|
|
Installing the RSP7000 Upgrade Kit in the Cisco 7000 Series Routers
Product Number UPG-RSP7000=
This document contains instructions for installing the 7000 Series Route Switch Processor (RSP7000) upgrade kit (UPG-RSP7000=) in the Cisco 7000 series routers: Cisco 7000 and Cisco 7010. This upgrade kit allows for 7500-series performance enhancements to the Cisco 7000 series routers. The RSP7000 upgrade kit includes the following components:
The RSP7000 upgrade kit requires that your Cisco 7000 series router is running Cisco Internetwork Operating System (Cisco IOS) Release 10.3(9), or later, Release 11.0(6), or later, or Release 11.1(1) or later.
The sections in this document include the following:
Following are brief descriptions of the Cisco 7000 and Cisco 7010 routers, the RSP7000, and the RSP7000CI.
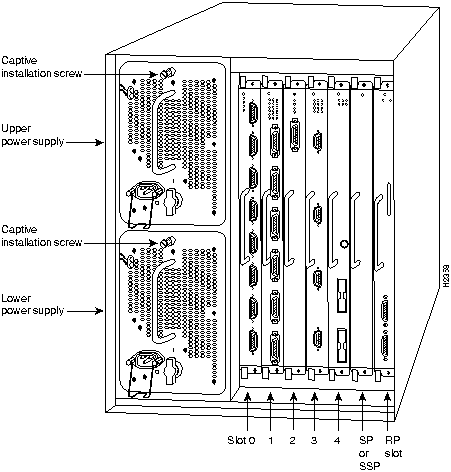
The Cisco 7000 is a seven-slot router chassis, which uses the new RSP7000. The Cisco 7000 provides up to five interface processor slots, and can accommodate the following CxBus-based interface processors: Fast Ethernet, Ethernet, Token Ring, Fiber Distributed Data Interface (FDDI), channel attachment, multichannel, serial, and so forth. The 7000 RSP and interface processors are keyed with guides on the backplane to prevent them from being fully inserted in the wrong slot.
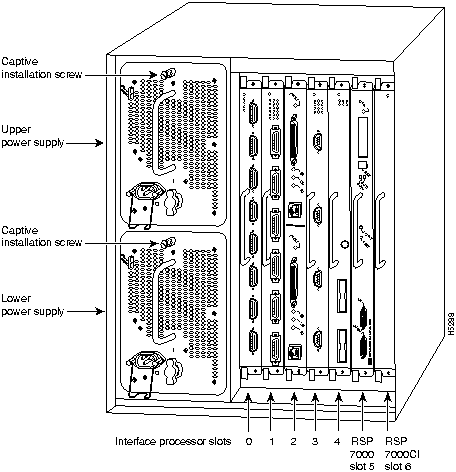
Figure 1 shows the rear of the Cisco 7000 router with the RSP7000 and RSP7000CI installed. In the Cisco 7000 series, two slots are reserved for the 7000 Route Switch Processor (RSP7000), which contains the system processor and performs packet switching functions, and the 7000 Chassis Interface (RSP7000CI) board, which contains all of the environmental monitoring functions for the Cisco 7000, when configured with the new 7000 RSP. The remaining slots (0 through 4) are for interface processor.
Figure 1 : Cisco 7000 with RSP7000 and RSP7000CI Installed
The Cisco 7010 is a five-slot chassis, which uses the new RSP7000 (and the RSP7000CI), and provides up to three interface processor slots that can accommodate the following CxBus-based interface processors: Fast Ethernet, Ethernet, Token Ring, Fiber Distributed Data Interface (FDDI), channel attachment, multichannel, serial, and so forth. The processor and interface processors are keyed with guides on the backplane to prevent them from being fully inserted in the wrong slot.
