|
|
PA-H and PA-2H HSSI Port Adapter Installation and Configuration
Product Numbers: PA-H(=) and PA-2H(=)
This configuration note describes the installation and configuration of the PA-H and PA-2H High-Speed Serial Interface (HSSI) port adapters, which can be used in the Cisco 7200 series routers, and on the second-generation Versatile Interface Processor (VIP2) in all Cisco 7500 series and in Cisco 7000 series routers using the 7000 Series Route Switch Processor (RSP7000) and 7000 Series Chassis Interface (RSP7000CI). (Refer to the section "Software and Hardware Requirements" on page 4.)
For complete descriptions of interface subcommands and the configuration options available for interfaces, and which support HSSI port adapter functionality, refer to the appropriate software configuration publication listed in the section "If You Need More Information."
This configuration note is organized into the following three parts:
The section "Cisco Connection Online," on page 38, includes general reference information.
The Cisco Internetwork Operating System (Cisco IOS) software running your router contains extensive features and functionality. The use of many of many of these features is easier if you have more information at hand. For information on configuring the Cisco 7000 series or 7500 series routers and VIP2, or the Cisco 7200 series, the following documentation resources are available:
HSSI Port Adapter Installation Prerequisites
This section provides software requirements, a list of parts and tools you will need to perform the port adapter installation, and safety and ESD-prevention guidelines to help you avoid injury and damage to the equipment during installation. Also included is information on the systems in which port adapters can be installed and overview information on interface specifications.
The following sections discuss general information and information about port adapter installation requirements:
Software and Hardware Requirements
The HSSI port adapters (PA-H and PA-2H) require that the host Cisco 7000 series, Cisco 7500 series, or Cisco 7200 series router is running Cisco IOS Release 11.1(6)CA or later.
In the Cisco 7000 series and Cisco 7500 series routers, there are no restrictions on slot locations or sequence; however, in the Cisco 7200 series routers, there are specific configuration guidelines that must be observed for high-bandwidth port adapters.
Refer to the publication Cisco 7200 Series Port Adapter Hardware Configuration Guidelines (Document Number 78-3471-xx), which shipped with your Cisco 7200 series chassis and is also available on the Cisco Connection Documentation, Enterprise Series CD-ROM.
You need the following tools and parts to install a port adapter. If you need additional equipment, contact a service representative for ordering information.
Following are safety guidelines that you should follow when working with any equipment that connects to electrical power or telephone wiring.
Electrical Equipment Guidelines
Follow these basic guidelines when working with any electrical equipment:
Use the following guidelines when working with any equipment that is connected to telephone wiring or to other network cabling:
Preventing Electrostatic Discharge Damage
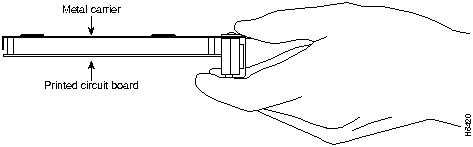
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) damage, which can occur when electronic cards or components are improperly handled, results in complete or intermittent failures. Port adapters and processor modules consist of printed circuit boards that are fixed in metal carriers. Electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding and connectors are integral components of the carrier. Although the metal carrier helps to protect the board from ESD, use a preventive antistatic strap during handling.
Following are guidelines for preventing ESD damage:
What Are the HSSI Port Adapters?
The HSSI port adapters (PA-H and PA-2H) provide up to two high-speed serial interfaces. (See Figure 1 and Figure 2.)
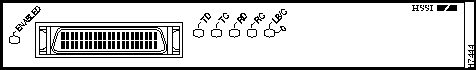
Figure 1 : PA-H Port Adapter, Faceplate View
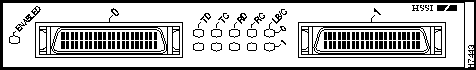
Figure 2 : PA-2H Port Adapter, Faceplate View
The PA-H and PA-2H port adapters can be installed on a VIP2 in port adapter slot 0 and port adapter slot 1, or in the Cisco 7200 series routers in any of the chassis' port adapter slots; slots 1 through 6 in the Cisco 7206, or slots 1 through 4 in the Cisco 7204.
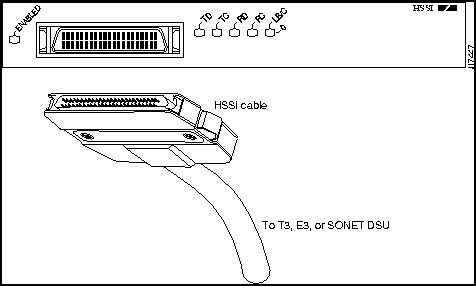
Each HSSI port is a female, 50-pin, SCSI-II-type connector. You must use an HSSI interface cable to connect the interface with an external data service unit (DSU). Refer to the section "HSSI Port Adapter Receptacles, Cables, and Pinouts," on page 10, for descriptions of HSSI cables.
Both HSSI port adapters conform to BABT/TC/130 and EIA/TIA-612 and EIA/TIA-613 standards. PA-H provides a single network interface for Cisco 7000 series or Cisco 7500 series routers, and PA-2H provides two interfaces. HSSI network interfaces reside on modular port adapters, which provide a direct connection between the high-speed bus in the router and the external networks. Each HSSI provides a full-duplex synchronous serial interface for transmitting and receiving data at rates of up to 52 megabits per second (Mbps).
HSSI, which was recently standardized as EIA/TIA 612/613, provides access to services at T3 (45 Mbps), E3 (34 Mbps), and Synchronous Optical Network (SONET) STS-1 (51.82 Mbps) rates. The actual rate of the interface depends on the external data service unit (DSU) and the type of service to which it is connected.
The port adapter supports both 16- and 32-bit cyclic redundancy checks (CRCs). The default is 16-bit CRCs; to enable 32-bit CRCs, you use a configuration command. For a description of the CRC function, refer to the section "Configuring Cyclic Redundancy Checks" on page 22.
