|
|
This chapter describes trunk line monitoring and some troubleshooting procedures that you can follow if you encounter a problem.
Loss of data can cause external protocols to retransmit, resulting in network congestion and delays. To avoid loss of data, line quality must be kept very high. The line card control process (LCC) continually monitors line quality on each trunk using the switch's Trunk Up-Down (TUD) protocol. This protocol detects a trunk that is down or line quality that is poor. When a trunk that was down comes back up, the TUD protocol returns it to service.
The TUD protocol monitors line quality by having each switch send short test messages at regular intervals. When a switch starts up, it begins sending TUD messages down each trunk that it supports. If the local switch receives TUD messages consistently from the remote switch, it declares the trunk up.
If a switch misses an established number of TUD messages from a trunk, it declares the trunk down. When the trunk is declared down, a trap displays indicating the change of status. The following is a typical trunk down message:
Link down trap from Light7, System Up Time: 23 Hr 29 Min 50 Sec Port: 5.0
When the trunk comes up again, the switch sends another trap. The following is a typical trunk up message:
Link up trap from Light7, System Up Time: 23 Hr 29 Min 55 Sec Port: 5.0
A trunk may go down temporarily and come back up shortly without intervention. However, if the trunk remains down or transitions constantly in and out of service, you must find and correct the problem. Use the loopback tests described in this section to isolate the faulty component. A loopback test is a software or hardware test that alters the flow of data so that an electronic signal is returned to its sender.
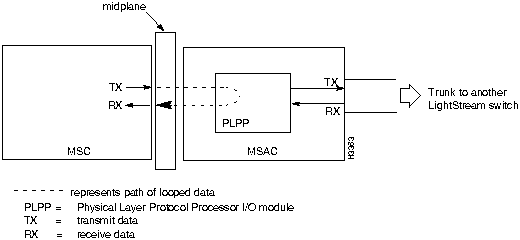
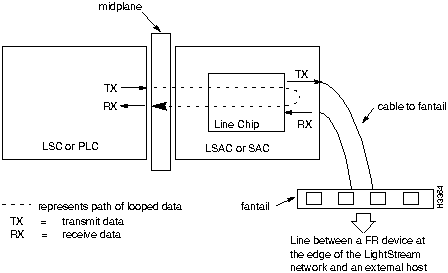
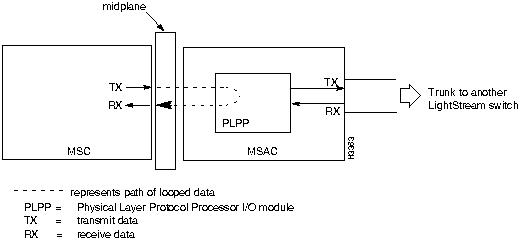
Trunks can be directly connected or they can be connected with data service unit/channel service unit (DSU/CSU) devices through telephone lines. Figure 6-1, Figure 6-2, and Figure 6-3 illustrate the major components of the switch-to-switch connection over a trunk. A trunk interface loop occurs in the circuitry within the switch and does not involve components external to the switch.
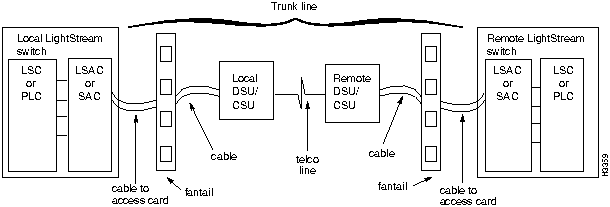
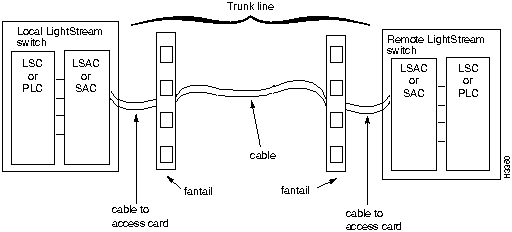
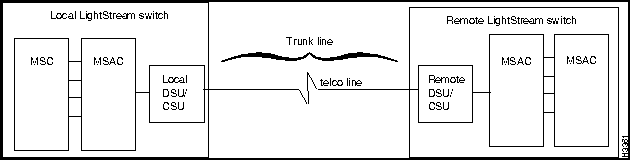
Fault Isolation for Link Down Events
Most trunk failures are temporary, caused by problems on the telephone company line. A trunk is usually returned to service within a short period without any intervention on your part and before the telephone company finds anything wrong.
