|
|
Installing the SBus Adapter Software
This chapter explains how to install the SBus adapter software, which includes an FDDI SBus driver and an SNMP agent. If the software needs to be removed from your system, see the appendix "Running the FDDI deinstall Script."
To install the SBus adapter software, you need a SPARCstation or SPARCserver with a floppy disk drive in your network. Separate procedures are included for SunOS 4.1.x (see the following section, "SunOS Installation") and Solaris 2.x and later operating systems (see the section "Installing the Solaris 2.x Driver Using the pkgadd Script" later in this chapter).
You should be familiar with the UNIX system and a UNIX text editor. You also need to know the following:
For the SunOS 4.1.x installation, you should have 2,700 kilobytes (KB) of disk space in the /usr directory. If you are installing a new kernel (linkable driver), make sure you have 1,600 KB available in your root directory for the new kernel. Use the df command to check available disk space.
The Solaris 2.x installation procedure automatically checks for enough disk space.
The SunOS driver floppy disk contains both loadable and kernel-resident drivers. If you use the loadable driver, you can load or unload the driver into the kernel at any time. The loadable driver is appropriate for systems that boot from a local disk. The kernel-resident driver is built into a new kernel.
The SBus adapter software disk contains an installation script called install.fddi that adds an SNMP agent and installs a loadable or kernel-resident driver.
Following is an overview of this section on how to install software packages on your SunOS 4.1.x system:
![]()
Copying the SunOS Driver Files
Perform the following tasks to load the new SunOS driver files:
Running the SunOS Install Script
Now you need to invoke the SBus adapter software installation script using the install.fddi command.
The script asks various questions about the kind of installation you want to perform, and about your system. Specifically, it asks for the following information:
SunOS Loadable Driver Installation
Perform the following tasks to install the SunOS loadable driver:
Files Added or Modified During Installation of the
The installation of the loadable FDDI driver removes any existing /etc/hostname.fddix files to prevent the rc.boot script from bringing up the interfaces.
The installation also modifies the following files:
The installation procedure adds the following text to rc.local to load the loadable driver and bring up the interfaces. This must occur before NIS and other networking daemons are started.
In this example, console-fddi is the name of the fddi interface.
The installation procedure adds the following text to /etc/loadable. If this file does not exist, the installation creates one.
The installation procedure creates the following files and links in /dev:
SunOS Linkable, Kernel-Resident Driver Installation
The following steps describe how to install the SunOS linkable, kernel-resident driver:
Files Added or Modified During Installation
The installation of the linkable driver creates /etc/hostname.fddix files so that the rc.boot script brings up each interface when the system boots.
Software running on a Solaris 2.x system is installed in packages using the pkgadd command. Refer to the pkgadd(1m), pkgrm(1m), and pkginfo(1m) man pages for more information.
Following is an overview of this section on how to install software packages on your Solaris 2.x system:
Your Solaris driver floppy disk contains the following packages:
Copying the Solaris 2.x Files on a Local System
Perform the following steps to load the new software on to your local SPARCstation or SPARCserver running Solaris 2.x :
Copying the Solaris 2.x Files From a Remote Workstation
Perform the following steps to load the new software on your local SPARCstation or SPARCserver running Solaris 2.x from a remote workstation:
Copying the Solaris 2.x Files from Diskette to Tape to Workstation
You can load the Solaris driver on a SPARCstation or SPARCserver running Solaris 2.x if you cannot mount a remote floppy drive over the NFS network. You need another workstation with a floppy drive and a tape drive to perform the floppy-to-tape duplication.
Transfer the Solaris driver software to media (for example, 4-mm, 8-mm, or QIC cartridge tape) that is compatible with the workstation that requires the SBus driver by performing the following steps:
The following steps are performed at the workstation requiring the SBus driver.
Installing the Solaris 2.x Driver Using the pkgadd Script
This script asks various questions about the kind of installation you want to perform, and about your system. Specifically, it asks for the following information:
Perform the following tasks to use the Solaris pkgadd script:
Setting Up Routers for SunOS 4.1.x
When you install an FDDI SBus adapter in a system with an existing Ethernet interface, it automatically becomes a router serving both the FDDI and Ethernet networks. The router is known to the Ethernet network by its Ethernet IP address and host name, and to the FDDI network by its FDDI IP address and host name.