The BABT605559 marking on the HSSI port adapters signifies that the (HSSI) port adapters meet United Kingdom directive 605559 and have been designed to BABT/TC/130 standards. The BABT label is located on the top of each HSSI port adapter (PA-H and PA-2H); Figure 3 shows the BABT label for HSSI port adapters.
Figure 3 : BABT Label for HSSI Port Adapters
The following additional sections discuss information specific to the HSSI port adapters:
Port Adapter Locations on the VIP2 and in the Cisco 7200 Series Router
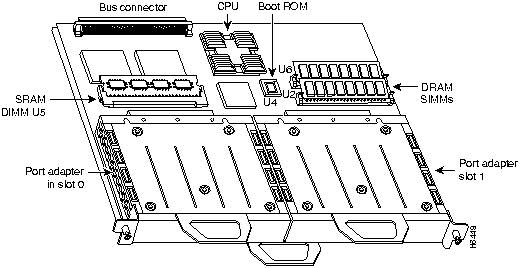
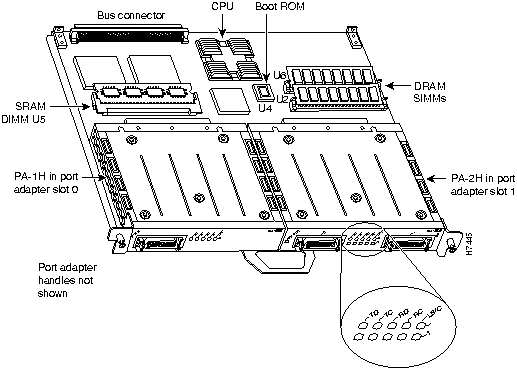
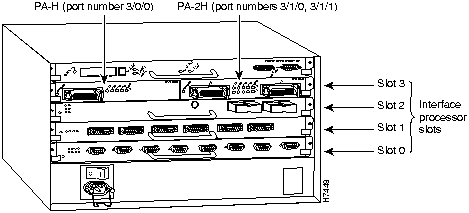
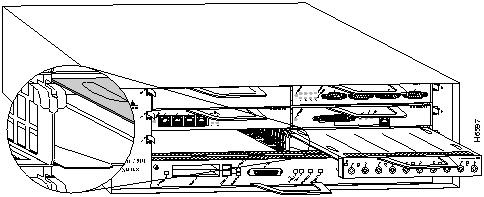
Figure 4 shows a VIP2 with installed port adapters. With the VIP2 oriented as shown in Figure 4, the left port adapter is in port adapter slot 0, and the right port adapter is in port adapter slot 1. Port adapters have handles that allow for easy installation and removal; however, they are occasionally not shown in this publication to highlight port adapter faceplate detail. In the Cisco 7000, Cisco 7507, and Cisco 7513 chassis the VIP2 is installed vertically. In the Cisco 7010 and Cisco 7505 chassis the VIP2 is installed horizontally.
Figure 4 : Two Port Adapters on the VIP2 (Horizontal Orientation Shown)
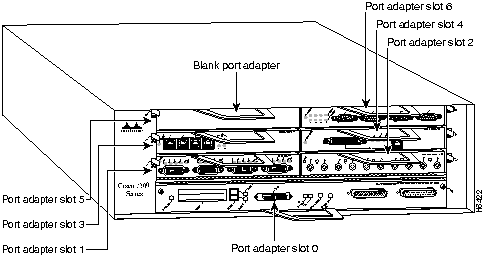
Figure 5 shows a Cisco 7206 with port adapters installed. In the Cisco 7206, port adapter slot 1 is in the lower left position, and port adapter slot 6 is in the upper right position. (The Cisco 7204 is not shown, but has four port adapter slots; PA-H and PA-2H can be installed in any of these four slots.)
Figure 5 : Port Adapter Slots in the Cisco 7206
The HSSI port adapter has two rows of five status LEDs, one row of five for each HSSI port on the port adapter (TD, TC, RD, RC, and LB/C), and one ENABLED LED for the port adapter. (See Figure 6.)
Figure 6 : LEDs on the HSSI Port Adapter (Partial Front View of PA-2H Shown)
After system initialization, the enabled LED, which is present on all interface processors, goes on to indicate that the port adapter has been enabled for operation.
The following conditions must be met before the HSSI port adapter is enabled:
If any of these conditions is not met, or if the initialization fails for other reasons, the enabled LED does not go on.
The five additional status LEDs on the HSSI port adapter indicate the following:
HSSI Port Adapter Receptacles, Cables, and Pinouts
Two types of cables are available for use with the HSSI port adapter: the HSSI interface cable used to connect your router to an external DSU (and HSSI network) and a null modem cable, which allows you to connect two routers back to back. Both HSSI cables conform to EIA/TIA-612 and EIA/TIA-613 specifications. The HSSI ports on PA-H and PA-2H are considered to be DTE devices.
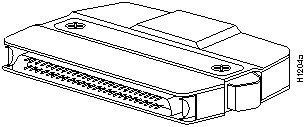
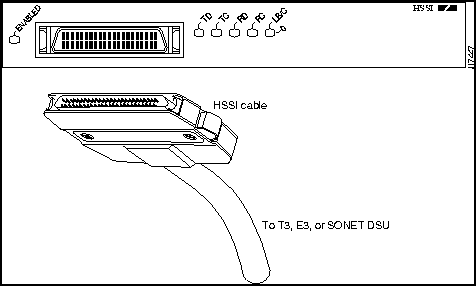
The HSSI cable connects the HSSI port adapter with the external DSU. The HSSI cable is 10-feet (3.048 meters) long. The maximum HSSI cable length allowed is 50 feet (15.24 meters). Figure 7 shows the 50-pin connector used at each end of the HSSI interface cable. Table 1 lists the pinout.
