|
|
This appendix contains information about how to isolate problems with the router and includes the following sections:
The key to problem solving in this system is to try to isolate the problem to a specific subsystem. By comparing what the system is doing to what it should be doing, the task of isolating the problem is greatly simplified.
When problem solving, consider the following subsystems:
Troubleshooting the Power and Cooling Systems
Check the following items to help isolate the problem:
For information about obtaining technical support, refer to the section "Obtaining Service and Support" in the "Overview of the Router" chapter.
Troubleshooting the Ports, Cables, and Connections
Check the following items to help isolate the problem:
For information about obtaining technical support, refer to the section "Obtaining Service and Support" in the "Overview of the Router" chapter.
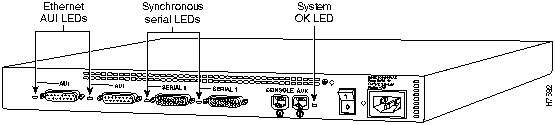
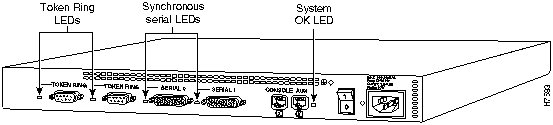
The LEDs indicate the current operating condition of the router. You can observe the LEDs, note any fault condition that the router is encountering, and then contact your system administrator or customer service, if necessary. For information about how to contact customer service, refer to the section "Obtaining Service and Support" in the "Overview of the Router" chapter.
Figure A-1 to Figure A-7 show the location of the LEDs on the rear panel of the routers. The power LED, at the right of the auxiliary port, lights up when the system is working properly. All of the other LEDs indicate activity by flickering. When there is heavy activity on a port, the LED might be ON constantly. If an LED is not ON when the port is active and the cable is connected correctly, there might be a problem with the port.
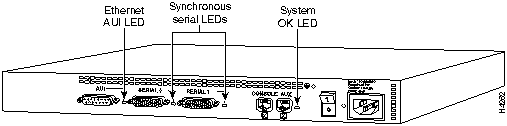
Figure A-2 : Model 2502 LEDs
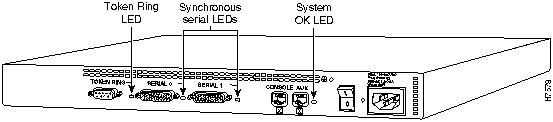
Figure A-3 : Model 2503 LEDs
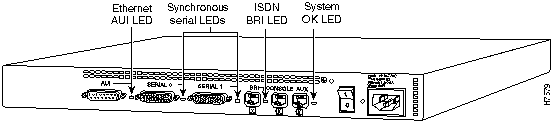
Figure A-4 : Model 2504 LEDs
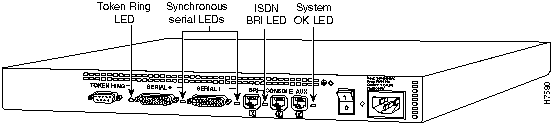
Figure A-5 : Model 2513 LEDs
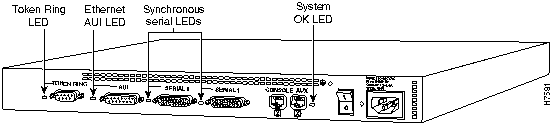
Figure A-6 : Model 2514 LEDs
|
|
Copyright 1988-1996 © Cisco Systems Inc.