|
|
CDDI and FDDI Module Software Configuration
Copper Distributed Data Interface (CDDI) is the implementation of Fiber Distributed Data Interface (FDDI) protocols over STP and UTP cabling. CDDI transmits over relatively short distances (about 100 meters), providing data rates of 100 Mbps, using a dual-ring architecture to provide redundancy. FDDI is a LAN standard, defined by ANSI X3T9.5, specifying a 100-Mbps token-passing network using fiber-optic cable, with transmission distances of up to 2 km. FDDI also uses a dual-ring architecture to provide redundancy. This chapter describes how to use the console port to configure the CDDI/FDDI ports of the Catalyst 5000 series switch.
The features you can customize have default values that will most likely suit your environment and probably need not be changed. The default values of these features are set as follows:
If needed, you can customize the preceding features to fit your particular configuration. Perform any of the following tasks that apply to your configuration. Each task is covered in a subsection that follows.
Customizing the Default IPX Protocol Translations
As a normal function, the Catalyst 5000 series switch can forward IPX packets received on FDDI ports to Ethernet ports, or it can forward IPX packets received on Ethernet ports to FDDI ports. To do this, the switch must be configured for specific IPX protocol translations. By default, the following IPX protocol translations are configured:
You can customize these settings if your environment requires it.
Setting the FDDI SNAP to Ethernet Translation
The FDDI SNAP frame can be translated into the following Ethernet frames:
To specify the FDDI protocol to which Ethernet 8023RAW packets are translated, perform the following steps in privileged mode:
| Task | Command |
|---|---|
| |
set bridge ipx snaptoether {8023 | SNAP | EII | 8023RAW } |
| |
show bridge |
Figure 8-1 : set bridge ipx snaptoether 8023 Command Example
Console> (enable) set bridge ipx snaptoether 8023 Bridge snaptoether default IPX translation set. Console> (enable)
Figure 8-2 : show bridge Command Example
Console> (enable) show bridge
APaRT Enabled
FDDICHECK Enabled
IP fragmentation Enabled
Default IPX translations:
FDDI SNAP to Ethernet 8023
FDDI 802.2 to Ethernet 8023raw
Ethernet 802.3 Raw to FDDI snap
Console> (enable)
Setting the FDDI 802.2 to Ethernet Translation
The FDDI 802.2 frame can be translated into the following Ethernet frames:
To specify the Ethernet frame to which IPX FDDI SNAP packets are translated, perform the following steps in privileged mode:
| Task | Command |
|---|---|
| |
set bridge ipx 8022toether {8023 | SNAP | EII | 8023RAW } |
| |
show bridge |
The following example sets the IPX translation protocol for FDDI 802.2 to 802.3:
Figure 8-3 : set bridge ipx 8022 toether 8023 Command Example
Console> (enable) set bridge ipx 8022toether 8023 Module 4 8022toether translation set. Console> (enable)
The following example sets the IPX translation protocol for FDDI SNAP to Ethernet SNAP:
Figure 8-4 : set bridge ipx snaptoether snap Command Example
Console> (enable) set bridge ipx snaptoether snap Module 4 snaptoether translation set Console> (enable)
Figure 8-5 : show bridge Command Example
Console> (enable) show bridge
APaRT Enabled
FDDICHECK Enabled
IP fragmentation Enabled
Default IPX translations:
FDDI SNAP to Ethernet snap
FDDI 802.2 to Ethernet 8023
Ethernet 802.3 Raw to FDDI snap
Console> (enable)
Setting the Ethernet 802.3 RAW to FDDI Protocol
The Ethernet 802.3 RAW protocol can be translated into the following FDDI protocols:
To specify the FDDI frames to which 8023RAW Ethernet packets are translated, perform the following steps in privileged mode:
| Task | Command |
|---|---|
| |
set bridge ipx 8023rawtofddi {8022 | SNAP | FDDIRAW} |
| |
show bridge |
Figure 8-6 : set bridge ipx 8023rawtofddi 8022 Command Example
Console> (enable) set bridge ipx 8023rawtofddi 8022 Module 4 8023rawtofddi translation set. Console> (enable)
Figure 8-7 : show bridge Command Example
Console> (enable) show bridge
FDDICHECK Enabled
IP fragmentation Enabled
Default IPX translations:
FDDI SNAP to Ethernet snap
FDDI 802.2 to Ethernet 8023
Ethernet 802.3 Raw to FDDI 8022
Console> (enable)
Setting the Minimum Time to Transfer the FDDI PHY Line State
The TL_MIN parameter sets the minimum time to transmit an FDDI physical sublayer (PHY) line state before advancing to the next physical connection management (PCM) state. This setting affects the station and switch interoperability and might hinder the implementation of FDDI repeaters. By default, the TL_MIN parameter is set to 40 microseconds. Normally, you will not need to adjust this parameter. However, you can customize the TL_MIN setting if needed. To do this, perform the following steps in privileged mode:
| Task | Command |
|---|---|
| |
set fddi tlmin mod_num/port_num usecs |
| |
show fddi |
Figure 8-8 : set fddi tlmin Command Example
Console> (enable) set fddi tlmin 4/1 40 Port 4/1 tlmin set to 40. Console> (enable)
Figure 8-9 : show fddi Command Example
Console> show fddi Mod SMT User-Data T-Notify TReq --- -------------------------- -------- ------- 4 Engineering 15 3500 5 abc 20 150000 Port Tlmin Ler-CutOff Ler-Alarm ----- -------- ---------- --------- 4/1 40 10 11 4/2 40 10 11 5/1 40 10 11 5/2 40 9 12 Console>
Setting the Interval between Neighbor Notification Frames
The TNotify parameter sets the interval (in seconds) between neighbor notification frames. These frames are sent out to notify neighboring devices of FDDI module MAC addresses. Usually, the default setting of 30 seconds is sufficient. By shortening the interval, you cause more notification frames to be sent. However, if you need to adjust this setting, perform the following steps in privileged mode:
| Task | Command |
|---|---|
| |
set fddi tnotify mod_num time |
| |
show fddi |
Figure 8-10 : set fddi tnotify Command Example
Console> (enable) set fddi tnotify 4/1 15 Module 4 tnotify set to 15. Console> (enable)
Figure 8-11 : show fddi Command Example
Console> show fddi Mod SMT User-Data T-Notify TReq --- -------------------------- -------- ------- 4 Engineering 15 3500 5 abc 20 150000 Port Tlmin Ler-CutOff Ler-Alarm ----- -------- ---------- --------- 4/1 40 10 11 4/2 40 10 11 5/1 40 10 11 5/2 40 9 12 Console>
Setting the Timer for Negotiating TRT
The TRequest parameter specifies the FDDI switch's desired value for the Token Ring Timer (TRT) for negotiating the TRT with other stations. The TRT is used to control ring scheduling during normal operation and to detect and recover from serious ring error situations. Whenever the TRT value expires, the station uses the TRequest value to negotiate with other stations for the lowest value. The default setting of 16,5000 microseconds is sufficient for most networks. However, if you need to modify this setting, perform the following steps in privileged mode:
| Task | Command |
|---|---|
| |
set fddi treq mod_num time |
| |
show fddi |
Figure 8-12 : set fddi trequest Command Example
Console> (enable) set fddi trequest 4 3500 Mac 4/1 treq set to 3500. Console> (enable)
Figure 8-13 : show fddi Command Example