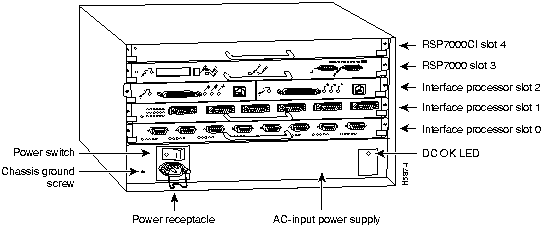
Figure 2 shows the rear of the Cisco 7010 router with the RSP7000 and RSP7000CI installed. In the Cisco 7010, slots 3 and 4 are reserved for the RSP7000, which contains the system processor and performs packet switching functions, and the RSP7000CI board, which contains all of the environmental monitoring functions for the Cisco 7010. The remaining three slots (slots 0 through 2) are for interface processors.
Figure 2 : Cisco 7010 with RSP7000 and RSP7000CI Installed
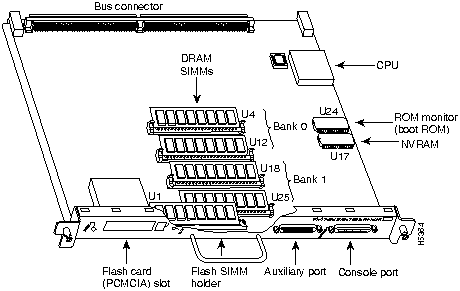
The RSP7000 is a new main system processor module for the Cisco 7000 series chassis. It combines all of the switched routing and high-speed switching functions of the separate Route Processor (RP) and Switch Processor (SP), which are used in the Cisco 7000 series routers, but with improved performance on a single processor module. The RSP7000 contains the central processing unit (CPU) and most of the memory components for the Cisco 7000 series chassis.
The RSP7000CI, shown in Figure 4, consists of a printed circuit board attached to a metal carrier. The RSP7000CI has no user-configurable jumpers or switches, and its faceplate contains no LEDs. The RSP7000CI is distinguishable only by the label on its faceplate, which reads 7000 Series Chassis Interface. (See Figure 4.) The RSP7000CI provides the environmental monitoring and power supply monitoring functions for the Cisco 7000 series chassis. The RSP7000CI isolates the CPU and system software from chassis-specific variations.
The functions of the RSP7000CI are as follows:
Before you begin this installation, review the safety guidelines in this section to avoid injuring yourself or damaging the processor module.
Following are safety guidelines that you should follow when working with any equipment that connects to electrical power or telephone wiring.
Electrical Equipment Guidelines
Follow these basic guidelines when working with any electrical equipment:
Use the following guidelines when working with any equipment that is connected to telephone wiring or to other network cabling:
Preventing Electrostatic Discharge Damage
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) damage, which can occur when electronic cards or components are improperly handled, results in complete or intermittent failures. Electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding and connectors are integral components of the carrier. Use a preventive antistatic strap whenever handling a processor module.
Following are guidelines for preventing ESD damage:
The RSP7000 upgrade kit requires that your Cisco 7000 series router is running Cisco Internetwork Operating System (Cisco IOS) Release 10.3(9), or later, Release 11.0(6), or later, or Release 11.1(1) or later.
The show version and show hardware commands display the current hardware configuration of the router, including the system software version that is currently loaded and running. The show microcode command lists the bundled microcode (target hardware) version for each processor type. The show controller cbus command shows the microcode version you are running. (For complete descriptions of show commands, refer to the Router Products Configuration Guide and Router Products Command Reference publications.)
You can determine the current version of software or microcode stored in ROM either by removing the processor module and checking the ROM labels or by configuring the system to boot the system software or microcode from ROM, reloading the system, and using show commands to check the version that is loaded and running. Refer to the appropriate software documentation for complete configuration instructions and examples.
If the displays indicate that the required system software and microcode is not available in your system, contact a customer service representative for upgrade information. (Refer to the section "Customer Information Online" at the end of this document.)
