|
|
This chapter describes procedures used to confirm that the hardware and software installation and configuration procedures were successful. The following sections are included:
This section describes the LEDs used to confirm and troubleshoot operation of the Catalyst 5000 series modules. The LEDs on the supervisor engine module indicate the system power and processor status; LEDs on the switching modules indicate the status of the individual switching module and their interfaces.
The status LEDs on the supervisor engine module and switching modules go on to indicate that the modules are powered up. When on, they do not necessarily mean that the interface ports are functional or enabled. Additionally, although the LEDs for many interface types go on at the initial system startup, they do not indicate an accurate status until the interface is configured.
All status LEDs go on when the module receives power. The color of the LED indicates the actual status of the ports and modules. The following sections contain details about the meanings of each color.
The LEDs on the supervisor engine module indicate the system status; the system includes the fan assembly, power supply(ies), and supervisor engine module. The PS1 and PS2 LEDs on the supervisor engine module go on when the power supply is receiving AC source power and providing DC power to the internal system components. The power supply monitors its own temperature and internal voltages. For a description of the power supply shutdown conditions and threshold status levels, refer to the section "Environmental Monitoring and Reporting" in the chapter "Defining the Catalyst 5000 Series Switch."
The supervisor engine module LEDs are shown in Figure 9-1, Figure 9-2, and Figure 9-3 and described in Table 9-1.
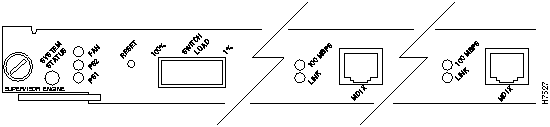
Figure 9-2 : LEDs for Multimode Fiber-Optic Supervisor Engine Module
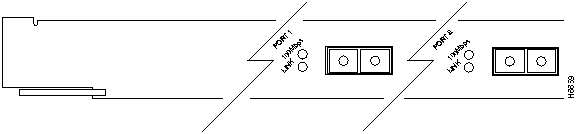
Figure 9-3 : LEDs for Single-Mode Fiber-Optic Supervisor Engine Module
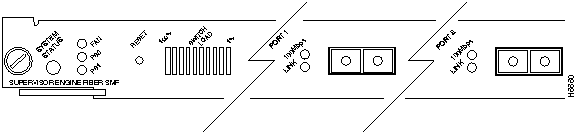
Table 9-1 : Supervisor Engine Module LEDs
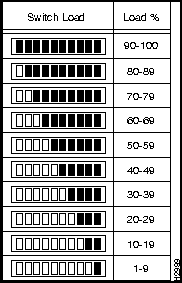
The switch load-meter LEDs provide a visual indication (as an approximate percentage) of the current traffic load over the backplane. (See Figure 9-4.)
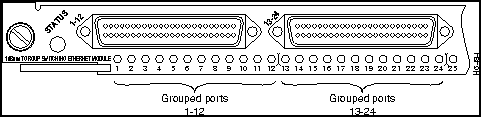
Group Switching Ethernet Module (10BaseT 48 Port) LEDs
The LEDs provide status information for the module and individual 10BaseT Ethernet port connections. The LEDs are shown in Figure 9-5 and described in Table 9-2.
Figure 9-5 : Group Switching Ethernet Module (10BaseT 48 Port) LEDs
Table 9-2 : Group Switching Ethernet Module LED Descriptions
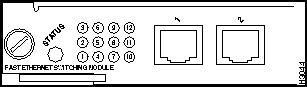
Ethernet Switching Module (10BaseT 24 Port) LEDs
The LEDs provide status information for the module and individual 10BaseT Ethernet port connections. The LEDs are shown in Figure 9-6 and described in Table 9-3.
Figure 9-6 : Ethernet Switching Module (10BaseT 24 Port) LEDs
Table 9-3 : Ethernet Switching Module (10BaseT 24 Port) LED Descriptions
Ethernet Switching Module (10BaseFL12 Port) LEDs
The LEDs provide status information for the module. The LED is shown in Figure 9-7 and described in Table 9-4.