Console> show fddi Mod SMT User-Data T-Notify TReq --- -------------------------- -------- ------- 4 Engineering 15 3500 5 abc 20 150000 Port Tlmin Ler-CutOff Ler-Alarm ----- -------- ---------- --------- 4/1 40 10 11 4/2 40 10 11 5/1 40 10 11 5/2 40 9 12 Console>
Specifying the User Data String
The user-data string identifies the user data string in the SMT MIB of an FDDI module. The default value is "Catalyst 5000." This value should be modified to a more meaningful description. To modify this parameter, perform the following steps in privileged mode:
| Task | Command |
|---|---|
| |
set fddi userdata mod_num userdata_string |
| |
show fddi |
Figure 8-14 : set fddi Command Example
Console> (enable) set fddi userdata 4 Engineering Module 4 userdata set to Engineering. Console> (enable)
Figure 8-15 : show fddi Command Example
Console> show fddi Mod SMT User-Data T-Notify TReq --- -------------------------- -------- ------- 4 Engineering 15 3500 5 abc 20 150000 Port Tlmin Ler-CutOff Ler-Alarm ----- -------- ---------- --------- 4/1 40 10 11 4/2 40 10 11 5/1 40 10 11 5/2 40 9 12 Console>
IP fragmentation allows the Catalyst 5000 series switch to fragment large FDDI IP frames (frames greater than 1514 bytes) into multiple smaller packets so that they can be transmitted on an Ethernet segment. By default, IP fragmentation is enabled. If you want the large packets to be dropped instead of fragmented, disable fragmentation:
| Task | Command |
|---|---|
| |
set ip fragmentation disable |
| |
show ip route |
To reenable IP fragmentation, perform the following steps in privileged mode:
| Task | Command |
|---|---|
| |
set ip fragmentation enable |
| |
show ip route |
Figure 8-16 : set ip fragmentation disable Command Example
Console> (enable) set ip fragmentation disable IP fragmentation disabled for module 4 Console> (enable)
Figure 8-17 : show ip route Command Example
Console> (enable) show ip route Fragmentation Redirect Unreachable ------------- -------- ----------- disabled enabled disabled Destination Gateway Flags Use Interface --------------- --------------- ------ ---------- --------- 172.20.0.0 172.20.22.181 U 0 sc0 default default UH 0 sl0 Console> (enable)
Disabling ICMP Unreachable Messages
When enabled, the switch returns an ICMP unreachable message to the Internet source host whenever it receives an IP datagram that it cannot deliver. When disabled, the switch does not notify the Internet source host when it receives an IP datagram that it cannot deliver. You can disable unreachable messages enabled if desired. To do this, perform the following steps in privileged mode:
| Task | Command |
|---|---|
| |
set ip unreachable disable |
| |
show ip route |
To reenable IP unreachable messages, perform the following steps in privileged mode:
| Task | Command |
|---|---|
| |
ip unreachable enable |
| |
show ip route |
Figure 8-18 : set ip unreachable disable Command Example
Console> (enable) set ip unreachable disable Console> (enable)
Figure 8-19 : show ip route Command Example
Console> (enable) show ip route Fragmentation Redirect Unreachable ------------- -------- ----------- disabled enabled disabled Destination Gateway Flags Use Interface --------------- --------------- ------ ---------- --------- 172.20.0.0 172.20.22.181 U 0 sc0 default default UH 0 sl0 Console> (enable)
Setting the Link Error Rate Alarm
The LER-Alarm value defines the link error rate (LER) at which a link connection exceeds a preset alarm threshold. This value is used in the link error rate threshold test. The default setting of 8 (10¯8) link errors per second is sufficient for most networks. However, if you need to modify this setting, perform the following steps in privileged mode:
| Task | Command |
|---|---|
| |
set fddi alarm mod_num/port_num value |
| |
show fddi |
Figure 8-20 : set fddi alarm Command Example
Console> (enable) set fddi alarm 4/1 11 Port 4/1 alarm value set to 11. Console> (enable)
Figure 8-21 : show fddi Command Example
Console> show fddi Mod SMT User-Data T-Notify TReq --- -------------------------- -------- ------- 4 Engineering 15 3500 5 abc 20 150000 Port Tlmin Ler-CutOff Ler-Alarm ----- -------- ---------- --------- 4/1 40 10 11 4/2 40 10 11 5/1 40 10 11 5/2 40 9 12 Console>
Setting the Link Error Rate Cutoff
The LER-Cutoff value determines the link error rate (LER) at which a connection will be flagged as faulty. This value is used in the link error rate threshold test. The default setting of 7 (10¯7) is sufficient for most networks. However, if you need to modify this setting, perform the following steps in privileged mode:
| Task | Command |
|---|---|
| |
set fddi cutoff mod_num/port_num value |
| |
show fddi |
Figure 8-22 : set fddi cutoff Command Example
Console> (enable) set fddi cutoff 4/1 10 Port 4/1 cutoff value set to 10. Console> (enable)
Figure 8-23 : show fddi Command Example
Console> show fddi Mod SMT User-Data T-Notify TReq --- -------------------------- -------- ------- 4 Engineering 15 3500 5 abc 20 150000 Port Tlmin Ler-CutOff Ler-Alarm ----- -------- ---------- --------- 4/1 40 10 11 4/2 40 10 11 5/1 40 10 11 5/2 40 9 12 Console>
Assign a name to each port. To set a port name, perform the following steps in privileged mode:
| Task | Command |
|---|---|
| |
set port name mod_num/port_num [name_string] |
| |
show port mod_num/port_num |
Figure 8-24 : set port name Display Example
Console> (enable) set port name 1/1 Router Connection Port 1/1 name set.
Figure 8-25 : show port Command Example
Console> show port 4
Port Name Status Vlan Level Duplex Speed Type
---- ----------------- -------- ---------- ------ ------ ----- -----
4/1 FDDI A standby 1 half 100 FDDI
4/2 FDDI B connect 1 half 100 FDDI
Ler
Port CE-State Conn-State Type Neig Con Est Alm Cut Lem-Ct Lem-Rej-Ct Tl-Min
---- -------- ---------- ---- ---- --------------- ---------- ---------- ------
4/1 isolated standby A U yes 9 11 10 0 0 40
4/2 isolated active B U yes 9 11 10 0 0 1340000
Last-Time-Cleared
----------------------------
Tues Aug 22 1995, 18:28:51
Console>
Setting Up an FDDI 802.10 Configuration
The FDDI module is basically an FDDI-Ethernet translation bridge. It translates packets on the external FDDI ring into Ethernet packets within the Catalyst 5000. That is, inside the Catalyst 5000 Ethernet VLAN packets are translated into FDDI VLAN packets and encoded in 802.10 format with a SAID value before they are transmitted across an external FDDI trunk to another Catalyst 5000. The Catalyst 5000 that receives the packets from the trunk decodes the 802.10 format using the SAID value and internally translates the FDDI VLAN packets into Ethernet VLAN packets. Each Ethernet VLAN requires a unique FDDI VLAN translation.
For example, to connect Ethernet VLAN 20 in switch 1 to Ethernet VLAN 20 in switch 2, as shown in Figure 8-26, you would use a VTP server to set up the configuration as follows:
Figure 8-26 : FDDI 802.10 Configuration Example
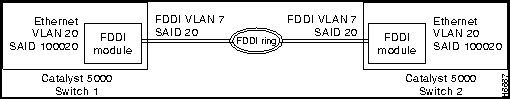
The Catalyst 1200 series switch is hardcoded with a specific VLAN-to-SAID configuration. Therefore, if you are connecting a Catalyst 5000 Ethernet VLAN to a Catalyst 1200 Ethernet VLAN, the SAID value of the FDDI VLAN must be the same value as the Ethernet VLAN. For example, if a Catalyst 1200 Ethernet VLAN value is 20, the translation FDDI VLAN SAID value must be 20.
