|
|
This chapter provides the following troubleshooting sections:
The FastHub front-panel LEDs facilitate troubleshooting during system operation. Table 6-1 lists symptoms and possible causes associated with system problems and provides corrective actions. See Table 6-2 to isolate faults associated specifically with the power distribution system.
Table 6-1 : Problems and Recommended Responses
| Symptom | Possible Cause | Corrective Action |
|---|---|---|
| System status LED is off. | Power cord not connected. | Plug in both ends of power cord. |
| System status LED is solid amber. | Power problem related to FastHub main system board (not the internal power supply or RPS). | Call Cisco Systems. |
| Port status LED is off. | Devices not powered. | Ensure both devices have power. |
| Cable connection loose. | Verify connection at both ends of cable. | |
| Wrong cable type. | Verify cable type (crossover vs. straight-through). | |
| Incorrect wiring. | See "Appendix B" for pinout information. | |
| Faulty cable. | Replace cable with a known good one. | |
| Port status LED is rapidly alternating green/amber. | Autopartition, jabber, or isolated (carrier integrity error). | Verify port termination and check integrity of connected devices. |
| Port status LED is solid amber (port disabled or autopartitioned). | Device at other end is malfunctioning. | Investigate device at other end of cable attached to disabled port. |
| Port disabled. | Enable port through in-band or out-of-band management. | |
| All port expansion module port LEDs off. | Module not properly seated in backplane connector. | Reinsert module. |
| NMM status LED is off. | Module not properly seated in backplane connector. | Reinsert module. |
| NMM status LED is flashing amber. | POST failure. | Attach a monitor to the console port to display the diagnostic console. See the "NMM POST Failures" section in this chapter for troubleshooting information. |
| NMM status LED is solid amber. | NMM is in standby mode. | Use the diagnostic console described in the "Diagnostic Console Menu" section in this chapter to reset the FastHub. |
Table 6-2 : Isolating Power Distribution Problems
| System Status LED | RPS LED | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| Solid green | Off | Power OK (no RPS or RPS not powered on). |
| Solid green | Solid green | Power OK (RPS powered on and OK). |
| Solid green | Solid amber | FastHub power supply not powered on, RPS connected but not OK.
FastHub power supply powered on, RPS either not powered on or not OK. |
| Solid green | Flashing green | FastHub power supply and RPS are powered on. If you are using the RPS, the FastHub power cord must not be plugged in. If you are using the FastHub power supply, the RPS can be connected but must be powered off. |
When the FastHub is powered up or reset, the NMM begins its POST. Failure of the POST generates a "POST failed" message as shown in Figure 6-1. POST failures are usually not fatal, unless they happen to the RAM test or the timer interrupt test. When a non-fatal POST failure occurs, the repeater begins forwarding packets, but the system LED turns amber, and a POST-failure message displays on the management console screen. See Table 6-3 for POST test failure descriptions.
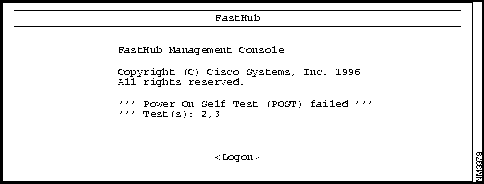
| Test Number | Failure Indication |
|---|---|
| 1 | Processor RAM functionality is lost. |
| 2 | Console port failure. Must use in-band management; other functionality not effected. |
| 3 | Ethernet address failure. A default addressing is used. |
| 4 | Timer interrupt functionality is lost. |
| 5, 6 | Real-time clock failure. System date and time functionality is lost. |
| 7 | Port loopback failure. Some port functionality is lost. |
The diagnostic console is for those instances when the FastHub firmware has been corrupted or the present FastHub configuration prevents the firmware from executing properly. The diagnostic console logon screen shown in Figure 6-2 is displayed when the firmware has been corrupted.
Figure 6-2 : Diagnostic Console Logon
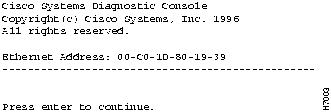
If you have defined a password for the FastHub, you are prompted for the password. If you have forgotten the password, you can obtain a factory-installed password by calling Cisco Systems and providing the Ethernet address displayed on the screen.
If no password has been defined, press Return to display the diagnostic console shown in Figure 6-3.
Displaying the Diagnostic Console
You might need the diagnostic console even though the firmware is valid. This could happen, for example, if the FastHub configuration prevents the firmware from executing properly and you cannot display the normal management console.
Use the following procedure to override the normal firmware startup and immediately display the diagnostic console shown in Figure 6-3.
Use the diagnostic console menu, shown in Figure 6-3, to troubleshoot firmware problems and, after resolving the problem, bring up the firmware.
Figure 6-3 : Diagnostic Console
[C] Continue with standard system startup. Select this option after you have resolved the firmware problems with options [U] or [S]. It brings up the debugged or upgraded firmware.
[U] Upgrade operation firmware (XMODEM). Select this option to initiate a firmware upgrade. This option works only with XMODEM and only uses the default EIA/TIA-232 parameters:
Use the following procedure to upgrade the firmware with the XMODEM protocol.
[S] System Debug Interface. Select this option to display the System Debug Interface menu, shown in Figure 6-4. You can use this menu to reset the NMM console port or you can reset the entire FastHub to factory defaults.
Use this menu, shown in Figure 6-4, to reset the NMM console port or to reset the entire FastHub to factory defaults. You can also use the management console to perform these functions.
Figure 6-4 : System Debug Interface G] Generic I/O. For Cisco personnel only.
[M] Memory CPU (I/O). For Cisco personnel only.
[V] View Management Console password. Use this option to view the password currently assigned to the management console. If no password has been configured, the following message displays:
[R] Return system to factory defaults. Use this option to return the FastHub to its factory default settings. All static and dynamic addresses are removed, as is the IP address and all configured system parameters. Enter Y or N and press Return. The changes take effect the next time the FastHub is reset.
[R] Reset main console RS232 interface to 9600, 8, 1, N. Select this option if you have lost the management console connection because of an improper modem configuration. The next time the FastHub is reset, the default RS-232 configuration is used.
Copyright 1988-1996 © Cisco Systems Inc.

Operation firmware version: Status:
Validity of the current firmware. If the current image is not valid, option C on the diagnostic console is not displayed.
Boot firmware version:
Write-protected part of the firmware that supports the diagnostic console.

No password has been set.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()