Figure 9-7 : Ethernet Switching Module (10BaseFL 12 Port) LEDs
Table 9-4 : Ethernet Switching Module (10BaseFL 12 Port) LED Descriptions
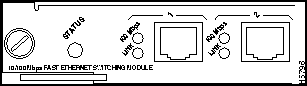
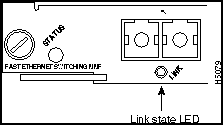
10/100 Mbps Fast Ethernet Switching Module (10/100BaseTX 12 Port) LEDs
The LEDs provide status information for the module and individual 10/100 Mbps Fast Ethernet interface connections. The LEDs are shown in Figure 9-9 and described in Table 9-6.
Figure 9-8 : 10/100 Mbps Fast Ethernet Switching Module (10/100BaseTX 12 Port) LEDs
Table 9-5 : 10/100 Mbps Fast Ethernet Switching Module (10/100BaseTX 12 Port) LED Descriptions
Fast Ethernet Switching Module (100BaseTX 12 Port) LEDs
The LEDs provide status information for the module and individual Fast Ethernet interface connections. The LEDs are shown in Figure 9-9 and described in Table 9-6.
Figure 9-9 : Fast Ethernet Switching Module (100BaseTX 12 Port) LEDs
Table 9-6 : Fast Ethernet Switching Module (100BaseTX 12 Port) LED Descriptions
Fast Ethernet Switching Module (100BaseFX 12 Port) LEDs
The LEDs on the faceplate of the Fast Ethernet switching module (100BaseFX 12 port), shown in Figure 9-10, are described in Table 9-7.
Figure 9-10 : Fast Ethernet Switching Module (100BaseFX 12 Port) LEDs
Table 9-7 : Fast Ethernet Switching Module (100BaseFX 12 Port) LED Descriptions
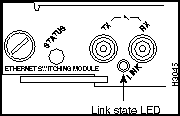
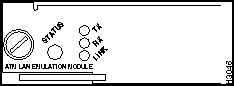
ATM LAN Emulation Module (UTP) LEDs
The LEDs provide status information for the module and individual ATM port connection. The LEDs are shown in Figure 9-11 and described in Table 9-8.
Figure 9-11 : ATM LAN Emulation Module (UTP) LEDs
Table 9-8 : ATM LAN Emulation Module (UTP) LED Descriptions
ATM LAN Emulation Module (Single-Mode and Multimode Fiber) LEDs
The LEDs provide status information for the module and individual port connections. The LEDs are shown in Figure 9-12 and described in Table 9-9.
Figure 9-12 : ATM LAN Emulation Module (Single-Mode and Multimode Fiber) LEDs
Table 9-9 : ATM LAN Emulation Module (Single-Mode and Multimode) LED Descriptions
The LEDs provide status information for the module and individual CDDI port connections. The LEDs are shown in Figure 9-13 and described in Table 9-10.
Figure 9-13 : CDDI Module LEDs
Table 9-10 : CDDI Module LED Descriptions
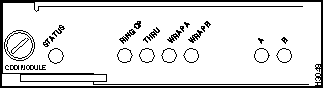
FDDI Module MMF (Multimode Fiber) LEDs
The LEDs provide status information for the module and individual FDDI port connections. The LEDs are shown in Figure 9-14 and described in Table 9-11.
Figure 9-14 : FDDI Module MMF (Multimode Fiber) LEDs
Table 9-11 : FDDI Module MMF (Multimode Fiber) LED Descriptions
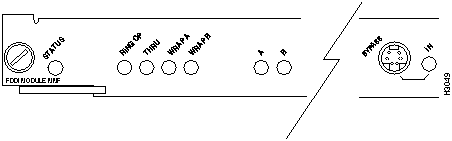
FDDI Module SMF (Single-Mode Fiber) LEDs
The LEDs provide status information for the module and individual FDDI port connections. The LEDs are shown in Figure 9-15 and described in Table 9-12.