You must identify the failed portion of the trunk. To do this, you run a series of loopback tests to segment the trunk from end to end, starting at the I/O board of the switch and progressing out from the switch. This progressive process tests each segment in sequence to find the exact location of the failure.
The loopback tests allow you to pinpoint a fault by successively looping a signal at various points. The LS2020 switch provides two loopback tests: remote and internal.
Only Frame Relay ports and trunk ports have active port management protocols that automatically verify the port's ability to process data.
The remote loopback test loops data from an external device through the I/O module and back. This test verifies that the data sent from the remote end can cross the telco line or cable, pass through the I/O module, and return to the remote end.
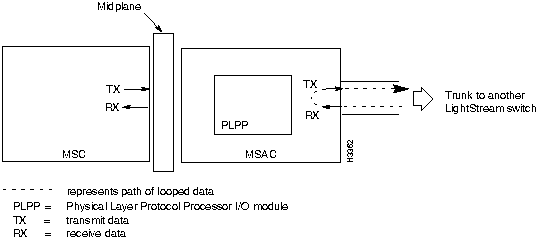
The internal loopback test loops data from the line card to the line chip or to the physical layer protocol processor (PLPP) I/O module to see if the relevant I/O module is able to receive intact data. If this loop is successful, you know that the data can reach the I/O module properly. However, you do not know if the I/O module correctly encodes the data that will be sent out onto the line.
The line chip and the PLPP I/O module take bytes from the line card and convert them into the required form to be sent out from the access card. The line chip encodes frames or cells into SDLC frames. The PLPP I/O module encodes cells into the ATM standard cell payload format for T3 or E3, depending on the access card.
This procedure tells you how to loop data through a trunk between two LS2020 trunk ports. If you know that data is not passing on a trunk between two trunk ports, follow these steps to set up a remote loop on one of the trunk ports:
Figure 6-4 : Remote Loop on an MS Trunk Port Figure 6-5 : Internal Loop on an MS Trunk Port This section describes the procedure for looping data through a Frame Relay port. The line from the port connects an LS2020 switch to an external device provided by another vendor. If you receive an indication that data is not passing between the LS2020 switch Frame Relay port and the host, or that the line is unreliable, use this looping procedure to isolate the problem.
Figure 6-6 : Remote Loop on an LS Edge Port Figure 6-7 : Intermal Loop on an LS Edge Port
The procedure for looping other (non-Frame Relay) edge ports is nearly identical to the procedure for looping Frame Relay ports, except that there is no need to reconfigure the net interface type. Therefore, to loop test any other type of edge port, follow the steps in the preceding "Looping Edge Ports" section, but disregard Steps 1 and 5.
This procedure allows you to unloop the port when you finish a loopback test. Whenever you run a loopback test on a port, you must unloop the port when you finish. However, if you proceed from one type of loopback test to another type on a particular port (from internal to remote, for example), you need not unloop the port before you start the next loopback test.
To unloop a port, enter the following at the Where
<c.p> is the port you want to unloop. The port number is in card.port format
(card = 2 to 10; port = 0 to 7).
The administrative status on the port changes from testing to up and the operational status changes from testing to either up or down.
Activating (or Deactivating) a Port
This procedure allows you to set a particular port (except a frame forwarding port) to active, inactive, or testing. If a port is set to active, it is up and passing data. If a port is set to inactive, it is down and cannot pass data. If a port is set to testing, you can set up software loops on the I/O components of the board itself, but not on the DSU/CSU.