You must install the RSP7000 in the appropriate chassis' 7000 RSP slot. (See Figure 1, on page 2, for the Cisco 7000, or Figure 2, on page 3, for the Cisco 7010.) For the RSP7000 to operate properly, the Cisco 7000 and Cisco 7010 chassis must also be configured with the RSP7000CI.
Following are the tools and equipment that you will need to complete this replacement:
Flash Memory Card Replacement and Formatting Prerequisites
If you have a Flash memory card installed in the PCMCIA slot of your RP, you must reformat it if you want to use it with your new RSP7000. Using the RSP7000, you cannot read data on the RP's Flash memory card, nor can you use it as bootable media. You must reformat the RP's Flash card before you can use it with the RSP7000. Flash memory cards formatted on the RP-based systems (7000 series routers) are formatted differently from Flash memory cards formatted on RSP-based systems (7500 series routers).
Overview of Processor Module Replacement
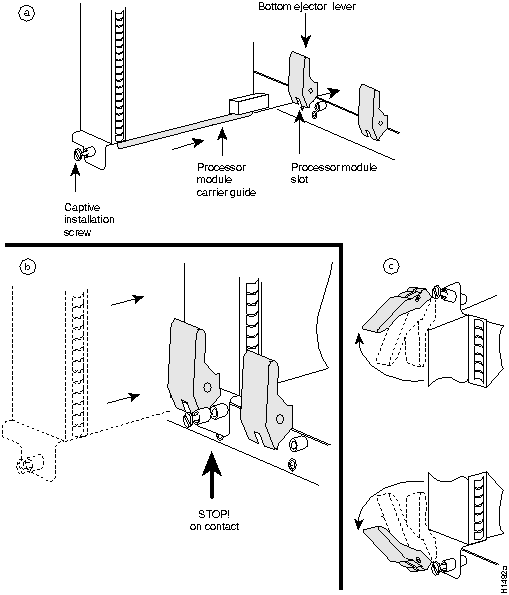
Figure 5 on page 9 shows a detail of the ejector lever mechanism in a vertical position that is appropriate for the Cisco 7000. The processor module slots in the Cisco 7010 are oriented horizontally. When you simultaneously push the ejector levers inward (toward the carrier handle), the levers push the processor into the slot and ensure that the board connectors are fully seated in the backplane.
In the Cisco 7000, the RSP7000 must be installed in the 7000 RSP slot (slot 5) and the RSP7000CI must be installed in the 7000 CI slot (slot 6). In the Cisco 7010, the RSP7000 must be installed in the 7000 RSP slot (slot 3) and the RSP7000CI must be installed in the 7000 CI slot (slot 4).
Figure 5 : Ejector Levers and Captive Installation Screw
Figure 6 shows how to orient a card for installation in the Cisco 7000. During installation, refer to this illustration if you have a Cisco 7000.
Figure 6 : Card-Installation Orientation in the Cisco 7000
Figure 7 shows how to orient a card for installation in the Cisco 7010. During installation, refer to this illustration if you have a Cisco 7010.
Figure 7 : Card-Installation Orientation in the Cisco 7010
Saving and Retrieving the Configuration File
This section describes the procedures for saving and retrieving the system configuration. Configuration information resides in two places when the router is operating: the default (permanent) configuration in NVRAM, and the running (temporary) memory in RAM. The default configuration always remains available; NVRAM retains the information even when the power is shut down. The current information is lost when if the system power is shut down. The current configuration contains all nondefault configuration information that you added with the configure command, the setup command facility, or by editing the configuration file.
The copy running-config startup-config command adds the current configuration to the default configuration in NVRAM, so that it will also be saved when power is shut down. Whenever you make changes to the system configuration, issue the copy running-config startup-config command to ensure that the new configuration is saved.