Figure 9-15 : FDDI Module SMF (Single-Mode Fiber) LEDs
Table 9-12 : FDDI Module SMF (Single-Mode Fiber) LED Descriptions
Use the telnet command to start a Telnet connection to a remote host:
The syntax descriptions for each parameter are as follows
An example of the telnet command is as follow:
Enter the ping command to send Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) echo request packets to another node on the network to confirm the connection to that node. Enter Ctrl-C to stop "pinging."
The syntax descriptions for each parameter are as follows:
Following are sample results of the ping command:
In the following ping command example, a host with IP alias elvis is pinged a single time, then pinged once per second until Ctrl-C is entered to stop pinging:
Enter the show system command to display the power supply, fan, temperature alarm, system, and modem status; the number of days, hours, minutes, and seconds since the last system restart; the baud rate; the MAC address range; and the system name, location, and contact.
In the following example, the system status and other information is displayed:
Using the show configuration Command
Enter the show config command to display the current system configuration:
Copyright 1988-1996 © Cisco Systems Inc.
![]()
LED
Description
Status
The switch performs a series of self-tests and diagnostic tests.
If all the tests pass, the Status LED is green.
If any test fails, the Status LED is red.
During system boot or if the module is disabled, the LED is orange.
If the redundant power supply is installed but not turned on or receiving AC input, the status LED is red.
If the fan module fails, the status is red.
Fan
Indicates whether or not the fan is operational.
If the fan is operational, the fan LED is green.
If the fan is not operational, the fan LED is red.
PS1, left bay
If the power supply in the left bay is operational, the PS1 LED is green.
If the power supply in the left bay is not operational, switched off, or not receiving AC input, in the left bay the PS1 LED is red.
If the left bay power supply is off or not installed, the PS1 LED is red.
PS2, right bay
If the power supply in the right bay is operational, the PS2 LED is green.
If the power supply in the right bay is not operational, switched off, or not receiving AC input, the PS2 LED is red.
If the left bay power supply is off or not installed, the PS2 LED is red.
100 Mbps
If the port is operating at 100 Mbps, the LED is green.
Link
If the port is operational, the LED is green.
If the link has been disabled by software, the LED is orange.
If the link is bad and has been disabled due to a hardware failure, the LED flashes orange.
If no signal is detected, the LED is off.
LED
Description
Status
The switch performs a series of self-tests and diagnostic tests.
If all the tests pass, the status LED is green.
If a test other than an individual port test fails, the status LED is red.
During system boot or if the module is disabled, the LED is orange.
During self-test diagnostics, the LED is orange.
If the module is disabled, the LED is orange.
Link
If the port is operational (a signal is detected), the LED is green.
If the link has been disabled by software, the LED is orange.
If the link is bad and has been disabled due to a hardware failure, the LED flashes orange.
If no signal is detected, the LED is off.

LED
Description
Status
The switch performs a series of self-tests and diagnostic tests.
If all the tests pass, the status LED is green.
If a test other than an individual port test fails, the status LED is red.
During system boot or if the module is disabled, the LED is orange.
During self-test diagnostics, the LED is orange.
If the module is disabled, the LED is orange.
Link
If the port is operational (a signal is detected), the LED is green.
If the link has been disabled by software, the LED is orange.
If the link is bad and has been disabled due to a hardware failure, the LED flashes orange.
If no signal is detected, the LED is off.
LED
Description
Status
The switch performs a series of self-tests and diagnostic tests.
If all the tests pass, the status LED is green.
If a test other than an individual port test fails, the status LED is red.
During system boot or if the module is disabled, the LED is orange.
During self-test diagnostics, the LED is orange.
If the module is disabled, the LED is orange.
Link
If the port is operational (a signal is detected), the LED is green.
If the link has been disabled by software, the LED is orange.
If the link is bad and has been disabled due to a hardware failure, the LED flashes orange.