The following is an example of the show port status display:
Operational status is the port's actual status and administrative status is the status that you set.
The following are examples of the traps that display when the port goes up (first example) or down (second example).
Activating (or Deactivating) a Frame Forwarding Port
This section presents the procedure for activating or deactivating a particular frame forwarding port. When you activate a port, a virtual channel connection (VCC) is set up to a designated endpoint and traffic can flow over that connection. When you deactivate a port, no traffic can flow over the connection.
At the Where
<c.p> is the frame forwarding port you want to make active or inactive. The port number is in card.port format (card = 2 to 10; port = 0 to 7).
{activate | deactivate} specifies whether traffic can or cannot flow over the connection. The default is activate.
Activating (or Deactivating) a Frame Relay DLCI
This section presents the procedure for activating or deactivating a particular Frame Relay data link connection identifier (DLCI). When you activate a connection, traffic can flow over that connection. When you deactivate a connection, no traffic can flow over it.
At the Where
<c.p> is the port that contains the DLCI you want to make active or inactive. The port number is in card.port format (card = 2 to 10; port = 0 to 7).
<dlci#> is the DLCI you want to make active or inactive. The DLCI number can be between 16 and 991.
{activate | deactivate} specifies whether traffic can or cannot flow over the connection. The default is activate.
Activating (or Deactivating) an ATM UNI VCI
This procedure enables you to activate or deactivate a particular ATM UNI virtual channel identifier (VCI). When a connection is activated, traffic can flow over it. When a connection is deactivated, no traffic can flow over it.
At the Where
<c.p> is the port that contains the ATM VCI you want to activate or deactivate. The port number is in card.port format (card = 2 to 10; port = 0 to 7).
<atm vci#> is the ATM VCI you want to activate or deactivate. The ATM VCI number must be in the range 1 through 32399, and may be further restricted depending on the type of line card.
{activate | deactivate} specifies whether traffic can or cannot flow over the connection. The default is activate.
Activating (or Deactivating) an ATM UNI VPI
This procedure enables you to activate or deactivate a particular ATM UNI virtual path identifier (VPI). When a connection is activated, traffic can flow over it. When a connection is deactivated, no traffic can flow over it.
At the Where
<c.p> is the port that contains the ATM VPI you want to activate or deactivate. The port number is in card.port format (card = 2 to 10; port = 0 to 7).
<atm vpi#> is the ATM VPI you want to activate or deactivate. The ATM VPI number must be in the range 1 through 32399, and may be further restricted depending on the type of line card.
{activate | deactivate} specifies whether traffic can or cannot flow over the connection. The default is activate.
Activating (or Deactivating) a Constant Bit Rate PVC
This procedure describes how to activate or deactivate a particular constant bit rate PVC. When you activate a connection, traffic can flow over that connection. When you deactivate a connection, no traffic can flow over it.
At the Where
<c.p> is the port that contains the cbrpvc you want to make active or inactive. The port number is in card.port format (card = 2 to 10; port = 0 to 7).
<PVC#> is the PVC you want to activate or deactivate. For the CEMAC, the PVC number is
{activate | deactivate} specifies whether traffic can or cannot flow over the connection. The default is activate.
This section describes the procedure for resetting a card from the TCS.
Be careful when resetting the active NP or switch cards. Resetting these cards brings down the entire switch and causes data loss for about 5 minutes on the card.
Loading Line Card Operational Software
This section tells you how to load line card operational software or diagnostics programs into the line cards, network processors, or switch cards. In addition to the operational software, the following diagnostic programs are available:
If you load diagnostics into a card, see the LightStream 2020 Hardware Reference & Troubleshooting Manual for detailed instructions on how to run the diagnostics and how to interpret the results.
To determine if you can communicate over a particular IP connection, use the ping command. The ping command sends an ICMP echo packet to the specified IP address. If IP is working at that address, IP sends an ICMP-echo-reply message to the sender.