Stations on an internetwork can be reached via multiple routes. When a standard SunOS system is booted, the route daemon (routed) sends out packets over both the Ethernet and the FDDI networks. The route daemon determines the optimal route between stations by relative hop count, not by the speed of the interface. Therefore, in cases where the hop counts are equal, the use of FDDI is not guaranteed. You can guarantee the use of FDDI for network commands by specifying the FDDI host name or IP address of the destination machine.
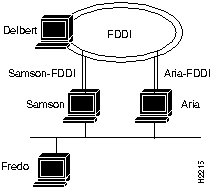
In Figure 3-1, two commands will each resolve the same physical file on the workstation called Aria.
Figure 3-1 : Setting Up a Router
If a user on Fredo mounts files on Delbert, then NFS traffic goes over the Ethernet to either Samson or Aria and from there over an FDDI network to Delbert. However, if a user on Samson mounts files on Aria, the NFS traffic can go over either the FDDI or Ethernet.
The user can specify which interface to use by including Aria's FDDI or Ethernet host name in the mount command, as follows:
Both these commands mount to the same physical files on Aria. However, the first results in NFS traffic being routed over the Ethernet networks, while the second results in NFS traffic being routed over the FDDI network.
Copyright 1988-1996 © Cisco Systems Inc.
tar -xvf /dev/rfd0
rcp -r cfddi console:/usr/local
if_fddi.o.sun4c deinstall.fddi
if_fddi.o.sun4m download_flash.README
fddi.INSTALL install.fddi
fddi.load.sun4c.o mibs/
fddi.load.sun4m.o snmpd
fddi_conf.c snmpd.cfddi
fddistat ttcp
README download_flash
![]()
console# ./install.fddi
You have invoked the ./install.fddi script, which is used to install
software for FDDI SBus Adapters.
There are two steps to the installation:
1) Install SNMP agent (optional).
2) Install FDDI SBus driver.
Is this install for a diskless station (y/n) [n]
Do you wish to install the SNMP agent (y/n) [y] ?
Copying snmpd.cfddi to /etc
Updating /etc/rc.local to start SNMP agent at boot time.
Installation of SNMP agent done.
Do you wish to install the FDDI SBus driver (y/n) [y]
You can install the FDDI SBUS driver
as a kernel resident driver or as a loadable driver.
Do you wish to install the loadable driver (y/n) [y] ?
Will the ethernet interface continue to be used
(y/n) [y] ?
How many FDDI interfaces are being installed in this machine [1] ?
Enter hostname for FDDI interface fddi0 [
console-fddi]:
You are using NIS, do you want to get ip address from NIS (y/n) [y] ?
Retrieved ipaddr 172.20.43.146 for host console-fddi
Enter IP address for FDDI interface fddi0 [172.20.43.146]:
Do you want the FDDI driver to be loaded after each reboot (y/n) [y] ?
Updating /etc/rc.local to load driver at boot time
Copying fddistat to /etc
Is the FDDI driver kernel resident and
do you want to rebuild the kernel now (y/n) [n]
optimizing tcp_sendspace && tcp_recvspace to 24K
Installation of FDDI SBus driver complete.
You should now halt the system, power down,
and install the FDDI SBus Adapter.
A log of the installation is in ./install.fddi.log
console#
adb -w fddi.load.sun4c.o
fddimode0?W 1
$q
adb -w fddi.load.sun4m.o
fddimode0?W 1
$q
adb -w /vmunix
fddimode0?W 1
$q
adb -w fddi.load.sun4c.o
nfddimaxtbd?W 8
fddimaxcopysz?W Ox1194
$q
adb -w /vmunix
nfddimaxtbd?W 8
fddimaxcopysz?W Ox1194
$q
![]()
SunOS Loadable Driver
# Load loadable modules.
if [ -f /etc/loadable ]; then
/etc/loadable
fi
ifconfig fddi0 console-fddi netmask + -trailers up
#
# Load the fddi driver.
#
if [ -f /dev/fddi.LOAD ]; then
if [ -f /dev/fddi.AUTOLOAD ]; then
/dev/fddi.LOAD
fi
fi
/dev/fddi.AUTOLOAD
/dev/fddi.INSTALL -> /usr/local/cfddi/fddi.INSTALL
/dev/fddi.LOAD -> /dev/fddi.INSTALL*
/dev/fddi.MKDEV -> /dev/fddi.INSTALL*
/dev/fddi.RMDEV -> /dev/fddi.INSTALL*
/dev/fddi.UNLOAD -> /dev/fddi.INSTALL*
/dev/fddi.load.sun4c.o -> /usr/local/cfddi/fddi.load.sun4c.o*
/usr/local/cfddi
console#
./install.fddi
You have invoked the ./install.fddi script, which is used to install
software for FDDI SBus Adapters.