Figure 7 : HSSI Interface Cable Connector
Table 1 : HSSI Interface Cable Pinout
The null modem cable can connect two routers directly back to back. The null modem cable is 10-feet (3.048 meters) long. The maximum null modem cable length allowed is 50 feet (15.24 meters). The two routers must be in the same location and can be two Cisco 7000 series routers, two Cisco 7500 series routers, two Cisco 7200 series routers, or any combination of each. A null modem connection allows you to verify the operation of the HSSI or to link the routers directly in order to build a larger node.
The null modem cable uses the same 50-pin connectors as the HSSI cable, but uses the pinout listed in Table 2. For connection and configuration instructions, refer to the section "Attaching a Null Modem Cable" on page 18.
Table 2 : HSSI Null Modem Cable Pinout
The HSSI port adapters are used on the VIP2, and can be installed in either port adapter slot 0 or port adapter slot 1. Figure 8 shows two HSSI port adapters installed on a VIP2 in port adapter slot 0 (PA-H) and slot 1 (PA-2H).
Figure 8 : VIP2 with HSSI Port Adapters in Port Adapter Slots 0 and 1
The following sections include information specific to the HSSI port adapters and their use on the VIP2 in Cisco 7000 series and Cisco 7500 series routers:
Installing or Replacing a Port Adapter on a VIP2
Depending on the circumstances you might need to install a new port adapter on a VIP2 motherboard or replace a failed port adapter in the field. In either case, you need a number 1 Phillips screwdriver, an antistatic mat onto which you can place the removed interface processor, and an antistatic container into which you can place a failed port adapter for shipment back to the factory.
When only one port adapter is installed on a VIP2, a blank port adapter must fill the empty slot to allow the VIP2 and router chassis to conform to electromagnetic interference (EMI) emissions requirements, and so that air flows through the chassis properly. If you plan to install a new port adapter, you must first remove the blank port adapter.
Following is the standard procedure for removing and replacing any type of port adapter on the VIP2:
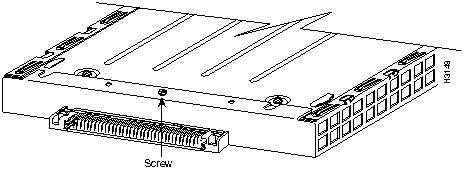
Figure 9 : Location of Port Adapter Screw, Partial Port Adapter View
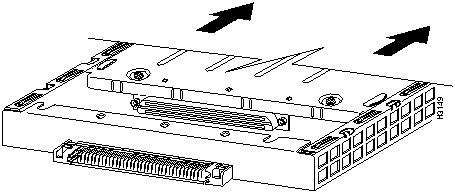
Figure 10 : Pulling a Port Adapter Out of a Slot, Partial Port Adapter View
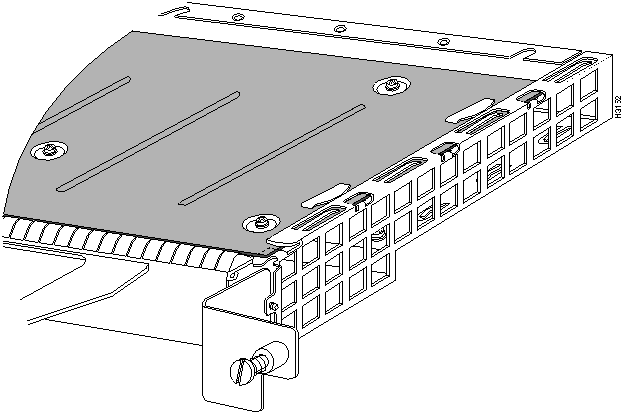
Figure 11 : Removing a Port Adapter
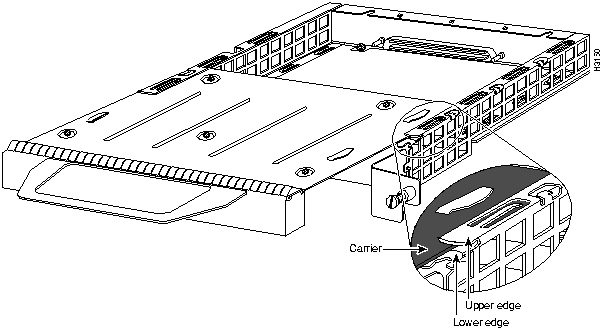
Figure 12 : Aligning the Carrier Edge with Upper and Lower Slot Edges, Partial View
This completes the procedure for installing a new port adapter or replacing a port adapter on a VIP2.
Attaching HSSI Port Adapter Interface Cables
On a single HSSI port adapter, you can use up to two HSSI connections (on PA-2H). HSSI cables are available only from Cisco Systems; they are not available from outside commercial cable vendors.
Connect HSSI cables to an HSSI port adapter as follows:
Figure 13 : Connecting HSSI Cables (Front View---PA-H Shown without Handle)
This completes the procedure for attaching HSSI cables to the HSSI port adapter. If you require a null-modem cable for your HSSI connection, refer to the section "Attaching a Null Modem Cable," which follows; otherwise, proceed to the section "Configuring the HSSI Interfaces" on page 19.
The null modem cable can connect two routers directly back to back. The two routers must be in the same location, and can be two Cisco 7000 series routers, two Cisco 7500 series routers, two Cisco 7200 series routers, or one of each. This setup allows you to verify the operation of the HSSI or to directly link the routers in order to build a larger node. The null modem cable uses the same 50-pin connectors as the HSSI cable, but uses the pinouts listed in Table 2.
To connect two routers, attach a null modem cable between an HSSI port on each router. Enable the internal transmit clock in both routers by entering the command hssi internal-clock.