To send the ICMP echo packet to a specified IP address, follow these steps:
Verifying Software Installation
Follow these steps to verify that all files and directories that were copied from the installation diskettes to the hard disk are intact. All relevant files used to verify software installation reside on the first diskette of the following installation diskette sets:
When you press Return, the following information displays after ckswinstall runs on the first set of software.
Because the software has been running for a period of time when you run ckswinstall, some files may have changed from the original installation. The software is probably not corrupted if you receive messages that any of the following directories or files have changed:
If ckswinstall detects errors in other directories or files, reinstall the software and repeat this procedure. For software installation instructions, see the LightStream 2020 Installation Guide and the LightStream 2020 Release Notes.
Copying a File Between LS2020 Switches
This section tells you how to copy files between different LS2020 switches. You can copy files from remote NP disks to local NP disks and vice versa. You may choose to copy files for a number of reasons, such as moving log files from a remote disk to a local disk so you can view them.
You move these files by using the file transfer protocol (ftp) from within the CLI shell command.
This section tells you how to diagnose port problems. The procedures (to be performed in sequence) described below include:
This procedure contains the basic port checks and verifies that the port is enabled.
To check the Measured Bit Rate entry, follow these steps.
Medium-Speed Configuration Parameters
On a medium-speed line card (MSC), a high error rate or a total lack of errors with data transfer not working can be caused by an incorrect setting of the cell payload scrambling attribute, the DS3 line type, or the cable length attributes. The next sections describe two parameter mismatches and some of their symptoms.
Mismatched Cell Payload Scrambling
On MSC trunks, cell payload scrambling is disabled by default. If one end of a trunk has cell payload scrambling enabled and the other end has cell payload scrambling disabled, packets appear to be received and transmitted without error in the port statistics display. The trunks will never come up, however, because the payload of the cells is scrambled at one end and not unscrambled at the other end. This causes the TUD protocol to fail.
A UNI port also appears to function normally without transmit or receive errors. However, the hosts that eventually try to reassemble the cells into useful data find that the data is corrupted. A series of AAL5 CRC errors occur if the calls carry AAL5-encoded data.
If the Line Type parameter is set incorrectly (dsx3Linetype mismatch), a very low error rate appears. An idle trunk regularly counts a receive error every 3 to 5 seconds.
Mismatched Framing on T3/E3 Ports
If you have difficulty bringing up a trunk port or UNI port, it may be because the two ends are not configured for the same framing type. Both ends must use the same framing type (PLCP, HEC, or G.804).
If there is a mismatch, the line status field in the output of the show port command displays the value "DS3_other_failure" for both ports.
To check the line status parameter, enter the show port c.p physical command.
To set the framing type so that it matches the other end, enter the set port c.p characteristics framing type {plcp | t3-hec | g-804} command.
To check connections, follow these steps:
To check the receive data, follow these steps:
To check line statistics, follow these steps:
The LSC CSU statistics are available only by means of a connection to the CSU through a serial line. If the CSU is connected to the DSU/CSU control port, the CSU can be reached with the csumon command from the Lynx shell. The CSU statistics for the MSC are available through use of the standard DS3 MIB variables; some can also be displayed through use of csumon. The CSU statistics for the CLC/OC3 card are available through use of the SONET MIB.
If the trunk does not come up or the Frame Relay port does not come up, perform the following steps to determine the problem.
Frame Relay Port Does Not Come Up
Table 6-1 : LCC Traps Text, Definitions, and Actions
If an FR, FF, UNI, or CBR VC is not created or if no data is being delivered over an FR VC, perform the procedures in this section.
An FR, FF, UNI, or CBR PVC Fails to Be Created
Table 6-2 : lastAtmError Text, Definitions, and Actions
No Data Being Delivered over a Frame Relay VC
Partial Data Is Being Delivered over the FR, FF, or UNI PVC
If partial data is being delivered over the FR, FF, or UNI PVC, check to see if the network is congested.
Partial Data Is Being Delivered over the CBR PVC
If partial data is being delivered over the CBR PVC, you need to reconfigure your targetdepth and maxdepth parameters to compensate for random cell delay variation.