If no signal is detected, the LED is off.
LED
Description
Status
The switch performs a series of self-tests and diagnostic tests.
If all the tests pass, the Status LED is green.
If a test other than an individual port test fails, the status LED is red.
During system boot or if the module is disabled, the LED is orange.
During self-test diagnostics, the LED is orange.
If the module is disabled, the LED is orange.
100-Mbps
If the port is operating at 100 Mbps, the LED is green.
If the port is operating at 10 Mbps, the LED is off.
Link (bottom LED)
If the port is operational (a signal is detected), the LED is green.
If the link has been disabled by software, the LED is orange.
If the link is bad and has been disabled due to a hardware failure, the LED flashes orange.
If no signal is detected, the LED is off.
LED
Description
Status
The switch performs a series of self-tests and diagnostic tests.
If all the tests pass, the Status LED is green.
If a test other than an individual port test fails, the status LED is red.
During system boot or if the module is disabled, the LED is orange.
During self-test diagnostics, the LED is orange.
If the module is disabled, the LED is orange.
Link (bottom LED)
If the port is operational (a signal is detected), the LED is green.
If the link has been disabled by software, the LED is orange.
If the link is bad and has been disabled due to a hardware failure, the LED flashes orange.
If no signal is detected, the LED is off.
LED
Description
Status
The switch performs a series of self-tests and diagnostic tests.
If all the tests pass, the status LED is green.
If a test other than an individual port test fails, the status LED is red.
During system boot or if the module is disabled, the LED is orange.
During self-test diagnostics, the LED is orange.
If the module is disabled, the LED is orange.
Link
If the port is operational (a signal is detected), the LED is green.
If the link has been disabled by software, the LED is orange.
If the link is bad and has been disabled due to a hardware failure, the LED flashes orange.
If no signal is detected, the LED is off.
LED
Description
Status
The switch performs a series of self-tests and diagnostic tests.
If all the tests pass, the status LED is green.
If a test other than an individual port test fails, the status LED is red.
During system boot or if the module is disabled, the LED is orange.
During self-test diagnostics, the LED is orange.
If the module is disabled, the LED is orange.
RX (Receive)
Whenever a port is receiving a packet, the receive (RX) LED is green for approximately 50 ms1; otherwise, it is off.
TX (Transmit)
Whenever a port is transmitting a packet, the transmit (TX) LED is green for approximately 50 ms; otherwise, it is off.
Link
The link LED displays the link integrity status of a LAN port. The link LED is green if the link integrity is good. The link LED will blink to indicate that a collision is detected on this link.
1 ms = milliseconds.

LED
Description
Status
The switch performs a series of self-tests and diagnostic tests.
If all the tests pass, the status LED is green.
If a test other than an individual port test fails, the status LED is red.
During system boot or if the module is disabled, the LED is orange.
During self-test diagnostics, the LED is orange.
If the module is disabled, the LED is orange.
RX (Receive)
Whenever the port is receiving a cell, the receive (RX) LED is green for approximately 50 ms1; otherwise, it is off.
TX (Transmit)
Whenever the port is transmitting a cell, the transmit (TX) LED is green for approximately 50 ms; otherwise, it is off.
Link
The link LED displays the link integrity status of the ATM port. The link LED is green if the link integrity is good. The link LED will blink to indicate that a collision is detected on this link.
1 ms = milliseconds.
LED
Description
Status
The switch performs a series of self-tests and diagnostic tests.
If all the tests pass, the status LED is green.
If a test other than an individual port test fails, the status LED is red.
During system boot or if the module is disabled, the LED is orange.
During self-test diagnostics, the LED is orange.
If the module is disabled, the LED is orange.
RingOp
Indicates whether or not the ring is operational.
If the ring is operational, the RingOp LED is green.
If the ring is not operational, the RingOp LED is off.
Thru
If the FDDI/CDDI A and B ports are connected to the primary and secondary rings, the Thru LED is green; otherwise, it is off.