You define Cisco 7000 series and Cisco 7500 series interfaces by interface type and physical slot/port adapter/port locations. (The output of the show interfaces command displays the logical unit number in both router types and the physical slot/port adapter/port location in the Cisco 7000 series and Cisco 7500 series.) Both router platforms use the same hssi internal-clock command to enable the internal transmit clock on the HSSI.
The following examples show the configure command syntax for the Cisco 7000 series and Cisco 7500 series. For complete configuration descriptions and examples, refer to the appropriate software publications.
Be sure to configure the HSSI port on both routers for an internal transmit clock. When the internal clock is enabled, the TC LED goes on. When the internal clock is enabled in both routers, the TC and RC LEDs on both of the connected HSSI ports go on.
To disconnect the null modem cable, disable the internal transmit clock with the command no hssi internal-clock. Use this command to turn off the transmit clock for each port on both routers. This completes the procedure for attaching a null-modem cable to your HSSI port adapter. Proceed to the section "Configuring the HSSI Interfaces."
Configuring the HSSI Interfaces
If you installed a new HSSI port adapter or if you want to change the configuration of an existing interface, you must enter Configuration mode using the configure command. If you replaced an HSSI port adapter that was previously configured, the system will recognize the new HSSIs and bring them up in their existing configuration.
After you verify that the new HSSI port adapter is installed correctly (the enabled LED goes on), use the privileged-level configure command to configure the new interfaces. Be prepared with the information you will need, such as the following:
For a summary of the configuration options available and instructions for configuring HSSI port adapters on the VIP2, refer to the appropriate configuration publications listed in the section "If You Need More Information" on page 2. The configure command requires privileged-level access to the EXEC command interpreter, which usually requires a password. Contact your system administrator if necessary to obtain EXEC-level access.
Determining Chassis Slot, Port Adapter, and HSSI Port Numbers
The following section describes how to identify chassis slot, port adapter, and Ethernet 10BASE-T interface port numbers.
In the router, physical port addresses specify the actual physical location of each interface port on the router interface processor end. (See Figure 14.) This address is composed of a three-part number in the format chassis slot/port-adapter/interface port, as follows:
Interface ports on the VIP2 maintain the same address regardless of whether other interface processors are installed or removed. However, when you move a VIP2 to a different slot, the first number in the address changes to reflect the new chassis slot number.
Figure 14 shows the port adapter slots and interface ports of a sample Cisco 7505 system. On the VIP2, the first port adapter slot number is always 0. The second port adapter slot number is always 1. The individual interface port numbers always begin with 0. The number of additional ports depends on the number of ports on a port adapter.
For example, the HSSI port on an HSSI port adapter in the first port adapter slot in chassis slot 3, is numbered 3/0/0. (See Figure 14.) If the HSSI port adapter was in port adapter slot 1, this same port would be numbered 3/1/0. Port adapters can occupy either port adapter slot; there are no restrictions.
Figure 14 : HSSI Port Number Example (Cisco 7505 Shown)
You can identify interface ports by physically checking the slot/port-adapter/interface port location on the back of the router or by using show commands to display information about a specific interface or all interfaces in the router.
The following steps describe a basic interface configuration. Press the Return key after each step unless otherwise noted. At any time you can exit the privileged level and return to the user level by entering disable at the prompt as follows:
Following is an example of a basic configuration procedure:
Configuring Cyclic Redundancy Checks
The HSSI port adapter uses a 16-bit CRC by default; it also supports a 32-bit CRC.
CRC is an error-checking technique that uses a calculated numeric value to detect errors in transmitted data. The sender of a data frame divides the bits in the frame message by a predetermined number to calculate a remainder or frame check sequence (FCS). Before it sends the frame, the sender appends the FCS value to the message so that the frame contents are exactly divisible by the predetermined number. The receiver divides the frame contents by the same predetermined number that the sender used to calculate the FCS. If the result is not 0, the receiver assumes that a transmission error occurred and sends a request to the sender to resend the frame.
In the example that follows, a single HSSI interface, on a VIP2 in interface processor slot 1, is configured for 32-bit CRC:
To disable CRC-32 and return to the default CRC-16 setting, specify the slot and port address and use the no crc32 command. For complete command descriptions and instructions, refer to the related software documentation.
To check the interface configuration using show commands, proceed to the section "Checking the Configuration."
After configuring the new interface, use the show commands to display the status of the new interface or all interfaces and the ping command to check connectivity.
Using show Commands to Verify the VIP2 Status
The following steps use show commands to verify that the new interfaces are configured and operating correctly.
If the interface is down and you configured it as up, or if the displays indicate that the hardware is not functioning properly, ensure that the network interface is properly connected and terminated. If you still have problems bringing the interface up, contact a service representative for assistance.
Using show Commands to Display Interface and System Information To display information about a specific interface, use the show interfaces command with the interface type and port address in the format show interfaces [type slot/port-adapter/port].
Following is an example of how the show interfaces [type slot/port-adapter/port] command displays status information (including the physical slot and port address) for the interfaces you specify. In this example, the HSSI-configured VIP2 is in chassis slot 1, in port adapter slot 0.
With the show interfaces type slot/port-adapter/port command, use arguments such as the interface type (hssi, and so forth) and the slot, port adapter, and port numbers (slot/port-adapter/port) to display information about a specific HSSI only.