If you replace the RSP7000, you will also replace the entire configuration (NVRAM resides in socket U17 on the RSP7000). If you upload (copy) the configuration file to a remote server before removing the RSP7000, you can retrieve it later and write it into NVRAM on the new RSP7000. If you do not upload the configuration file, you will have to use the configure command or the setup command facility to reenter the configuration information after you install the new RSP7000. For complete descriptions of these commands and instructions for using them, refer to the appropriate software documentation.
This procedure is not necessary if you are temporarily removing an RSP7000 that you will reinstall; the lithium batteries will retain the configuration in memory until you replace the RSP7000 in the system.
This procedure requires privileged-level access to the EXEC command interpreter, which usually requires a password. Refer to the description that follows and contact your system administrator if necessary, to obtain access.
Using the EXEC Command Interpreter
Before you use the configure command, you must enter the privileged level of the EXEC command interpreter with the enable command. The system prompts you for a password if one has been set.
The system prompt for the privileged level ends with a pound sign (#) instead of an angle bracket (>). At the console terminal, enter the privileged level as follows:
The pound sign (#) at the system prompt indicates that you are at the privileged level of the EXEC command interpreter; you can now execute the EXEC-level commands that are described in the following sections.
Before you attempt to upload or retrieve a file from a remote host, ensure that the connection is good between the router and the remote server. The packet internet groper (ping) program sends a series of echo request packets to the remote device and waits for a reply. If the connection is good, the remote device echoes them back to the local device.
The console terminal displays the results of each message sent: an exclamation point (!) indicates that the local device received an echo, and a period (.) indicates that the server timed out while awaiting the reply. If the connection between the two devices is good, the system will display a series of exclamation points (! ! !) or [ok]. If the connection fails, the system will display a series of periods ( . . . ) or [timed out] or [failed].
To verify the connection between the router and a remote host, issue the ping command followed by the name or Internet Protocol (IP) address of the remote server, then press Return. Although the ping command supports configurable options, the defaults, including interface processor as the protocol, are enabled when you enter a host name or address on the same line as the ping command. For a description of the configurable options, refer to the appropriate software documentation.
The following example shows a successful ping:
The following example shows the results of a failed ping:
If the connection fails, check the physical connection to the remote file server and verify that you are using the correct address or name, then ping the server again. If you are unable to establish a good connection, contact your network administrator or refer to the end of this document for instructions on contacting technical assistance.
Uploading (Copying) the Configuration File
Before you remove the RP and replace it with the RSP7000, you should upload the router's configuration file to a Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) file server, or else the configuration stored in the RP's Flash memory will be lost when you replace it. Before you upload (copy) the running configuration to the TFTP file server, ensure the following:
To store information on a remote host, enter the write network (or copy startup-config tftp) privileged EXEC command. The command prompts you for the destination host's address and a filename, then display the instructions for confirmation. When you confirm the instructions, the router sends a copy of the currently running configuration to the remote host. The system default is to store the configuration in a file called by the name of the router with -confg appended. You can either accept the default filename by pressing Return at the prompt, or enter a different name before pressing Return.
Follow these steps to upload (copy) the currently running configuration to a remote host:
Downloading (Retrieving) the Configuration File
After you install the new RSP7000, you can retrieve the saved configuration and copy it to NVRAM. To retrieve the configuration, enter configuration mode and specify that you will configure the router from the network. The system prompts you for a host name and address, the name of the configuration file stored on the host, and confirmation to reboot using the remote file.
You can access the router through a console terminal attached directly to the RSP7000 console port, or you can configure an interface port and Telnet to the router from a remote terminal.
Follow these steps to download (retrieve) the currently running configuration from a remote host:
Installing the RSP7000 Upgrade Kit
Following is a overview of the procedures for installing the RSP7000 upgrade kit in the Cisco 700 chassis.