There are two steps to the installation:
1) Install SNMP agent (optional).
2) Install FDDI SBus driver.
Is this install for a diskless station (y/n) [n] ?
n
Do you wish to install the SNMP agent (y/n) [y] ?
Copying snmpd.cfddi to /usr/etc
Installation of SNMP agent done.
Do you wish to install the FDDI SBus driver (y/n) [y] ?
You can install the FDDI SBUS driver
as a kernel resident driver or as a loadable driver.
Do you wish to install the loadable driver (y/n) [y] ?
Will the ethernet interface continue to be used (y/n) [y] ?
How many FDDI interfaces are being installed in this machine [1] ?
Enter hostname for FDDI interface fddi0 [console-fddi]:
Enter IP address for FDDI interfacefddi0 [172.20.43.146]:
Enter existing kernel configuration file [GENERIC]:
Enter new kernel configuration file [FDDI]:
Copying/updating files ...
Copying fddi_conf.c to /usr/kvm/sys/sunif
Copying if_fddi.o to /usr/kvm/sys/sun4c/OBJ
Adding config.fddi to /usr/kvm/sys/sun4c/conf/FDDI
Copying fddistat to /usr/etc
Rebuilding kernel ...
Doing a "make depend"
cc -sparc -c -O -Dsun4c -DGENERIC -DSUN4C_60 -DWINSVJ -DVDDRV -DASYNCHIO -DLWP -DVFSSTATS -DRFS -DCRYPT -DTCPDEBUG -DIPCSHMEM -DIPCSEMAPHORE -DIPCMESSAGE -DSYSAUDIT -DSYSACCT -DPCFS...
.
. (data omitted)
.
... -DSUN4C_60 -DWINSVJ -DVDDRV -DASYNCHIO -DLWP -DVFSSTATS -DRFS -DCRYPT -DTCPDEBUG -DIPCSHMEM -DIPCSEMAPHORE -DIPCMESSAGE -DSYSAUDIT -DSYSACCT -DPCFS -DHSFS -DTMPFS -DTFS -DLOFS -DNFSSERVER -DNFSCLIENT -DUFS -DQUOTA -DINET -DKERNEL -I. -I.. -I../.. confvmunix.c
loading vmunix
rearranging symbols
text data bss dec hex
1368064 226064 121768 1715896 1a2eb8
Installing kernel ...
Saving old /vmunix file in /vmunix.save
Copying vmunix to /vmunix
Installation of FDDI SBus driver complete.
You should now halt the system, power down,
and install the FDDI SBus Adapter.
A log of the installation is in ./install.fddi.log
console#
of the SunOS Linkable Driver
mount -r /dev/diskette /mnt
pkgadd -d /mnt
mount -r /dev/diskette /mnt
share -F nfs /mnt
sh /etc/init.d/nfs.server start
mount hostname
:/mnt /mnt
pkgadd -d /mnt
mount -r /dev/diskette /mnt
mount -r /dev/fd0 /mnt
tar cvf tapedevice
/mnt
/usr/local/fddi
tar xvf tapedevice
pkgadd -d /usr/local/fddi
The following packages are available:
1 CSCOmibs Solaris 2.X Mibs
(sparc) 4.1
2 SBUSfddi Solaris 2.X FDDI Driver
(sparc) 3.1
3 SBUSsnmp Solaris 2.X FDDI SNMP Agent
(sparc) 4.1
Select package(s) you wish to process (or 'all' to process
all packages). (default: all) [?,??,q]:
Processing package instance <CSCOmibs> from </sw/release/c300/driver/sun5/3.1/pkgbin>
Solaris 2.X Mibs
(sparc) 4.1
Cisco Systems, Inc.