Before setting up an FDDI 802.10 VLAN configuration, refer to the chapter "Configuring the Software" to set up a VTP domain; it is described in the section "Setting Virtual LANs (VLANs)." Also refer to the chapter "Configuring the Software" to set up trunks, as described in the section "Setting Trunks." After completing these tasks, perform the following steps in privileged mode to set up the FDDI 802.10 VLAN configuration:
| Task | Command |
|---|---|
| Provide a VLAN number and activate a VLAN in the management domain. Refer to Figure 8-27 for an example. This creates a VLAN but does not assign it to a port. VTP advertises the VLAN to all available trunks of all types (such as Ethernet or FDDI) that are set to on, for all Catalyst 5000s in the same management domain. | set vlan vlan_num |
| Assign the VLAN to an FDDI port. Provide the VLAN number, module number, and port number. Additionally use this commend to set up the native FDDI VLAN. Refer to Figure 8-28 for an example. | set vlan vlan_num mod_num/port_num |
| Create a VLAN with type FDDI. See Figure 8-29 for an example. | set vlan vlan_num type fddi |
| Map the Ethernet VLAN translation to an FDDI VLAN. Refer to Figure 8-30 for an example. | set vlan ether_vlan_num translation fddi_vlan_num
set vlan fddi_vlan_num translation ether_vlan_num |
| Turn trunking on for the FDDI port. (See Figure 8-31.) | set trunk mod_num /port_num on |
| Verify that the VLAN configuration is correct, including the mapping between Ethernet, FDDI, and token ring. If you use the show trunk command after a 30 second delay, you will see a display of the new VLAN that have been added to all Catalyst 5000 series switches. Figure 8-32 shows a sample display of the show vlan command. | show vlan [trunk | no trunk ]
show trunk |
The following examples add a new Ethernet and FDDI VLAN to the existing configuration.
Figure 8-27 : set vlan Command Example to Create a VLAN
Console> (enable) set vlan 33 VTP: vlan addition successful
Figure 8-28 : set vlan Command Example to Assign a VLAN to an Ethernet Port
Console> (enable) set vlan 33 2/13
VLAN 33 modified.
VLAN 1 modified.
VLAN Mod/Ports
---- -----------------------
33 1/2
2/13
4/1-2
Console> (enable)
Figure 8-29 : set vlan Command Example to Create an FDDI VLAN
Console> (enable) set vlan 333 type fddi VTP: vlan addition successful
Figure 8-30 : set vlan Command Example to Translate an Ethernet VLAN to an FDDI VLAN
Console> (enable) set vlan 33 translation 333 VTP: vlan modification successful
Figure 8-31 : set trunk Command Example
Console> (enable) set trunk 1/1 on Port 1/1 mode set to on. Console> (enable)
Figure 8-32 : show vlan Command Example
Console> (enable) show vlan
VLAN Name Type Status Mod/Ports
---- -------------------------- ----- --------- ----------------
1 default enet active 1/1
2/3-4,2/7-12,2/14-16,2/18-24
11 VLAN0011 enet active 2/1-2
22 VLAN0022 enet active 2/5-6
33 VLAN0033 enet active 2/13,2/17
111 VLAN0111 fddi active
222 VLAN0222 fddi active
333 VLAN0333 fddi active
1002 fddi-default fddi active
1003 token-ring-default tring active
1004 fddinet-default fdnet active
1005 trnet-default trnet active
VLAN SAID MTU RingNo BridgeNo StpNo Parent Trans1 Trans2
---- ---------- ----- ------ -------- ----- ------ ------ ------
1 100001 1500 0 0 0 0 0 0
11 100011 1500 0 0 0 0 111 0
22 100022 1500 0 0 0 0 222 0
33 100033 1500 0 0 0 0 333 0
111 100111 1500 0 0 0 0 11 0
222 100222 1500 0 0 0 0 22 0
333 33 1500 0 0 0 0 33 0
1002 101002 1500 0 0 0 0 0 0
1003 101003 1500 0 0 0 0 0 0
1004 101004 1500 0 0 0 0 0 0
1005 101005 1500 0 0 0 0 0 0
CAT4> (debug-eng)
Console> (enable)
Rejecting MAC Address Learning (fddicheck)
To cause an FDDI interface to reject the learning of MAC addresses that it previously learned from an Ethernet interface, perform the following steps in privileged mode:
| Task | Command |
|---|---|
| Enable the set bridge fddicheck command. Refer to Figure 8-35 for an example. | set bridge fddicheck enable |
| Use the show bridge command to determine if the fddicheck option is enabled. Refer to Figure 8-36 for an example. | show bridge |
This feature requires information from the CAM. Therefore, disabling APART also automatically disables fddicheck. To enable fddicheck, first enable APART.
