Serial-Num Hw Fw Sw Status
--- --------------- ------ -------- ---------- ------ ------ ----- ------
1 2 WS-X5009 000102691 1.40 1.12 1.12 ok
2 24 WS-X5010 000095702 1.302 1.12 1.12 ok
3 24 WS-X5010 000124907 1.304 1.12 1.12 ok
Mod MAC-Address(es)
--- ----------------------------------------
1 00-40-0b-90-b5-00 thru 00-40-0b-90-b8-ff
2 00-40-0b-30-04-f8 thru 00-40-0b-30-05-0f
3 00-40-0b-30-04-08 thru 00-40-0b-30-04-1f
Console> (enable)
catalyst-1:\
ht=ether:\
ha=0040b90b500:\
sm=255.255.255.0:\
ip=197.22.74.223
Task
Command
Configure the SNMP community strings. See Figure 5-7 for an example.
set snmp community read-only | read-write |
read-write-all community_string
Assign a trap receiver address and community. If you enter incorrect information, use the clear snmp trap command to delete the entry. Then reenter the set snmp trap command again.
set snmp trap rcvr_address rcvr_community
If desired, configure the switch so that it issues an authentication trap.
set snmp trap enable
Check the SNMP settings using the show snmp command. See Figure 5-8 for an example.
show snmp
Console> (enable) set snmp community read-only public
SNMP read-only community string set.
Console> (enable) set snmp community read-write private
SNMP read-write community string set.
Console> (enable) set snmp community read-write-all secret
SNMP read-write-all community string set.
To enable RMON on the Catalyst please use the following command:
Console> (enable) set snmp rmon enable
SNMP RMON support enabled.
Console> (enable) set snmp
Set snmp commands:
----------------------------------------------------------------------
set snmp community Set SNMP community string
set snmp help Show this message
set snmp rmon Set SNMP RMON
set snmp trap Set SNMP trap information
Console> (enable) set snmp trap
Usage:
set snmp trap <enable|disable>
[all|module|chassis|bridge|repeater|auth|vtp]
set snmp trap <rcvr_address> <rcvr_community>
(rcvr_address is ipalias or IP address, rcvr_community is string)
Console> (enable) set snmp trap enable all
All SNMP traps enabled.
Console> (enable)
Console> show snmp
RMON: Enabled
Traps Enabled: Chassis
Port Traps Enabled: None
Community-Access Community-String
---------------- --------------------
read-only public
Trap-Rec-Address Trap-Rec-Community
---------------- --------------------
192.122.173.42 public
Console>
Task
Command
Activate SNMP remote monitoring support. See Figure 5-9 for an example.
set snmp rmon enable
Check the SNMP settings using the show snmp command. Refer to Figure 5-10 for an example.
show snmp
Console> (enable) set snmp rmon enable
SNMP RMON support enabled.
Console> show snmp
RMON: Enabled
Traps Enabled: Chassis
Port Traps Enabled: None
Community-Access Community-String
---------------- --------------------
read-only public
Trap-Rec-Address Trap-Rec-Community
---------------- --------------------
192.122.173.42 public
Console>
![]()
Task
Command
Define the VLAN management domain, indicating the domain name, VLAN trunk protocol mode of operation, interval between VLAN advertisements, and password value. Figure 5-13 shows an example of the set vtp command.
set vtp [domain name] [mode mode] [interval interval] [passwd passwd]
Verify that the VLAN management domain configuration is correct. Figure 5-12 shows a sample display of the show vtp domain command.
show vtp domain
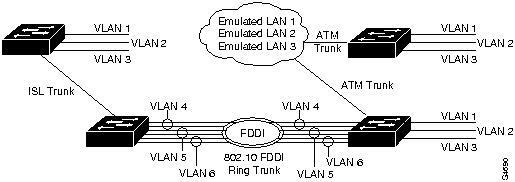
Define the VLAN, indicating the parameters described above: VLAN number, name, type, maximum transmission unit, SAID, state, ring number, bridge identification number, and number to indicate whether source routing should be set to transparent or bridging. A maximum of 250 VLANs can be active at any time. Figure 5-13 shows an example of the set vlan command. Figure 5-14 shows a diagram of the established VLANs, illustrating how VTP can traverse trunk connections using the ISL and 802.10 protocols and ATM LAN emulation (LANE). In Figure 5-14, Ethernet VLAN 1 is translated to FDDI VLAN 4 on the FDDI module, Ethernet VLAN 2 is translated to FDDI VLAN 5, and so on.
set vlan vlan_num [name name] [type type] [mtu mtu] [said said] [state state] [ring ring_number] [bridge bridge_number] [parent vlan_num] [stp stp_type] [translation vlan_num]
Verify that the VLAN configuration is correct. Figure 5-15 shows a sample display of the show vlan command.