The show version (or show hardware) command displays the configuration of the system hardware (the number of each interface processor type installed), the software version, the names and sources of configuration files, and the boot images. Following is an example of the show version command used with a Cisco 7000 series system with an RSP7000 processor:
To determine which type of port adapter is installed on a VIP2 in your system, use the show diag slot command. Specific port adapter information is displayed, as shown in the following example of a PA-2H HSSI port adapter in chassis slot 1:
Display all the current interface processors and their interfaces with the show controllers cbus command. Following is an example of the show controller cbus command that shows HSSI ports 1/0/0 and 1/0/1 on a PA-2H HSSI port adapter installed on a VIP2 in chassis slot 1:
Using the ping Command to Verify Network Connection The packet internet groper (ping) command allows you to verify that an interface port is functioning properly and to check the path between a specific port and connected devices at various locations on the network. This section provides brief descriptions of the ping command. After you verify that the system and VIP2 have booted successfully and are operational, you can use this command to verify the status of interface ports. Refer to the publications listed in the section "If You Need More Information," on page 2, for detailed command descriptions and examples.
The ping command sends an echo request out to a remote device at an IP address that you specify. After sending a series of signals, the command waits a specified time for the remote device to echo the signals. Each returned signal is displayed as an exclamation point (!) on the console terminal; each signal that is not returned before the specified time-out is displayed as a period (.). A series of exclamation points (!!!!!) indicates a good connection; a series of periods (.....) or the messages [timed out] or [failed] indicate that the connection failed.
Following is an example of a successful ping command to a remote server with the address 1.1.1.10:
If the connection fails, verify that you have the correct IP address for the server and that the server is active (powered on), and repeat the ping command. For complete descriptions of interface subcommands and the configuration options available for VIP2-related interfaces, and which support VIP2 functionality, refer to the publications listed in the section "If You Need More Information" on page 2.
Cisco 7200 Series and HSSI Port Adapters
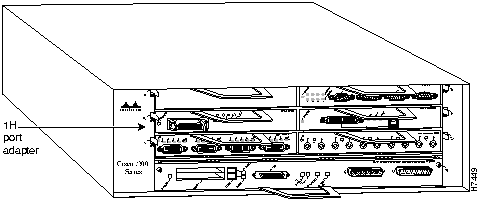
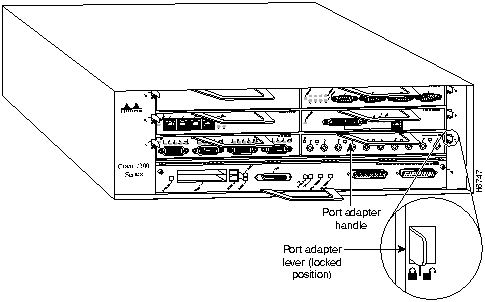
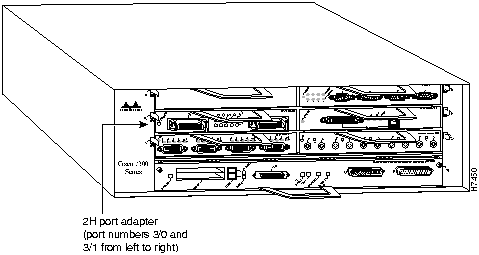
The HSSI port adapters are used in the Cisco 7200 series routers and can be installed in any of the available port adapter slots. Figure 15 shows an HSSI port adapter installed in port adapter slot 3 of a Cisco 7206.
Figure 15 : Cisco 7206 with an HSSI Port Adapter in Port Adapter Slot 3
The following sections include information that is specific to the HSSI port adapters and their use in the Cisco 7200 series routers:
Installing or Replacing a Port Adapter in Cisco 7200 Series Routers
Depending on your circumstances, you might need to install a new port adapter in a Cisco 7200 series router or replace a failed port adapter in the field. In either case, no tools are necessary; all port adapters available for the Cisco 7200 series connect directly to the router midplane and are locked into position by a port adapter lever. When removing and replacing a port adapter, you will need an antistatic mat onto which you can place a removed port adapter and an antistatic container into which you can place a failed port adapter for shipment back to the factory.
When a port adapter slot is not in use, a blank port adapter must fill the empty slot to allow the router to conform to EMI emissions requirements and to allow proper air flow across the port adapters. If you plan to install a new port adapter in a slot that is not in use, you must first remove a blank port adapter.
Following is the procedure for removing a port adapter from a Cisco 7200 series router:
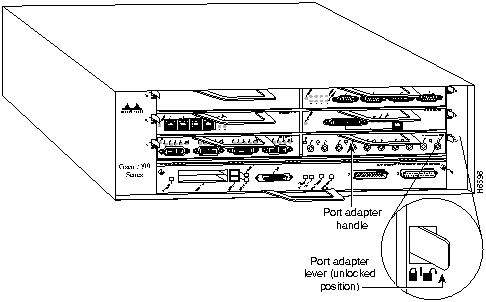
Figure 16 : Placing the Port Adapter Lever in the Unlocked Position (Cisco 7206 shown)
Figure 17 : Handling a Port Adapter
This completes the procedure for removing a port adapter from a Cisco 7200 series router.
Following is the procedure for installing a new port adapter in a Cisco 7200 series router:
Figure 18 : Aligning the Port Adapter Metal Carrier Between the Slot Guides (Cisco 7206 shown)
Figure 19 : Placing the Port Adapter Lever in the Locked Position (Cisco 7206 shown)
This completes the procedure for installing a new port adapter in a Cisco 7200 series router.
Attaching HSSI Port Adapter Interface Cables
On a single HSSI port adapter, you can use up to two HSSI connections. HSSI cables are available from Cisco Systems; they are not available from outside commercial cable vendors.
Connect HSSI cables to an HSSI port adapter as follows:
Figure 20 : Connecting HSSI Cables
This completes the procedure for attaching HSSI port adapter cables.
Configuring the HSSI Interfaces
If you installed a new HSSI port adapter or if you want to change the configuration of an existing interface, you must enter Configuration mode using the configure command. If you replaced an HSSI port adapter that was previously configured, the system will recognize each new HSSI and bring it up in its existing configuration.