RSP7000 Upgrade Kit Installation Overview
To install the RSP7000 upgrade kit, the following overview indicates the procedures that are required, after the router is powered down:
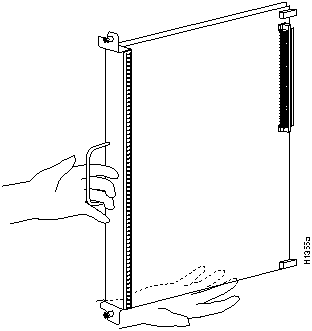
Follow these steps to remove the RP:
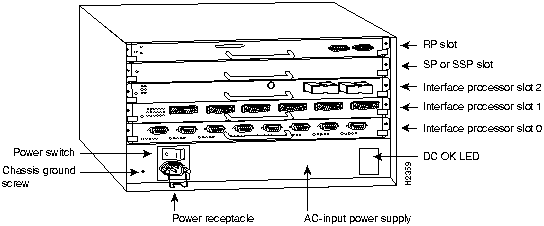
Figure 8 : Cisco 7000 with RP and SP (or SSP) Installed
Figure 9 : Cisco 7010 with RP and SP (or SSP) Installed
This completes the RP removal procedure.
The RSP7000CI is keyed for installation only in the RSP7000CI slot (slot 6 in the Cisco 7000, see Figure 1, and slot 4 in the Cisco 7010, see Figure 2).
Follow these steps to install an RSP7000CI:
This completes the RSP7000CI installation procedure.
Follow these steps to remove the SP (or SSP):
This completes the SP (or SSP) removal procedure.
The RSP7000 is keyed for installation only in the 7000 RSP slot (slot 5 in the Cisco 7000, see Figure 1, and slot 3 in the Cisco 7010, see Figure 2).
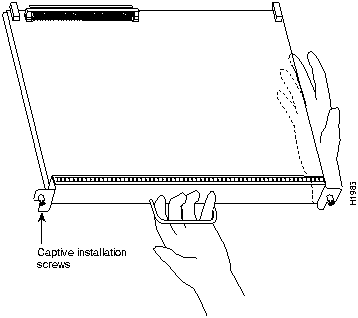
Follow these steps to install the RSP7000:
Use the following sections to verify that the RSP7000 upgrade kit operates properly in your Cisco 7000 series router.
Formatting the Flash Memory Card
If you had a Flash memory card installed in the PCMCIA slot of your RP, you must reformat it if you want to use it with your new RSP7000. You cannot read data on the RP's Flash memory card, or use it as bootable media, unless you reformat it. Flash memory cards formatted on the RP-based systems (7000 series routers) are formatted differently from Flash memory cards formatted on RSP-based systems (7500 series and RSP7000-based routers).
Use the following procedure to format a new Flash memory card:
The new Flash memory card is now formatted and ready to use.
Checking the RSP7000 Installation
Use the following information to verify that the RSP7000 operates properly. When you turn the system power back on, verify that the system boots and resumes normal operation.
Perform the following steps to verify that the RSP7000 is installed and functioning properly:
When you have verified all the conditions in Steps 2 through 5, the installation is complete.
If you replaced the RSP7000 and saved your configuration file to a remote server before doing so, proceed to the section "Downloading (Retrieving) the Configuration File" on page 14. If you replaced the RSP7000 and did not save the configuration, use the configure command or the setup command facility to reenter the configuration information. Refer to the appropriate software documentation for command descriptions and instructions for using them.
An error condition exists if no LEDs go on at power up or after initialization, or if the boot error or CPU halt LEDs go on and remain on. If this happens, refer to the troubleshooting information in the Cisco 7000 Hardware Installation and Maintenance or Cisco 7010 Hardware Installation and Maintenance publication to try to isolate the problem, or contact a service representative for assistance.
This completes checking the RSP7000 installation
Checking the RSP7000CI Installation
Verify that the RSP7000 is installed in the chassis' 7000 RSP slot (see Figure 1 on page 2 or Figure 2 on page 3). Verify that the RSP700CI is installed in the chassis' 7000 CI slot (see Figure 1 on page 2 or Figure 2 on page 3), and that the captive installation screws on both processor modules are tightened.