show vlan
Console (enable) set vtp
Usage:
set vtp [domain <name>][mode <mode>][interval <interval>]
[passwd <passwd>]
(name: 1-32 characters, mode = (client, server, transparent),
interval = 120-600 sec, passwd : 0-64 characters)
Console> (enable) set vtp domain engineering mode client interval 160
VTP: domain engineering modified
Console> (enable)
Console> show vtp domain
Domain Name Domain Index VTP Version Local Mode
------------------------------ ------------ ----------- -----------
engineering 1 1 client
Last Updater Vlan-count Max-vlan-storage Config Revision Notifications
--------------- ---------- ---------------- --------------- -------------
172.20.25.130 5 256 0 disabled
Console> (enable) set vlan
Usage:
set vlan <vlan_num> <mod/ports...>
set vlan <vlan_num> [name <name>][type <type>][mtu <mtu>][said <said>]
[state <state>] [ring <ring_number>]
[bridge <bridge_number>] [parent <vlan_num>]
[stp <stp_type>] [translation <vlan_num>]
(An example of mod/ports is 1/1,2/1-12,3/1-2,4/1-12
type = (ethernet, fddi, token_ring, fddi_net, tr_net)
name = 1..32 characters, status = (active, suspend)
vlan_num = 1..1005)
Console> (enable) set vlan 3 name engineering type ethernet
VTP: vlan addition successful
Console> (enable)
Console> (enable) show vlan
VLAN Name Type Status Mod/Ports
---- -------------------------- ----- --------- ----------------
1 default enet active 2/1-24
3/1-12
4/13-48
3 vlan3 enet active
55 vlan55 enet active
66 vlan66 fddi active
88 vlan88 tring active
99 vlan99 fddi active
1002 fddi-default fddi active
1003 token-ring-default tring active
1004 fddinet-default fdnet active
1005 trnet-default trnet active
VLAN SAID MTU RingNo BridgeNo StpNo Parent Trans1 Trans2
---- ---------- ----- ------ -------- ----- ------ ------ ------
1 100001 1500 0 0 0 0 0 0
3 100003 1500 0 0 0 0 0 0
55 100055 1500 0 0 0 0 0 0
66 100066 4500 5000 0 0 5000 0 0
88 100088 1500 0 0 0 0 0 0
99 100099 1500 0 0 0 0 0 0
1002 101002 4500 0 0 0 0 1 1003
1003 101003 4500 0 0 0 0 1 1002
1004 101004 4500 0 1004 0 0 0 0
1005 101005 4500 0 1005 0 0 0 0
Task
Command
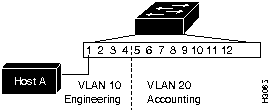
Define the VLAN and indicate the included ports. Figure 5-16 shows an example of the set vlan command. Figure 5-17 show a diagram of the established VLANs. In the example in Figure 5-16, VLAN 10, the engineering department, includes module 2, Ethernet ports 1 through 4. VLAN 20, the accounting department, includes module 2, Ethernet ports 5 through 24. The accounting and engineering departments are totally isolated from each other in this configuration.
set vlan vlan_num mod/ports
Verify that the VLAN configuration is correct. Figure 5-18 shows a sample display of the show vlan command.
show vlan
system1> (enable) set vlan 10 2/1-4
VLAN 10 modified.
VLAN 1 modified.
VLAN Mod/Ports
10 2/1-4
system1> (enable) set vlan 20 2/5-24
VLAN 20 modified.
VLAN 1 modified.
VLAN Mod/Ports
20 2/5-24
system1> (enable) show vlan
VLAN Mod/Ports
---- -----------------------------------------------------------------
1 1/1-2
10 2/1-4
20 2/5-24
system1> (enable)
Task
Command
Establish trunks on specific ports. Set the trunk to on to make it a trunk port, off to make it a non-trunk port, desirable to make it a trunk port if the port it is connected to allows trunking, or auto to make it a trunk port if the port it is connected to becomes set for trunking. Figure 5-19 shows an example of the set trunk command. Port 1 on module 1 is configured as a trunk.
set trunk mod_num/port_num
[ on | off | desirable | auto ] [vlans]
Verify that the trunk configuration is correct. Figure 5-20 shows a sample display of the show trunk command.
show trunk
Console> (enable) set trunk 1/2 5
Port 1/2 allowed vlans modified to 1-5.
Console> (enable) set trunk 1/1 desirable
Port 1/1 mode set to desirable.
Port 1/1 has become a trunk.
Console> (enable) show trunk
Port Mode Status
------- --------- ------------
1/1 desirable trunking
1/2 auto not-trunking
3/1 auto not-trunking
3/2 auto not-trunking
3/3 auto not-trunking
3/4 auto not-trunking
3/5 auto not-trunking
3/6 auto not-trunking
3/7 auto not-trunking
3/8 auto not-trunking
3/9 auto not-trunking
3/10 auto not-trunking
3/11 auto not-trunking
3/12 auto not-trunking
Port Vlans allowed
------- ---------------------------------------------------------------
1/1 1-1000
1/2 1-5
3/1 1-1000
3/2 1-1000
3/3 1-1000
3/4 1-1000
3/5 1-1000
3/6 1-1000
3/7 1-1000
3/8 1-1000
3/9 1-1000
3/10 1-1000
3/11 1-1000
3/12 1-1000
Port Vlans active
------- ---------------------------------------------------------------
1/1 1,55
1/2 1
3/1 1
3/2 1
3/3 1
3/4 1
3/5 1
3/6 1
3/7 1
3/8 1
3/9 1
3/10 1
3/11 1
3/12 1
Console> (enable)
Task
Command
Test the configuration using the ping command. The ping command sends an echo request to the host specified in the command line.
ping host
If necessary, reset the configuration to its default values and reenter the configuration information.
clear config
192.34.56.5 is alive
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()