Wrap A
If the FDDI/CDDI A port is connected to the ring and the B port is isolated, the Wrap A LED is green; otherwise, it is off.
Wrap B
If the FDDI/CDDI B port is connected to the ring and the A port is isolated, the Wrap B LED is green; otherwise, it is off.
Port A status
If the FDDI/CDDI A port is connected to the ring, the port A LED is green.
If the FDDI/CDDI A port receives a signal but fails to connect, or a dual homing condition exists, the port A LED is orange.
The LED is turned off if no receive signal is detected.
Port B status
If the FDDI/CDDI B port is connected to the ring, the port B LED is green.
If the FDDI/CDDI B port receives a signal but fails to connect, or a dual homing condition exists, the port B LED is orange.
The LED is turned off if no receive signal is detected.
In
The optical Bypass switch LED indicates the status of the device connected to the line module. When the LED is on, the Bypass switch is activated and is in Thru mode (the line module is attached to the dual ring).
LED
Description
Status
The switch performs a series of self-tests and diagnostic tests.
If all the tests pass, the status LED is green.
If a test other than an individual port test fails, the status LED is red.
During system boot or if the module is disabled, the LED is orange.
During self-test diagnostics, the LED is orange.
If the module is disabled, the LED is orange.
RingOp
Indicates whether or not the ring is operational.
If the ring is operational, the RingOp LED is green.
If the ring is not operational, the RingOp LED is off.
Thru
If the FDDI/CDDI A and B ports are connected to the primary and secondary rings, the Thru LED is green; otherwise, it is off.
Wrap A
If the FDDI/CDDI A port is connected to the ring and the B port is isolated, the wrap A LED is green; otherwise, it is off.
Wrap B
If the FDDI/CDDI B port is connected to the ring and the A port is isolated, the wrap B LED is green; otherwise, it is off.
Port A status
If the FDDI/CDDI A port is connected to the ring, the port A LED is green.
If the FDDI/CDDI A port receives a signal but fails to connect, or a dual homing condition exists, the port A LED is orange.
The LED is turned off if no receive signal is detected.
Port B status
If the FDDI/CDDI B port is connected to the ring, the port B LED is green.
If the FDDI/CDDI B port receives a signal but fails to connect, or a dual homing condition exists, the port B LED is orange.
The LED is turned off if no receive signal is detected.
In
The optical Bypass switch LED indicates the status of the device connected to the line module. When the LED is on, the Bypass switch is activated and is in Thru mode (the line module is attached to the dual ring).
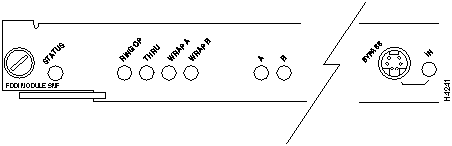
LED
Description
Status
The switch performs a series of self-tests and diagnostic tests.
If all the tests pass, the status LED is green.
If a test other than an individual port test fails, the status LED is red.
During system boot or if the module is disabled, the LED is orange.
During self-test diagnostics, the LED is orange.
If the module is disabled, the LED is orange.
RingOp
Indicates whether or not the ring is operational.
If the ring is operational, the RingOp LED is green.
If the ring is not operational, the RingOp LED is off.
Thru
If the FDDI/CDDI A and B ports are connected to the primary and secondary rings, the Thru LED is green; otherwise, it is off.
Wrap A
If the FDDI/CDDI A port is connected to the ring and the B port is isolated, the Wrap A LED is green; otherwise, it is off.
Wrap B
If the FDDI/CDDI B port is connected to the ring and the A port is isolated, the Wrap B LED is green; otherwise, it is off.
Port A status
If the FDDI/CDDI A port is connected to the ring, the port A LED is green.
If the FDDI/CDDI A port receives a signal but fails to connect, or a dual homing condition exists, the port A LED is orange.
The LED is turned off if no receive signal is detected.
Port B status
If the FDDI/CDDI B port is connected to the ring, the port B LED is green.