Figure 8-33 : set bridge fddicheck Command Example
Console> (enable) set bridge fddicheck enable FDDICHECK enabled Console> (enable)
Figure 8-34 : show bridge Command Example
Console> (enable) show bridge
APaRT Enabled
FDDICHECK Enabled
IP fragmentation Enabled
Default IPX translations:
FDDI SNAP to Ethernet 8023raw
FDDI 802.2 to Ethernet 8023
Ethernet 802.3 Raw to FDDI snap
Console> (enable)
Disabling Automatic Packet Recognition and Translation (APART)
To disable the software content-addressable memory (CAM) of the FDDI module, Packet Recognition and Translation (APART), and fddicheck command, perform the following steps in privileged mode:
| Task | Command |
|---|---|
| Disable the software content-addressable memory (CAM) of the FDDI module. Refer to Figure 8-35 for an example. | set bridge apart disable |
| Verify that the software content-addressable memory (CAM) of the FDDI module, APART, and fddicheck command are disabled. Refer to Figure 8-36 for an example. | show bridge |
This feature is typically used in an IP environment. It provides a slight performance increase. Disabling APART automatically disables fddicheck. When APART is
disabled, FDDI-to-Ethernet translation values are the settings configured with the set bridge IPX command.
Figure 8-35 : set bridge apart disable Command Example
Console> (enable) set bridge apart disable APaRT disabled Console> (enable)
Figure 8-36 : show bridge Command Example
Console> (enable) show bridge
APaRT Disabled
FDDICHECK Disabled
IP fragmentation Enabled
Default IPX translations:
FDDI SNAP to Ethernet 8023raw
FDDI 802.2 to Ethernet 8023
Ethernet 802.3 Raw to FDDI snap
Console> (enable)
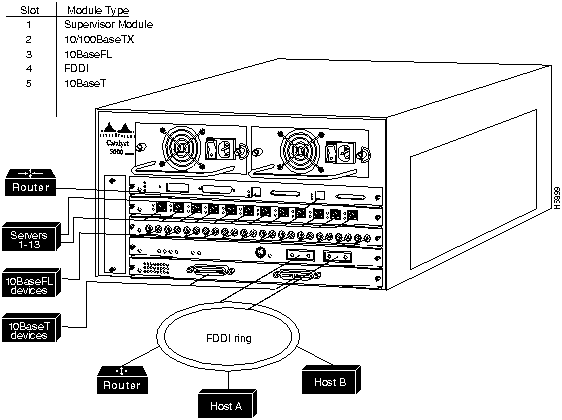
Single-Switch Configuration Example
A simple Catalyst 5000 series switch configuration example is shown in Figure 8-37. The configuration shows a case that includes the following elements:
See the "Configuring Ethernet and Fast Ethernet Software" chapter of the Catalyst 5000 Series Configuration Guide and Command Reference for examples of the Ethernet settings.
Figure 8-37 : Single Catalyst 5000 Series Switch Configuration
Multiple-Switch VLAN Configuration Without Trunking Example
VLAN groups can be set up across multiple Catalyst 5000 series switches without trunking if the switches have any two ports of the same VLAN connected, as shown in the example in Figure 8-38. You need to configure the VLANs individually for both switches using the set vlan command.
