|
|
The FastHub 100+ Series includes two stackable, manageable, 100-Mbps Class II repeaters:
A 16-port expansion module can be added to expand each FastHub unit to 32 100BaseT ports. Up to 4 FastHub units can be interconnected through a proprietary expansion cable to form a hub stack with a maximum of 128 ports. The four-unit hub stack operates as a single logical repeater with one network management module (NMM) per hub stack. Two hub stacks can be connected through the 100BaseT ports to support up to 254 ports in a single collision domain.
Cisco documentation and additional literature are available on a CD-ROM called Cisco Connection Documentation, Enterprise Series, which ships with your chassis. The CD is updated and shipped monthly, so it might be more up to date than printed documentation. To order additional copies of the Cisco Connection Documentation, Enterprise Series CD, contact your local sales representative or call Customer Service. The CD is available both as a single CD and as an annual subscription. You can also access Cisco technical documentation on the World Wide Web URL http://www.cisco.com.
Table 1-1 summarizes FastHub features.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Compatibility |
|
| Performance |
|
| Stackability |
|
| Manageability |
|
| Redundancy |
|
This section provides physical and functional descriptions of the two FastHub 100+ Series repeaters.
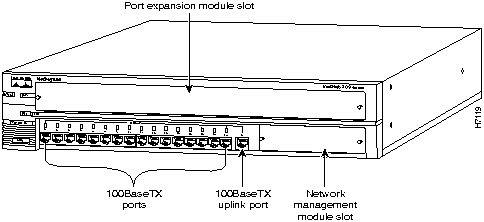
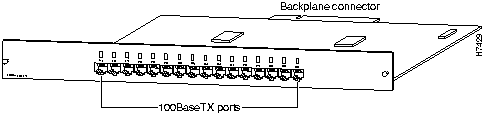
The FastHub 116T+ base unit (see Figure 1-1) provides 16 100Base TX ports for connecting to devices using Category 5 unshielded twisted-pair (UTP) cabling. The uplink port (port 16 to the right of port 16x) is not internally crossed, providing a means of cascading hubs using standard straight-through cables.
All 100BaseTX ports use RJ-45 twisted-pair connectors.
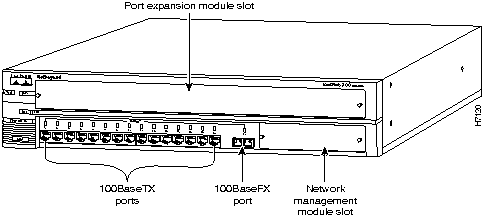
The FastHub 116C+ base unit (see Figure 1-2) provides 15 100BaseTX ports and
The 100BaseFX port uses an SC connector.
Figure 1-1 : FastHub 116T+ Base Unit Figure 1-2 : FastHub 116C+ Base Unit Understanding the Front Panel LEDs
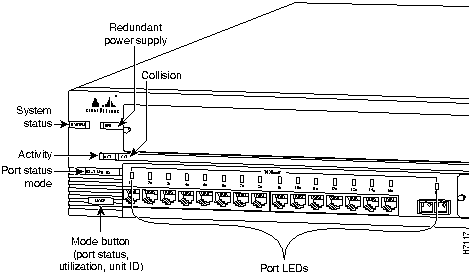
The FastHub LEDs enable you to monitor network activity and performance. Figure 1-3 shows the location of the LEDs (for simplicity, only the FastHub 116T+ base unit is shown; both base-unit LED locations and functions are identical).
The system status LED (see Table 1-2) shows whether a unit is powered and provides an indication of a problem with a unit's main system board.
Table 1-2 : System Status LED Description
The group collision LED (see Table 1-3) shows the frequency of collisions for all ports on a unit, including port expansion module ports. The LED flashes if one or more ports on the unit are involved in a collision.
In a hub stack, the group collision LEDs on individual units show the frequency of collisions across the entire collision domain. For example, if a port on unit 1 and a port on unit 2 both have collisions, the group collision LEDs on both units flash.
Table 1-3 : Group Collision LED Description
The group activity LED (see Table 1-4) shows network activity for all ports on a unit.
Table 1-4 : Group Activity LED Description
The RPS LED (see Table 1-5) shows the status of the RPS.
Table 1-5 : RPS LED Description
The NMM LED (see Table 1-6), located on the NMM front panel, shows the status of the NMM module.
Table 1-6 : NMM Status LED Description
Each FastHub port has an LED that operates in three modes:
Changing the Mode of the Port LEDs
To change the mode being displayed by a port LED, press the Mode button to highlight in sequence each of the modes: STAT, UTL, and ID. When the desired mode is on, release the button to make the change. As long as you hold the Mode button down, the on mode does not change.
The selected mode remains on for 30 seconds before returning to the default mode of STAT (port status).
STAT Mode
In STAT mode, port LEDs show individual port status (see Table 1-7).
Table 1-7 : Port Status LED Description
UTL Mode
Invoke the utilization mode by pressing the Mode button and releasing it when UTL is highlighted. In utilization mode, bandwidth usage is shown for the entire hub stack. The port LEDs show current bandwidth and the peak bandwidth usage that occurred since the last reset.
The far-right solid green LED denotes the peak bandwidth that was recorded since the last reset.
All LEDs to the left of the solid green LED operate in a scalable pattern, flashing green from left to right, to show the current bandwidth utilization. Table 1-8 lists the port LEDs and the bandwidth associated with each LED.
Table 1-8 : Utilization LEDs Scale
ID Mode
Invoke the ID mode by pressing the Mode button and releasing it when ID is highlighted. In ID mode, port LEDs show the ID number of each unit within the hub stack. For example, the FastHub with unit ID 3 has its port 3 LED on (green); all other port LEDs on unit 3 are off. The unit numbers coincide with the unit numbers displayed in the NMM management console screens.