Using the RSP7000CI and the temperature sensors on the RSP7000, the system displays warning messages on the console if chassis interface-monitored parameters exceed a desired threshold or if a blower failure occurs. You can retrieve and display environmental status reports with the show environment, show environment all, show environment last and show environment table commands. Parameters are measured and reporting functions are updated every 60 seconds. Use these show commands to verify that the RSP7000CI installation was successful. A brief description of each of these commands follows.
The show environment command display reports the current environmental status of the system. The report displays parameters that are out of the normal values. No parameters are displayed if the system status is normal. The example that follows shows the display for a system in which all monitored parameters are within Normal range.
Following is sample output of the show env command:
If the environmental status is not normal, the system reports the worst-case status level in the last line of the display.
The show environment last command retrieves and displays the NVRAM log showing the reason for the last shutdown (if the shutdown was related to voltage or temperature) and the environmental status at that time. Air temperature is measured and displayed, and the DC voltages supplied by the power supply are also displayed.An example of the show env last command follows for both the Cisco 7000 and Cisco 7010:
The show environment all command displays an extended report that includes the arbiter type, backplane type, power supply type (AC or DC), wattage and status, the number and type of intermittent power failures (if any) since the system was last powered on, and the currently measured values at the RSP7000 temperature sensors and the power supply voltages. An example of the show env all command follows for both the Cisco 7000 and Cisco 7010:
RSP7010#sho env all
Arbiter type 1, backplane type 70x0 (id 5)
Power supply #1 is 600W AC (id 1)
Active fault conditions: none
Active trip points: none
01234
Dbus slots: X X
card inlet hotpoint exhaust
CI(4) 22C/71F 34C/93F 24C/75F
Shutdown temperature source is 'hotpoint' on CI(4),
requested CI(4)
+12V measured at 12.31
+5V measured at 5.17
-12V measured at -11.89
+24V measured at 23.78
+2.5 reference is 2.49
If after several attempts, any component does not appear to be functioning properly, or if you experience trouble with the installation (for instance, if the holes in the board do not align with the backplane holes), contact a service representative or the Technical Assistance Center (TAC). (For the TAC phone number and email address, refer to the note at the end of this document.
This completes checking the RSP7000CI installation, and also completes the RSP7000 upgrade kit installation.
Cisco Information Online (CIO), is Cisco Systems' primary, real-time support channel. Maintenance customers and partners can self-register on CIO to obtain additional content and services.
Available 24 hours a day, 7 days a week, CIO provides a wealth of standard and value-added services to Cisco's customers and business partners. CIO services include product information, software updates, release notes, technical tips, the Bug Navigator, configuration notes, brochures, descriptions of service offerings, and download access to public and authorized files.
CIO serves a wide variety of users through two interfaces that are updated and enhanced simultaneously---a character-based version and a multimedia version that resides on the World Wide Web (WWW). The character-based CIO (called "CIO Classic") supports Zmodem, Kermit, Xmodem, FTP, Internet e-mail, and fax download options, and is excellent for quick access to information over lower bandwidths. The WWW version of CIO provides richly formatted documents with photographs, figures, graphics, and video, as well as hyperlinks to related information.
You can access CIO in the following ways:
For a copy of CIO's Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ), contact
Copyright 1988-1996 © Cisco Systems Inc.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Router>
enable
Password:
Router#
Router# ping 1.1.1.1
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 1.1.1.1, timeout is 2 seconds:
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 12/12/12 ms
Router#
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 1.1.1.1, timeout is 2 seconds:
.....
Success rate is 0 percent (0/5)
Router#
Router#
write net
Remote host []?
Router#
write net
Remote host []?
servername
Translating "servername"...domain server (1.1.1.1) [OK]
Name of configuration file to write [Router-confg]?
Write file Router-confg on host 1.1.1.1? [confirm]
Writing Router-confg .....