Figure 8-38 : Multiple Catalyst 5000 Series VLAN Configuration Without Trunking
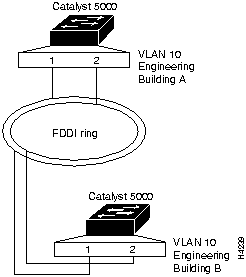
Setting and Displaying VLANs for Buildings A and B
The following example sets VLAN 10 for the Catalyst 5000 series switch in building A:
System1> (enable) set vlan 10 4/1 VLAN 10 modified. VLAN 1 modified. VLAN Mod/Ports ---- ----------------------- 10 4/1-2
The following example sets VLAN 10 for the Catalyst 5000 series switch in building B:
System2> (enable) set vlan 10 4/1 VLAN 10 modified. VLAN 1 modified. VLAN Mod/Ports ---- ----------------------- 10 4/1-2
The following example commands display the VLAN setting for the Catalyst 5000 in building A:
System1> (enable) show vlan 10
VLAN Name Type Status Mod/Ports
---- -------------------------- ----- --------- ----------------
10 VLAN0010 enet active 4/1-2
VLAN SAID MTU RingNo BridgeNo StpNo Parent Trans1 Trans2
---- ---------- ----- ------ -------- ----- ------ ------ ------
10 100010 1500 0 0 0 0 0 0
System1> (enable) show vlan
VLAN Name Type Status Mod/Ports
---- -------------------------- ----- --------- ----------------
1 default enet active 1/1-2
10 VLAN0010 enet active 4/1-2
20 VLAN0020 enet active 2/1-24
1002 fddi-default fddi active
1003 token-ring-default tring active
1004 fddinet-default fdnet active
1005 trnet-default trnet active
VLAN SAID MTU RingNo BridgeNo StpNo Parent Trans1 Trans2
---- ---------- ----- ------ -------- ----- ------ ------ ------
1 100001 1500 0 0 0 0 0 0
10 100010 1500 0 0 0 0 0 0
20 100020 1500 0 0 0 0 0 0
1002 101002 1500 0 0 0 0 0 0
1003 101003 1500 0 0 0 0 0 0
1004 101004 1500 0 0 0 0 0 0
1005 101005 1500 0 0 0 0 0 0
System1> (enable)
The following example commands display the VLAN setting for the Catalyst 5000 in building B:
System2> (enable) show vlan 10
VLAN Name Type Status Mod/Ports
---- -------------------------- ----- --------- ----------------
10 VLAN0010 enet active 4/1-2
VLAN SAID MTU RingNo BridgeNo StpNo Parent Trans1 Trans2
---- ---------- ----- ------ -------- ----- ------ ------ ------
10 100010 1500 0 0 0 0 0 0
System2> (enable) show vlan
VLAN Name Type Status Mod/Ports
---- -------------------------- ----- --------- ----------------
1 default enet active 1/1-2
10 VLAN0010 enet active 4/1-2
20 VLAN0020 enet active 2/1-24
1002 fddi-default fddi active
1003 token-ring-default tring active
1004 fddinet-default fdnet active
1005 trnet-default trnet active
VLAN SAID MTU RingNo BridgeNo StpNo Parent Trans1 Trans2
---- ---------- ----- ------ -------- ----- ------ ------ ------
1 100001 1500 0 0 0 0 0 0
10 100010 1500 0 0 0 0 0 0
20 100020 1500 0 0 0 0 0 0
1002 101002 1500 0 0 0 0 0 0
1003 101003 1500 0 0 0 0 0 0
1004 101004 1500 0 0 0 0 0 0
1005 101005 1500 0 0 0 0 0 0
|
|
Copyright 1988-1996 © Cisco Systems Inc.