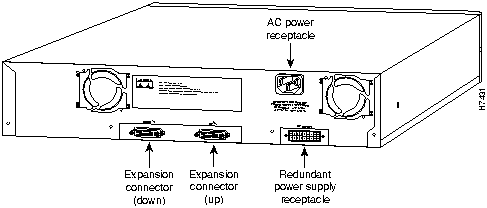
Figure 1-4 shows the location of the rear panel connectors.
Figure 1-4 : FastHub Rear Panel Connectors The FastHub has a slot for an optional 100BaseTX/16 port expansion module. This hot-insertable module (see Figure 1-5) provides an additional 16 100BaseTX ports, creating a 32-port repeater within a single unit.
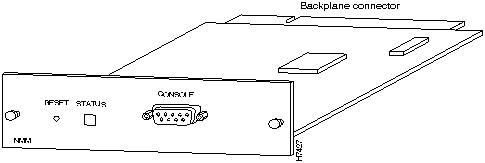
Figure 1-5 : 100BaseTX/16 Port Expansion Module The FastHub has a second, smaller slot in the bottom-right corner of the unit for an optional NMM. This hot-insertable module (see Figure 1-6) provides manageability for a hub stack on a per port, per unit, and per hub-stack basis. A single NMM can reside in any unit in the hub stack and manage all units in the hub stack.
Figure 1-6 shows the location of NMM front-panel components.
Figure 1-6 : Network Management Module For management redundancy, install a second NMM in the same hub stack. One module serves as the primary NMM, and the other operates in a standby role.
The NMM provides support for Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP), Telnet, terminal-based out-of-band management, and Remote Monitoring (RMON).
See the "Out-of-Band Management" chapter for detailed information on using the NMM management console.
This section describes several possible network configurations.
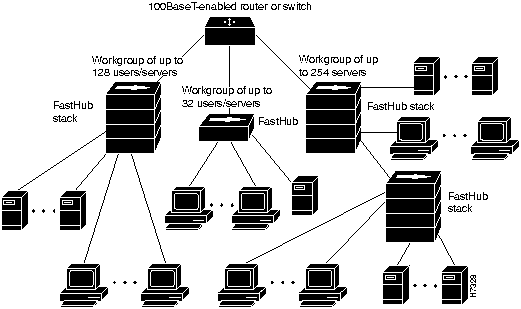
You can create 100-Mbps workgroups by interconnecting up to 4 FastHubs. The network can be further scaled by connecting two FastHub stacks together, as shown in Figure 1-7.
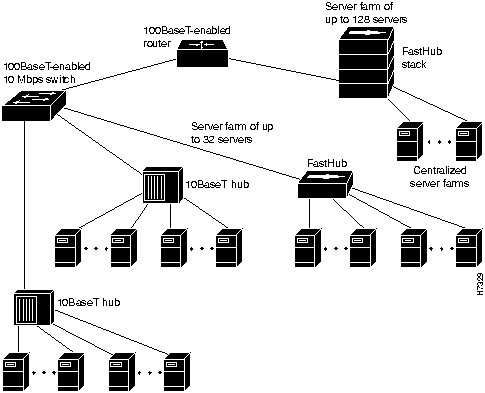
Figure 1-7 : Example Configuration: Workgroups You can create 100-Mbps server farms to increase centralized and decentralized server performance, as shown in Figure 1-8.
Figure 1-8 : Example Configuration: Server Farms
Copyright 1988-1996 © Cisco Systems Inc.
![]()
1 100BaseFX port. The 100BaseFX port provides for connecting to a device using two-strand, multimode fiber-optic cabling.
Color
System Status
Off
Unit powered off.
Solid green
Unit powered and operational; no power problems.
Solid amber
Unit powered but not operational; problem related to FastHub main system board (not the internal power supply or RPS).
Color
System Status
Off
No collision
Flashing amber
Collision
Solid amber
High number of collisions
Color
System Status
Off
No activity
Flashing green
Activity
Color
RPS Status
Off
RPS off or not installed.
Solid green
RPS operational.
Flashing green
RPS and FastHub power supplies are both powered on. Only one power source can be supplying power to a unit. If you are using the RPS, the FastHub power cord must not be plugged in. If you are using the FastHub power supply, the RPS can be connected but must be powered off.
Solid amber
RPS not operational.
Color
NMM Status
Off
FastHub not powered or NMM not properly seated.
Flashing green
NMM power-on self-test (POST) in progress.
Solid green
Primary NMM operational (enabled).
Solid amber
Secondary NMM operational (in standby).
Flashing amber
NMM failed POST.
Color
Port Status
Off
No link (link down).
Green
Link operational (with no activity).
Flashing green
Link operational (with activity).
Rapidly alternating green/amber
Faulty link1.
Alternating green/amber
FastHub reset in progress.
Solid amber
Port disabled (through in-band or out-of-band management).
1 This indication remains until the link fault is corrected. Possible causes are autopartition, jabber, and isolated (carrier integrity error). Note that this state should not be confused with the "no link status" (link down) indication where the link is not operational.
LED
Mbps Activity
Port 1
0 to 6.25
Port 2
12.5
Port 3
18.75
Port 4
25
Port 5
31.25
Port 6
37.5
Port 7
43.75
Port 8
50
Port 9
56.25
Port 10
62.50
Port 11
58.75
Port 12
75
Port 13
81.25
Port 14
87.5
Port 15
93.75
Port 16
100
230 VAC.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()