Write file Router-confg on host 1.1.1.1? [confirm]
Writing Router-confg: !!!! [ok]
Writing Router-confg .....
Router#
configure network
Host or network configuration file [host]?
IP address of remote host [255.255.255.255]?
1.1.1.1
Name of configuration file [router-confg]?
Configure using router-confg from 1.1.1.1? [confirm]
Booting router-confg from 1.1.1.1: ! ! [OK - 874/16000 bytes]
Booting Router-confg ..... [timed out]
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Router#
format slot0:
All sectors will be erased, proceed? [confirm]
Enter volume id (up to 30 characters):
MyNewCard
Formatting sector 1
Format device slot0 completed
Router#
GS Software (RSP-K), Version 10.3(9), RELEASED SOFTWARE
Copyright (c) 1986-1995 by cisco Systems, Inc.
Compiled Wed 10-May-95
System Bootstrap, Version 5.3(9)
Current date and time is Sat 5-13-1995 21:38:35
Boot date and time is Thur 5-11-1995 15:32:28
[displayed text omitted from this example]
![]()
Router# show env
All measured values are normal
RSP7000#sho env last
CI(6) Inlet previously measured at 22C/71F
CI(6) Hotpoint previously measured at 31C/87F
CI(6) Exhaust previously measured at 23C/73F
+12 Voltage previously measured at 12.12
+5 Voltage previously measured at 5.13
-12 Voltage previously measured at -11.84
+24 Voltage previously measured at 24.06
RSP7010#sho env last
CI(4) Inlet previously measured at 23C/73F
CI(4) Hotpoint previously measured at 35C/95F
CI(4) Exhaust previously measured at 25C/77F
+12 Voltage previously measured at 12.31
+5 Voltage previously measured at 5.17
-12 Voltage previously measured at -11.89
+24 Voltage previously measured at 23.78
RSP7000#sho env table
Sample Point LowCritical LowWarning HighWarning
HighCritical
CI(6) Inlet 44C/111F 50C/122F
CI(6) Hotpoint 54C/129F 60C/140F
CI(6) Exhaust
+12 Voltage 10.90 11.61 12.82 13.38
+5 Voltage 4.61 4.94 5.46 5.70
-12 Voltage -10.15 -10.76 -13.25 -13.86
+24 Voltage 20.38 21.51 26.42 27.65
2.5 Reference 2.43 2.51
Shutdown power supplies at 70C/158F
RSP7010#sho env table
Sample Point LowCritical LowWarning HighWarning
HighCritical
CI(4) Inlet 44C/111F 50C/122F
CI(4) Hotpoint 54C/129F 60C/140F
CI(4) Exhaust
+12 Voltage 10.90 11.61 12.82 13.38
+5 Voltage 4.61 4.94 5.46 5.70
-12 Voltage -10.15 -10.76 -13.25 -13.86
+24 Voltage 20.38 21.51 26.42 27.65
2.5 Reference 2.43 2.51
Shutdown power supplies at 70C/158F
RSP7000#sho env all
Arbiter type 1, backplane type 70x0 (id 5)
Power supply #1 is 700W (id 2), power supply #2 is removed (id 3)
Active fault conditions: none
Active trip points: none
0123456
Dbus slots: X X
card inlet hotpoint exhaust
CI(6) 21C/69F 30C/86F 22C/71F
Shutdown temperature source is 'hotpoint' on CI(6),
requested CI(6)
+12V measured at 12.12
+5V measured at 5.13
-12V measured at -11.84
+24V measured at 24.06
+2.5 reference is 2.49
http://www.cisco.com
cio.cisco.com
ciohelp@cisco.com.
For additional information, contact
cioteam@cisco.com.
tac@cisco.com.
To obtain general information about Cisco Systems, Cisco products, or upgrades, contact 800 553-6387, 408 526-7208, or
csrep@cisco.com.

![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()