|
|
Use the information in this appendix to help isolate problems you might encounter with Cisco 1600 series routers, or to rule out the router as the source of the problem.
This appendix contains the following sections:
For information about the Cisco 1600 series ROM monitor, refer to the appendix "ROM Monitor."
If you cannot locate the source of the problem, contact your local reseller for information on how to proceed. Before you call, have the following information ready:
Recovering a Lost Enable Password
This section describes how to recover a lost enable password.
Follow this procedure to recover a lost enable password:
The key to problem solving is to isolate the problem to a specific subsystem by comparing what the router is doing to what it should be doing.
When problem solving, consider the following subsystems of the router:
Troubleshooting WAN Interface Cards and Cables
Check for the following symptoms to help isolate the problem:
Troubleshooting the Power System
Check the following items to help isolate the problem:
This section describes problems related to the ISDN line that might occur with the router.
There are two commands that are useful when troubleshooting ISDN. The clear interface command, when entered with the bri keyword, terminates any active ISDN calls and resets the ISDN BRI interface. Enter the command as follows:
The clear controller command is used on routers with an ISDN BRI U interface. Entered with the bri keyword, this command performs the same function as the clear interface command, but also resets the ISDN line between the router and the central office switch. Enter the command as follows:
Table A-1 lists troubleshooting methods for ISDN-specific problems that might occur.
Table A-1 : Troubleshooting ISDN
The LEDs on the front panel of the router enable you to determine router performance and operation at a glance. This section contains information about reading the LEDs and using them to troubleshoot problems.
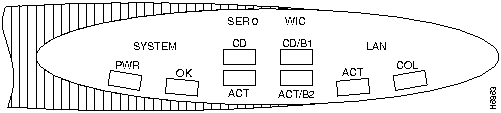
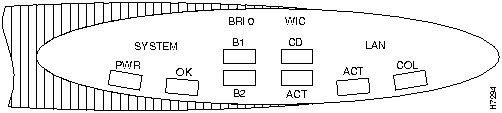
Figure A-1 and Figure A-2 illustrate the LEDs on the front panel of Cisco 1600 series routers.
Figure A-1 : Front Panel LEDs---Cisco 1601 and Cisco 1602
Table A-2 describes the front panel LEDs for the Cisco 1601 and Cisco 1602 routers.
Table A-2 : Front Panel LEDs---Cisco 1601 and Cisco 1602
Figure A-2 : Front Panel LEDs---Cisco 1603 and Cisco 1604
Table A-3 describes the front panel LEDs for the Cisco 1603 and Cisco 1604 routers.
Table A-3 : Front Panel LEDs---Cisco 1603 and Cisco 1604
Table A-4 describes the rear panel LEDs. For illustrations of these LEDs and the rear panel of the routers, refer to Figure 1-2 through Figure 1-5 in the chapter "Overview."
Table A-4 : Rear Panel LED Descriptions
Table A-5 describes the LEDs that appear on the front panel of each card.
Table A-5 : WAN Interface Card LED Descriptions
For more information on WAN interface cards, refer to the chapter "Using WAN Interface Cards."
Copyright 1988-1996 © Cisco Systems Inc.
Router>
show version
rommon 2>
confreg 0x142
rommon 2>
i
--- System Configuration Dialog ---
Press RETURN to get started!
Router>
Router>
enable
Router#
Router#
show startup-config
Router#
configure terminal
9600 baud
8 data bits
No parity generated or checked
1 stop bit
Router# clear interface bri0
Router# clear controller bri0
Symptom
Checks
Causes and Solutions
Router is on, OK LED (next to ISDN S/T port) is off (Cisco 1603 and ISDN S/T WAN interface card)
Router is on, NT1 LED is off (Cisco 1604 and ISDN U WAN interface card)
NT1 LED is on, OK LED (next to ISDN S/T port) is off (Cisco 1604)
Cisco 1604 cannot create an ISDN connection to the remote router when an ISDN device is connected to the ISDN S/T port
ISDN device attached to the Cisco 1604 ISDN S/T port does not operate correctly.
Cannot make an ISDN connection to remote device (Cisco 1603, Cisco 1604, ISDN WAN interface cards)
Use the isdn switch-type command to configure correct switch type.
LED
Color
Description
SYSTEM PWR
Green
Indicates that the router is turned on, that DC power is being supplied to the router.
SYSTEM OK
Green
Indicates that the router has successfully booted. Blinks during the boot cycle.
LAN ACT
Green
Indicates that data is being sent to or received from the local Ethernet LAN.
LAN COL
Yellow
Flashing indicates packet collisions on the local Ethernet LAN.
SER 0 CD
Green
SER 0 ACT
Green
WIC CD/B1
Green
WIC ACT/B2
Green
LED
Color
Description
SYSTEM PWR
Green
Indicates that the router is turned on, that DC power is being supplied to the router.
SYSTEM OK
Green
Indicates that the router has successfully booted. Blinks during the boot cycle.
LAN ACT
Green
Indicates that data is being sent to or received from the local Ethernet LAN.
LAN COL
Yellow
Flashing indicates packet collisions on the local Ethernet LAN.
BRI 0 B1
Green
Indicates an ISDN connection on B-channel 1.
Note for Cisco 1604 only---If an ISDN device connected to the ISDN S/T port is using B-channel 1, the LED will go on,
BRI 0 B2
Green
Indicates an ISDN connection on B-channel 2.
Note for Cisco 1604 only---If an ISDN device connected to the ISDN S/T port is using B-channel 2, the LED will go on,
WIC CD
Green
Indicates an active connection on the WAN interface card serial port.
WIC ACT
Green
Indicates that data is being sent over the WAN interface card serial port.
LED
Color
Description
All Models:
LINK
Green
Indicates 10BaseT link integrity. Does not go on when connected to an Ethernet network through the AUI port.
OK (for Flash memory PC Card)
Green
Indicates that the Flash memory card is correctly installed.
Cisco 1601:
RDY
Green
Indicates that a serial port cable connection has been made to a modem or DSU/CSU.
Cisco 1602:
LOOPBACK
Yellow
Indicates that the DSU/CSU is in CSU or DSU loopback mode.
ALARM
Yellow
Indicates an alarm condition on the DSU/CSU port.
CARRIER
Green
Indicates line synchronization or connection on the DSU/CSU port.
Cisco 1603:
OK (next to ISDN BRI S/T port)
Green
Indicates that a physical connection has been established with the ISDN central office switch.
Cisco 1604:
NT1
Green
Indicates that a physical connection has been established from the router's internal NT1 to the ISDN central office switch.
OK (next to ISDN S/T port)
Green
Indicates that the device connected to the router's ISDN S/T port has established a physical connection with the ISDN central office switch.
Card
LEDs
Color
Description
Synchronous serial
CONN
Green
ISDN BRI S/T
Green
Green
Green
ISDN BRI U
Green
Green
Green
1 DTE = data terminal equipment.
2 DSR = data set ready.
3 DCD = data carrier detect.
4 CTS = Clear To Send.
5 DTR = data terminal ready.
6 RTS = Request To Send.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()