After you verify that the new HSSI port adapter is installed correctly (the enabled LED goes on), use the privileged-level configure command to configure the new interfaces. Be prepared with the information you will need, such as the following:
For a summary of the configuration options available and instructions for configuring the HSSIs on a Cisco 7200 series router, refer to the appropriate configuration publications listed in the section "If You Need More Information" on page 2.
The configure command requires privileged-level access to the EXEC command interpreter, which usually requires a password. Contact your system administrator if necessary to obtain EXEC-level access.
Selecting Port Adapter Slot and HSSI Port Numbers
The following section describes how to identify port adapter slot and HSSI port numbers.
Physical port addresses specify the actual physical location of each interface port on the router. (See Figure 21.) This address is composed of a two-part number in the format port adapter slot number/interface port number, as follows:
Interface ports maintain the same address regardless of whether other port adapters are installed or removed from the slot. However, when you move a port adapter to a different slot, the first number in the address changes to reflect the new chassis slot number.
Figure 21 shows the port adapter slots and interface ports of a Cisco 7206. The port adapter slot numbers start with 1 and continue through 6 (slot 0 is always reserved for the Fast Ethernet port on the I/O controller---if present). The individual interface port numbers always begin with 0. The number of additional ports depends on the number of ports on a port adapter.
For example, the two HSSI ports on an HSSI port adapter in port adapter slot 3 would have the following addresses: 3/0 and 3/1. (See Figure 21.) If the HSSI port adapter was in port adapter slot 1, these same interface ports would be numbered 1/0 and 1/1.
Figure 21 : Cisco 7206 HSSI Port Number Example
You can identify interface ports by physically checking the slot/interface port location on the front of the router or by using show commands to display information about a specific interface or all interfaces in the router.
The following steps describe a basic interface configuration. Press the Return key after each step unless otherwise noted. At any time you can exit the privileged level and return to the user level by entering disable at the prompt as follows:
Following is an example of a basic configuration procedure:
To check the interface configuration using show commands, proceed to the section "Checking the Configuration."
After configuring the new interface, use the show commands to display the status of the new interface or all interfaces and use the ping command to check connectivity.
Using show Commands to Verify the New Interface Status
The following steps use show commands to verify that the new interfaces are configured and operating correctly.
If the interface is down and you configured it as up, or if the displays indicate that the hardware is not functioning properly, ensure that the network interface is properly connected and terminated. If you still have problems bringing the interface up, contact a service representative for assistance.
Using show Commands to Display Interface and System Information
To display information about a specific interface, use the show interfaces command with the interface type and port address in the format show interfaces [type slot/port].
The following example of the show interfaces hssi type slot/port command shows all of the information specific to the first HSSI port (interface port 0) in port adapter slot 5:
With the show interfaces type slot/port command, use arguments such as the interface type (hssi, and so forth), and the port adapter slot and port number (slot/port) to display information about a specific HSSI only.
Display all the current interface processors and their interfaces with the show controllers command. Following is an example of the show controller command that shows HSSI ports 1/0 and 1/1 on a PA-2H HSSI port adapter installed in chassis slot 1:
The show version (or show hardware) command displays the configuration of the system hardware (the number of each port adapter type installed), the software version, the names and sources of configuration files, and the boot images. Following is an example of the output from the show version command:
To determine which type of port adapter is installed in your system, use the show diag slot command. Specific port adapter information is displayed, as shown in the following example of an HSSI port adapter in chassis slot 5:
For complete command descriptions and examples for the Cisco 7200 series routers, refer to the publications listed in the section "If You Need More Information" on page 2.
Using the ping Command to Verify Network Connection
The packet internet groper (ping) command allows you to verify that an interface port is functioning properly and to check the path between a specific port and connected devices at various locations on the network. This section provides brief descriptions of the ping command. After you verify that the system has booted successfully and is operational, you can use this command to verify the status of interface ports. Refer to the publications listed in the section "If You Need More Information" on page 2, for detailed command descriptions and examples.
The ping command sends an echo request out to a remote device at an IP address that you specify. After sending a series of signals, the command waits a specified time for the remote device to echo the signals. Each returned signal is displayed as an exclamation point (!) on the console terminal; each signal that is not returned before the specified time-out is displayed as a period (.). A series of exclamation points (!!!!!) indicates a good connection; a series of periods (.....) or the messages [timed out] or [failed] indicate that the connection failed.
Following is an example of a successful ping command to a remote server with the address 1.1.1.10:
If the connection fails, verify that you have the correct IP address for the server and that the server is active (powered on), and repeat the ping command.
For complete descriptions of interface subcommands and the configuration options available for Cisco 7200 series-related interfaces and functionality, refer to the publications listed in the section "If You Need More Information" on page 2.
Cisco Connection Online (CCO), formerly Cisco Information Online (CIO), is Cisco Systems' primary, real-time support channel. Maintenance customers and partners can self-register on CCO to obtain additional content and services.
Available 24 hours a day, 7 days a week, CCO provides a wealth of standard and value-added services to Cisco's customers and business partners. CCO services include product information, software updates, release notes, technical tips, the Bug Navigator, configuration notes, brochures, descriptions of service offerings, and download access to public and authorized files.
CCO serves a wide variety of users through two interfaces that are updated and enhanced simultaneously---a character-based version and a multimedia version that resides on the World Wide Web (WWW). The character-based CCO supports Zmodem, Kermit, Xmodem, FTP, and Internet e-mail, and is excellent for quick access to information over lower bandwidths. The WWW version of CCO provides richly formatted documents with photographs, figures, graphics, and video, as well as hyperlinks to related information.
You can access CCO in the following ways:
For a copy of CCO's Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ), contact ccohelp@cisco.com. For additional information, contact ccoteam@cisco.com.
Copyright 1988-1996 © Cisco Systems Inc.
![]()
![]()
![]()
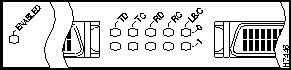
Signal Name
+ Side Pin No.