If the FDDI/CDDI B port receives a signal but fails to connect, or a dual homing condition exists, the port B LED is orange.
The LED is turned off if no receive signal is detected.
In
The optical Bypass switch LED indicates the status of the device connected to the line module. When the LED is on, the Bypass switch is activated and is in Thru mode (the line module is attached to the dual ring).
telnet host [ port ]
host
The remote host to connect to.
port
A specific port on the remote host to connect to.
Console> (enable) telnet help
Usage: telnet <host> [port]
(host is ipalias or IP address in dot notation: a.b.c.d)
Console> (enable) telnet elvis
Trying 192.122.174.11...
Connected to elvis.
Escape character is '^]'.
UNIX(r) System V Release 4.0 (elvis)
login: fred
Password:
Last login: Thu Feb 15 09:25:01 from forster.cisc.rum
Sun Microsystems Inc. SunOS 5.4 Generic July 1994
You have new mail.
% logout
Console> (enable)
ping -s host [packet_size] [packet_count]
-s
Causes ping to send one datagram per second, printing one line of output for every response received. The ping command does not return any output when no response is received.
host
The IP address or IP alias of the host.
packet_size
(Optional) The number of bytes in a packet, from 1 to 2,000 bytes, with a default of 56 bytes. The actual packet size is eight bytes larger because the switch adds header information.
packet_count
(Optional) The number of packets to send.
Console> ping elvis
elvis is alive
Console> ping -s elvis
ping elvis: 56 data bytes
64 bytes from elvis: icmp_seq=0. time=11 ms
64 bytes from elvis: icmp_seq=1. time=8 ms
64 bytes from elvis: icmp_seq=2. time=8 ms
64 bytes from elvis: icmp_seq=3. time=7 ms
64 bytes from elvis: icmp_seq=4. time=11 ms
64 bytes from elvis: icmp_seq=5. time=7 ms
64 bytes from elvis: icmp_seq=6. time=7 ms
^C
----elvis PING Statistics----
7 packets transmitted, 7 packets received, 0% packet loss
round-trip (ms) min/avg/max = 7/8/11
Console>
Console> show system
PS-Status Fan-Status Temp-Alarm Sys-Status Uptime d,h:m:s
--------- ---------- ---------- ---------- --------------
ok ok off ok 27,17:05:50
Modem Baud MAC-Address-Range
-------- ----- -------------------------------------
disabled 9600 00-04-0b-a0-04-1f to 00-04-0b-a0-05-56
System Name System Location System Contact
------------------------ ------------------------ ----------------------
WBU-Catalyst-5000 5 Closet 202 1/F Luis x5529
Console>
Console> show config
begin
set password $1$FMFQ$HfZR5DUszVHIRhrz4h6V70
set enablepass $1$FMFQ$HfZR5DUszVHIRhrz4h6V70
set prompt Console>
!
#system
set system baud 9600
set system modem disable
set system name Catalyst 5000
set system location Sunnyvale, CA
set system contact Bob Lewis
!
#snmp
set snmp rmon enable
set snmp community read-only public
set snmp community read-write private
set snmp community read-write-all secret
set snmp trap 171.69.194.181 public
set snmp trap disable
!
#vlan/trunk
clear trunk all
!
set vlan 1 1/1-2,2/1-24
!
#trunks
!
#MAC filters
clear filter all
!
#cam
set cam agingtime 0
!
#spantree
#vlan 1
set spantree enable 1
set spantree fwddelay 20 1
set spantree hello 2 1
set spantree maxage 20 1
set spantree priority 45 1
set spantree portpri 1/1 32
set spantree portcost 1/1 100
set spantree portpri 1/2 32
set spantree portcost 1/2 100
set spantree portpri 2/1 32
set spantree portcost 2/1 100
.
.
.
set spantree portpri 2/24 32
set spantree portcost 2/24 100
!
#vlan trunk/monitor
!