Copyright 1988-1996 © Cisco Systems Inc.
cli>
prompt:
cli>
set port <c.p> loop remote
cli>
prompt:
cli>
set port <c.p> loop internal
cli>
prompt:
cli>
set port <c.p> unloop
cli>
prompt to set the netinterfacetype attribute to NNI:
cli>
set port <c.p> framerelay netinterfacetype nni
cli>
prompt:
cli>
set port <c.p> loop remote
cli>
set port <c.p> loop remote
cli>
prompt:
cli>
set port <c.p> unloop
cli>
prompt:
cli> set port <c.p> framerelay netinterfacetype uni
cli>
prompt:
cli> set port <c.p> unloop
cli>
prompt, enter
cli>
set port <c.p> {active | inactive | testing}
cli>
prompt:
show port <c.p> status
cli>
show port 5.0 status
Admin Status: Up
Oper Status: Up
Oper loop: none
Admin loop: none
Last Oper Change: 25 Hr 2 Min 58 Sec ago
Link up trap from Light7, System Up Time: 23 Hr 29 Min 55 Sec
Port: 5.0
Link down trap from Light7, System Up Time: 23 Hr 29 Min 50 Sec
Port: 5.0
cli>
prompt, enter
cli> set port <c.p> frameforwarding {activate|deactivate}
cli>
prompt, enter
cli> set port <c.p> dlci <dlci#> {activate|deactivate}
cli>
prompt, enter
cli> set port <c.p> vci <vci#> {activate|deactivate}
cli>
prompt, enter
cli> set port <c.p> vpi <vpi#> {activate|deactivate}
cli>
prompt, enter:
cli> set port <c.p> cbr <PVC#> {activate|deactivate}
always 1.
cli>
prompt, enter
cli>
protected
Enter password:
cli>
prompt, enter
*
cli>
set tcs <card#> reset
cli>
prompt, enter
cli>
protected
Enter password:
cli>
prompt:
*
cli>
loadcard <slot#> [<load address>] <file name>
/usr/diag/diag_np1.aout (NP card diags)
/usr/diag/diag_ls1.aout (low-speed line card diags)
/usr/diag/diag_ms1.aout (medium-speed line card diags)
/usr/diag/diag_plc1.aout (packet line card diags)
/usr/diag/diag_clc1.aout (cell line card diags)
*
cli>
connect 1 diagnostic
~~q
bash#
ping [packet size] <host name>
*cli>
ping Light5
PING Light5 (127.1.24.35) 64 data bytes
64 bytes from 127.1.24.35: icmp_seq=0 time=100ms
64 bytes from 127.1.24.35: icmp_seq=1 time= 00ms
64 bytes from 127.1.24.35: icmp_seq=2 time= 00ms
^C
_ Light5 PING Statistics
3 packets transmitted, 3 packets received, 0 packet loss
round-trip (ms) min/avg/max = 0/33/100
directory by entering the following at the bash# prompt:
bash#
cd /
bash#
ckswinstall
You inserted diskette 1 of the System set.
Starting verification of installation.
Verifying the System directories.
The System directories have been verified.
Verifying the System hard links.
The System hard links have been verified.
Verifying the System symbolic links.
The System symbolic links have been verified.
Verifying the System special files.
The System special files have been verified.
Finished verification of installation.
/usr/oper/.profile
/usr/npadmin/.profile
/usr/fldsup/.profile
/usr/etc/ftpdlog
/usr/etc/inetdlog
/usr/etc/rlogindlog
/usr/etc/rshdlog
/usr/etc/telnetdlog
/usr/etc/tftpdlog
cli>
prompt, enter
cli>
protected
Enter password:
cli>
prompt, enter
*
cli>
shell "ftp <IP address or name of the NP you want to copy files to or from>"
Connected to 127.1.22.25.
220 emtb5 FTP server (Version 4.162 Tue Nov 1 10:50:37 PST 1988) ready.