Using </opt> as the package base directory.
## Processing package information.
## Processing system information.
## Verifying disk space requirements.
## Checking for conflicts with packages already installed.
## Checking for setuid/setgid programs.
Installing Solaris 2.X Mibs as <CSCOmibs>
## Installing part 1 of 1.
/opt/CSCOmibs/INSTALL
/opt/CSCOmibs/README
/opt/CSCOmibs/cisco-adapter.mib <symbolic link>
/opt/CSCOmibs/cisco-stack.mib <symbolic link>
/opt/CSCOmibs/rfc1213.mib
/opt/CSCOmibs/rfc1285.mib
/opt/usr/OV/snmp_mibs/cisco-adapter
/opt/usr/OV/snmp_mibs/cisco-stack
/opt/usr/snm/agents/cisco-adapter.oid
/opt/usr/snm/agents/cisco-adapter.schema
/opt/usr/snm/agents/cisco-stack.oid
/opt/usr/snm/agents/cisco-stack.schema
/opt/usr/snm/agents/rfc1285.oid
/opt/usr/snm/agents/rfc1285.schema
[ verifying class <mibs> ]
Installation of <CSCOmibs> was successful.
Processing package instance <SBUSfddi> from </sw/release/c300/driver/sun5/3.1/pkgbin>
Solaris 2.X FDDI Driver
(sparc) 3.1
Copyright (c) 1991-1995 Cisco Systems, Inc.
Using </> as the package base directory.
Is this installation for a diskless station [n] [y,n,?,q]
Is the FDDI Adapter currently installed in the machine [y] [y,n,?,q]
Will the ethernet interface continue to be used [y] [y,n,?,q]
How many FDDI interfaces are being installed in this machine [1] [1-4,?,q]
NIS is running, Do you want to get ip addresses from NIS [y] [y,n,?,q]
Enter hostname for FDDI interface fddi0 [console-fddi0] [?,q]
Enter IP address for FDDI interface fddi0 [172.20.43.146] [?,q]
## Processing package information.
## Processing system information.
## Verifying disk space requirements.
## Checking for conflicts with packages already installed.
## Checking for setuid/setgid programs.
This package contains scripts which will be executed with super-user
permission during the process of installing this package.
Do you want to continue with the installation of this package [y,n,?]
Installing Solaris 2.X FDDI Driver as <SBUSfddi>
## Installing part 1 of 1.
/kernel/drv/fddi
[ verifying class <driver> ]
/opt/SBUSfddi/README
/opt/SBUSfddi/dflash.4.1.X
/opt/SBUSfddi/dflash.solaris
/opt/SBUSfddi/download_flash
/opt/SBUSfddi/download_flash.README
/opt/SBUSfddi/fddistat
/opt/SBUSfddi/network_download
/opt/SBUSfddi/ttcp
[ verifying class <tools> ]
## Executing postinstall script.
Running add_drv to add driver to system ...
Creating file //etc/hostname.fddi0 with host console-fddi
If the FDDI Adapter is currently active you must reboot
after this installation in order for the new driver to be loaded.
Activating interface fddi0 with hostname: console-fddi ip address: 172.20.43.146
Installation of <SBUSfddi> was successful.
Processing package instance <SBUSsnmp> from </sw/release/c300/driver/sun5/3.1/pkgbin>
Solaris 2.X FDDI SNMP Agent
(sparc) 4.1
Copyright (c) 1991-1995 Cisco Systems, Inc.
Using </> as the package base directory.
## Processing package information.
## Processing system information.
## Verifying disk space requirements.
## Checking for conflicts with packages already installed.
## Checking for setuid/setgid programs.
Installing Solaris 2.X FDDI SNMP Agent as <SBUSsnmp>
## Installing part 1 of 1.
/etc/init.d/snmpsetup
/etc/snmpd.cfddi
[ verifying class <snmp> ]
/etc/rc2.d/K90snmpsetup <linked pathname>
/etc/rc2.d/S90snmpsetup <linked pathname>
Installation of <SBUSsnmp> was successful.
console#
fredo@samson => mount aria:/usr/etc/install
/usr/etc/install
fredo@samson => mount aria-FDDI:/usr/etc/install
/usr/etc/install
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()