#ip
set interface sc0 192.122.174.220 255.255.255.0 192.122.174.255
set redirect enable
set route 0.0.0.0 192.122.174.102 1
set arp agingtime 1200
!
#cdp
set cdp 1/1 enable 60
set cdp 1/2 enable 60
set cdp 2/1 enable 60
set cdp 2/2 enable 60
set cdp 2/3 enable 60
.
.
.
set cdp 2/24 enable 60
!
#ipalias
set ipalias default 0.0.0.0
set ipalias cres 192.122.173.42
set ipalias calypso 171.69.194.181
!
#alias
!
#port monitoring
set monitor 1 1/1 both
set monitor disable
!
#module 1
set port enable 1/1
set port name 1/1
set port duplex 1/1 half
set port speed 1/1 -1315
set port level 1/1 high
set port enable 1/2
set port name 1/2
set port duplex 1/2 half
set port speed 1/2 504
set port level 1/2 normal
!
#module 2
set module enable 2
!
set port enable 2/1
set port name 2/1 network
set port duplex 2/1 half
set port level 2/1 normal
set port enable 2/2
set port name 2/2
set port duplex 2/2 half
set port level 2/2 normal
.
.
.
set port enable 2/24
set port name 2/24
set port duplex 2/24 half
set port level 2/24 normal
!
#module 3 empty
!
#module 4 empty
!
#module 5 empty
end
Enter the show port command to display the current system configuration:
Console> (enable) show port
Port Name Status Vlan Level Duplex Speed Type
---- -------------------- ---------- ---------- ------ ------ ----- --------------
1/1 Management Port notconnect 1 normal half 100 100BaseTX
1/2 InterSwitchLink connected trunk normal half 100 100BaseTX
2/1 Dennis connected 10 normal a-half a-10 10/100BaseTX
2/2 Luis notconnect 10 normal auto auto 10/100BaseTX
2/3 Iris notconnect 10 normal auto auto 10/100BaseTX
2/4 Nancy connected 10 normal a-half a-10 10/100BaseTX
2/5 Arthur notconnect 20 normal auto auto 10/100BaseTX
2/6 Ron notconnect 20 normal auto auto 10/100BaseTX
2/7 Connie disabled 20 normal auto auto 10/100BaseTX
2/8 Bill notconnect 20 normal auto auto 10/100BaseTX
2/9 notconnect 20 normal auto auto 10/100BaseTX
2/10 notconnect 20 normal auto auto 10/100BaseTX
2/11 notconnect 20 normal auto auto 10/100BaseTX
2/12 notconnect 20 normal full 10 10BaseT
Port Align-Err FCS-Err Xmit-Err Rcv-Err
---- ---------- ---------- ---------- ----------
1/1 0 0 0 0
1/2 1 0 0 0
2/1 0 0 0 0
2/2 0 0 0 0
2/3 0 0 0 0
2/4 30 0 0 0
2/5 0 0 0 0
2/6 0 0 0 0
2/7 0 0 0 0
2/8 0 0 0 0
2/9 0 0 0 0
2/10 0 0 0 0
2/11 0 0 0 0
2/12 0 0 0 0
Port Single-Col Multi-Coll Late-Coll Excess-Col Carri-Sens Giants
---- ---------- ---------- ---------- ---------- ---------- ----------
1/1 0 0 0 0 0 0
1/2 680 418 0 1 0 -
2/1 756 99 0 0 0 0
2/2 0 0 0 0 0 0
2/3 0 0 0 0 0 0
2/4 409 403 0 11 0 1256
2/5 0 0 0 0 0 0
2/6 0 0 0 0 0 0
2/7 0 0 0 0 0 0
2/8 0 0 0 0 0 0
2/9 0 0 0 0 0 0
2/10 0 0 0 0 0 0
2/11 0 0 0 0 0 0
2/12 0 0 0 0 0 0
Last-Time-Cleared
--------------------------
Wed Dec 27 1995, 16:09:47
Console> (enable)
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()