Name (127.1.22.25:oper):
331 Password required for oper.
Password:
230 User oper logged in.
ftp>
ftp>
put /usr/tmp/mma/mma.traplog [<new name>]
cli>
prompt:
*
cli>
shell "ls -l"
cli>
set tcs <card#> power {on|off}
cli>
show port <c.p> all
cli>
prompt:
cli>
show port <c.p> all
(INFO) LCC_3037 at 19.28/94 14:27:52 EDT (10/28/94 18:27:52 GMT)
LCC port 7000 unable to source clock at 70001 bits/second.
cli>
prompt:
cli>
show port <c.p> all
cli>
prompt:
cli>
show port <c.p> statistics
cli>
show port 5001 statistics
Octets Rcvd: 256748059
Normal Cells Rcvd: 4844303
cli>
prompt or by entering ^P:
cli>
show port <c.p> statistics
cli>
show port 5001
Octets Rcvd: 256748059 (Delta: 5830 Rate: 971.66/sec)
Normal Cells Rcvd: 4844303 (Delta: 109 Rate: 18.16/sec)
cli>
prompt:
cli>
show port <c.p> statistics
cli>
show port 5001 statistics
Octets Rcvd: 256748059
Normal Cells Rcvd: 4844303
cli>
prompt or by entering ^P:
cli>
show port <c.p> statistics
cli>
prompt:
cli>
show port <c.p> statistics
cli>
show port 5001 statistics
Octets Rcvd: 234061260
Normal Packets Rcvd: 294944229
Multicast Pacets Rcvd: 0
Discarded Rcvd Packets: 107
Receive Errors: 56702
Unknown Protocols Rcvd: 0
Octets Sent: 1068586222
Normal Packets Sent: 2046089974
Multicast Packets Sent: 0
Discarded Output Packets: 8490
Output Errors: 12
cli>
prompt:
cli>
show port <c.p> all
cli>
set trap "LCC_3*"
Trap Text
Definition
Action
LCC_3000 "lccFrLmiSendVc write error portid %d"
Indicates an internal error.
Report this problem to Cisco Systems, Inc.
LCC_3008 "Frame Relay Port %d - data unused DLCI %d"
An LMI type mismatch exists. If the DLCI reported is 1023, the host is sending FRIF frames and the Frame Relay edge port is configured for ANSI or ITU/TSS. If the DLCI reported is 0, the host is sending ANSI or ITU/TSS frames to an FR edge port configured for FRIF.
Verify the configuration on the attached equipment, and change the LS2020 Frame Relay port to match.
LCC_3013 "Frame Relay Port %d - LMI unknown IE %d at offset %d"
The equipment is noncompliant or the port is configured as an LMI type Q.933-a.
Verify the configuration on the attached equipment, and change the LS2020 Frame Relay port to match.
LCC_3017 "Frame Relay Port %d - LMI missing mandatory IE, mask=%x"
The equipment is noncompliant or the port is configured as an LMI type Q.933-a.
Verify the configuration on the attached equipment, and change the LS2020 Frame Relay port to match.
LCC_3027 "Frame Relay Port %d - LMI missing lockshift5"
The equipment is noncompliant or the port is configured as an LMI type Q.933-a.
Verify the configuration on the attached equipment, and change the LS2020 Frame Relay port to match.
LCC_3005 "Frame Relay Port %d - frame too small"
There are serious incompatibilities or corruption of data.
Check that the attached equipment is configured for Frame Relay and check the line quality.
LCC_3006 "Frame Relay Port %d - EA bit incorrect"
This indicates serious incompatibilities or corruption of data.
Verify that the attached equipment is configured for Frame Relay and check the line quality.
LCC_3007 "Frame Relay Port %d - data on unstarted DLCI %d"
The edgeport device is sending data on a DLCI that does not have PVCs configured for it.
Verify the end user equipment configuration. You may need to configure a new PVC for the LS2020 network.
LCC_3009 "Frame Relay Port %d - Frame too small, size %d"
This indicates serious incompatibilities or corruption of data.