-- Side Pin No.
Direction1
Router DSU
SG (Signal Ground)
1
26
---
RT (Receive Timing)
2
27
<---
CA (DCE Available)
3
28
<---
RD (Receive Data reserved)
4
29
<---
LC (Loopback circuit C)
5
30
<---
ST (Send Timing)
6
31
<---
SG (Signal Ground)
7
32
---
TA (DTE Available)
8
33
--->
TT (Terminal Timing)
9
34
--->
LA (Loopback circuit A)
10
35
--->
SD (Send Data)
11
36
--->
LB (Loopback circuit B)
12
37
--->
SG (Signal Ground)
13
38
---
5 (Ancillary to DCE)
14--18
39--43
--->
SG (Signal Ground)
19
44
---
5 (Ancillary from DCE)
20--24
45--49
<---
SG (Signal Ground)
25
50
---
1 Router is + side (DTE). DSU is side (DCE).
Signal Name
From Pins
Direction
To Pins
Signal Name
RT (Receive Timing)
2, 27
--->
9, 34
TT (Terminal Timing)
CA (DCE available)
3, 28
--->
8, 33
TA (DTE Available)
RD (Receive Data)
4, 29
--->
11, 36
SD (Send Data)
LC (Loopback C)
5, 30
--->
10, 35
LA (Loopback A)
ST (Send Timing)
6, 31
--->
6, 31
ST (Send Timing)
TA (DTE available)
8, 33
--->
3, 28
CA (DCE Available)
TT (Terminal Timing)
9, 34
--->
2, 27
RT (Receive Timing)
LA (Loopback A)
10, 35
--->
5, 30
LC (Loopback C)
SD (Send Data)
11, 36
--->
4, 29
RD (Receive Data)
GND (Ground)
1, 26,
7, 32,
13, 38,
19, 44,
25, 50
1, 26,
7, 32,
13, 38,
19, 44,
25, 50
GND (Ground)
Loopback (not connected)
12, 37
12, 37
Loopback (not connected)
Not used
14--18, 20--24, 39--43, 45--49
14--18, 20--24, 39--43, 45--49
Not used
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Cisco7000/7500Series# configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Router(config)#
Enter configuration commands...
Cisco7000/7500Series(config)# interface hssi 1/0/0
Cisco7000/7500Series(config-int)# hssi internal-clock
Cisco7000/7500Series(config-int)# ^z
Router# disable
Router>
Router#
configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Router(config)#
Router(config)#
interface
hssi 1/0/0
Router(config-int)#
ip address 1.1.1.10 255.255.255.0
Router(config-int)#
no shutdown
Router#
copy running-config startup-config
[OK]
Router#
Router# configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Router(config)#
Router(config)# interface hssi 1/0/0
Router(config-int)# crc32
Ctrl-z
Router# sh int h 1/0/0
Hssi1/0/0 is up, line protocol is up
Hardware is cyBus HSSI
Internet address is 5.8.1.1/24
MTU 4470 bytes, BW 45045 Kbit, DLY 200 usec, rely 255/255, load 1/255
Encapsulation HDLC, loopback not set, keepalive not set
Last input 2d22h, output 00:00:19, output hang never
Last clearing of "show interface" counters 2d20h
Queueing strategy: fifo
Output queue 0/40, 0 drops; input queue 0/75, 0 drops
5 minute input rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
5 minute output rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
0 packets input, 0 bytes, 0 no buffer
Received 0 broadcasts, 0 runts, 0 giants, 0 parity
0 input errors, 0 CRC, 0 frame, 0 overrun, 0 ignored, 0 abort
4084 packets output, 1298712 bytes, 0 underruns
0 output errors, 0 applique, 0 interface resets
0 output buffer failures, 0 output buffers swapped out
0 carrier transitions
Router# show version
Cisco Internetwork Operating System Software
IOS (tm) GS Software (RSP-A), Version 11.1(6)CA(2.0) [mpo 105]
Copyright (c) 1986-1995 by cisco Systems, Inc.
Compiled Fri 06-Oct-95 12:22 by mpo
Image text-base: 0x600088A0, data-base: 0x605A4000
ROM: System Bootstrap, Version 5.3(16645)
ROM: GS Bootstrap Software (RSP-BOOT-M), Version 11.1(1.2), MAINTENANCE INTERIME
Router uptime is 4 hours, 22 minutes
System restarted by reload
System image file is "slot0:rsp-a111-6-20", booted via slot0
cisco RSP7000 (R4600) processor with 16384K bytes of memory.
R4600 processor, Implementation 32, Revision 2.0
Last reset from power-on
G.703/E1 software, Version 1.0.
Bridging software.
X.25 software, Version 2.0, NET2, BFE and GOSIP compliant.
Chassis Interface.
(additional displayed text omitted from this example)
2 HSSI network interfaces.
125K bytes of non-volatile configuration memory.
20480K bytes of Flash PCMCIA card at slot 0 (Sector size 128K).
8192K bytes of Flash internal SIMM (Sector size 256K).
Configuration register is 0x2
Router# show diag 1
Slot 1:
Physical slot 1, ~physical slot 0xE, logical slot 1, CBus 0
Microcode Status 0xC
Master Enable, LED, WCS Loaded
Board is analyzed
Pending I/O Status: Console I/O
EEPROM format version 1
VIP2 controller, HW rev 2.3, board revision A0
Serial number: 03516552 Part number: 73-1684-03
Test history: 0x00 RMA number: 00-00-00
Flags: cisco 7000 board; 7500 compatible
EEPROM contents (hex):
0x20: 01 15 02 03 00 35 A8 88 49 06 94 03 00 00 00 00
0x30: 50 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
Slot database information:
Flags: 0x4 Insertion time: 0x14E8 (3d00h ago)
VIP Controller Memory Size: Unknown
PA Bay 0 Information:
HSSI PA, 2 ports
EEPROM format version 1
HW rev FF.FF, Board revision UNKNOWN
Serial number: 4294967295 Part number: 255-65535-255
Router# sh cont cbus
MEMD at 40000000, 2097152 bytes (unused 4416, recarves 3, lost 0)
RawQ 48000100, ReturnQ 48000108, EventQ 48000110
BufhdrQ 48000130 (2647 items), LovltrQ 48000148 (19 items, 1632 bytes)
IpcbufQ 48000150 (24 items, 4096 bytes)
3570 buffer headers (48002000 - 4800FF10)
pool0: 13 buffers, 256 bytes, queue 48000138
pool1: 704 buffers, 1536 bytes, queue 48000140
pool2: 159 buffers, 4480 bytes, queue 48000158
pool3: 4 buffers, 4512 bytes, queue 48000160
(additional displayed text omitted from this example)
slot1: VIP2, hw 2.3, sw 21.40, ccb 5800FF30, cmdq 48000088, vps 8192
software loaded from flash slot0:vip2_21-40
FLASH ROM version 255.255
Mueslix HSSI(2) HW Revision 0x2, FW Revision 1.23
Hssi1/0/0, applique is Hssi DTE
gfreeq 48000158, lfreeq 480001C8 (4480 bytes), throttled 0
rxlo 4, rxhi 159, rxcurr 0, maxrxcurr 0
txq 48001A00, txacc 48001A02 (value 106), txlimit 106
Hssi1/0/1, applique is Hssi DTE
gfreeq 48000158, lfreeq 480001D0 (4480 bytes), throttled 0
rxlo 4, rxhi 159, rxcurr 0, maxrxcurr 0
txq 48001A08, txacc 48001A0A (value 106), txlimit 106
(additional displayed text ommitted from this example)
Router# ping 1.1.1.10 <Return>
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echoes to 1.1.1.10, timeout is 2 seconds:
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/15/64 ms
Router#
![]()
![]()
![]()
Router# disable
Router>
Router#
configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Router(config)#
Router(config)#
interface
hssi 2/0
Router(config-int)#
ip address 1.1.1.10 255.255.255.0
Router(config-int)#
no shutdown
Router#
copy running-config startup-config
[OK]
Router#
Router# show int h 5/0
Hssi5/0 is up, line protocol is up
Hardware is M2T-HSSI
Internet address is 5.8.1.2/24
MTU 4470 bytes, BW 45045 Kbit, DLY 200 usec, rely 252/255, load 1/255
Encapsulation HDLC, loopback not set, keepalive not set
Last input never, output never, output hang never
Last clearing of "show interface" counters never
Queueing strategy: fifo
Output queue 0/40, 0 drops; input queue 0/75, 0 drops
5 minute input rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
5 minute output rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
0 packets input, 0 bytes, 0 no buffer
Received 0 broadcasts, 0 runts, 0 giants
0 parity
1 input errors, 1 CRC, 0 frame, 1 overrun, 0 ignored, 0 abort
1 packets output, 24 bytes, 0 underruns
0 output errors, 0 applique, 1 interface resets
0 output buffer failures, 0 output buffers swapped out
0 carrier transitions TM=down CA=up LC=down
Router# show cont
(additional display text ommitted from this example)
M2T-HSSI: show controller:
PAS unit 0, subunit 0, f/w version 1-23, rev ID 0x1, version 2
idb = 0x608E3340, ds = 0x608E50C0, ssb=0x608E5A84
Clock mux=0x35, ucmd_ctrl=0x8, port_status=0x25
maxdgram=4474, bufpool=64Kb, 128 particles
TM=down CA=up LC=down
line state: up
HSSI DTE cable, received clockrate 51838976
(additional display text ommitted from this example)
Router# show version
Cisco Internetwork Operating System Software
IOS (tm) 7200 Software (C7200-J-M), Version 11.1(6)CA(2.0) [biff 103]
Copyright (c) 1986-1996 by cisco Systems, Inc.
Compiled Fri 09-Aug-96 21:14 by biff
Image text-base: 0x60010890, data-base: 0x605F0000
ROM: System Bootstrap, Version 11.1(11855) [beta 2], INTERIM SOFTWARE
ROM: 7200 Software (C7200-J-M), Version 11.1(13027) [biff 100]
Router uptime is 23 hours
System restarted by reload
System image file is "biff/c7200-j-mz", booted via tftp from 1.1.1.254
cisco 7200 (R4700) processor with 22528K/10240K bytes of memory.
R4700 processor, Implementation 33, Revision 1.0 (Level 2 Cache)
Last reset from power-on
Bridging software.
SuperLAT software copyright 1990 by Meridian Technology Corp).
X.25 software, Version 2.0, NET2, BFE and GOSIP compliant.
TN3270 Emulation software (copyright 1994 by TGV Inc).
(additional display text ommitted from this example)
2 HSSI network interfaces.
125K bytes of non-volatile configuration memory.
8192K bytes of Flash internal SIMM (Sector size 256K).
Configuration register is 0x0
Router# show diag 5
Slot 5:
HSSI port adapter, 2 ports
Port adapter is analyzed
Port adapter insertion time 00:17:13 ago
Hardware revision 1.0 Board revision UNKNOWN
Serial number 3560089 Part number 73-1801-03
Test history 0x0 RMA number 00-00-00
EEPROM format version 1
EEPROM contents (hex):
0x20: 01 10 01 00 00 36 52 99 49 07 09 03 00 00 00 00
0x30: 06 00 00 00 FF FF FF 00 FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF
Router# ping 1.1.1.10 <Return>
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echoes to 1.1.1.10, timeout is 2 seconds:
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/15/64 ms
Router#

![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()