Verify that the attached equipment is configured for Frame Relay and check the line quality.
LCC_3010 "Frame Relay Port %d - Invalid LMI header at offset %d"
The equipment is noncompliant or the port is configured as an LMI type Q.933-a.
Verify the configuration on the attached equipment and change the LS2020 Frame Relay port to match.
LCC_3011 "Frame Relay Port %d - Invalid LMI message type %d"
The equipment is noncompliant, the port is configured as an LMI type Q.933-a, or the edge port device supports a feature that the LS2020 switch does not. For example, the asynchronous status notification message.
Ignore the message or configure the edge port device not to send the asynchronous status notification message (if applicable).
LCC_3012 "Frame Relay Port %d - LMI IE Truncated at offset %d"
This indicates serious incompatibilities or corruption of data.
Verify that the attached equipment is configured for Frame Relay, and verify the line quality.
LCC_3014 "Frame Relay Port %d - Repeated LMI mandatory IE %d at offset %d"
The equipment is noncompliant or the port is configured as an LMI type Q.933-a.
Verify that the attached equipment is configured for Frame Relay, and check the line quality.
LCC_3015 "Frame Relay Port %d - LMI frame contains wrong IE %d at offset %d"
The equipment is noncompliant or the port is configured as an LMI type Q.933-a.
Verify that the attached equipment is configured for Frame Relay, and check the line quality.
LCC_3016 "Frame Relay Port %d - LMI message contains %d excess bytes"
The equipment is noncompliant or the port is configured as an LMI type Q.933-a.
Verify that the attached equipment is configured for Frame Relay, and check the line quality.
LCC_3018 "Frame Relay Port %d - LMI received invalid report type %d"
The equipment is noncompliant or the port is configured as an LMI type Q.933-a.
Verify that the attached equipment is configured for Frame Relay, and check the line quality.
LCC_3019 "Frame Relay Port %d - LMI frame contained invalid PVC DLCI %d"
The equipment is noncompliant or the port is configured as an LMI type Q.933-a.
Verify that the attached equipment is configured for Frame Relay, and check the line quality.
LCC_3020 "Frame Relay Port %d - LMI frame reported too many PVCs"
The Frame Relay LMI has been configured for too few PVCs for a port.
Increase the Max Supported Vc variable to be equal to or greater than the number of VCs allowed on that port.
LCC_3021 "Frame Relay Port %d - LMI frame received with DLCIs misordered"
The equipment is noncompliant or the port is configured as an LMI type Q.933-a.
Verify that the attached equipment is configured for Frame Relay, and check the line quality.
LCC_3022 "Frame Relay Port %d - LMI expected report type %d, got %d"
The equipment is noncompliant or the port is configured as an LMI type Q.933-a.
Verify that the attached equipment is configured for Frame Relay, and check the line quality.
LCC_3026 "Frame Relay Port %d - LMI out of buffers to send message"
The NP is being overused.
Report this problem to Cisco Systems, Inc.
LCC_3028 "Frame Relay Port %d - LMI frame contained invalid PVC status"
Either noncompliant equipment problems or a piece of the equipment does not have the same revision of the standard the LS2020 equipment has.
Check the configuration on the attached equipment or configure the standards to match one another.
LCC_3029 "Frame Relay Port %d - Provider Primitives invalid/incomplete"
Failed internal consistency checks.
Report this problem to Cisco Systems, Inc.
LCC_3030 "Frame Relay Port %d - LMI bad IE length %d at offset %d"
The equipment is noncompliant or the port is configured as an LMI type Q.933-a.
Verify that the attached equipment is configured for Frame Relay, and check the line quality.
LCC_3025 "Frame Relay Port %d - LMI"
The Max Supported VCs was set incorrectly, or the card Max Supported VCs was set incorrectly.
Reset the Max Supported VC and card Max Supported VC attributes correctly.
LCC_3036 "FR Port %d LMI timer expired without required message, Imi DLCI %d, user (1)/net(2) %d"
The local LMI sends this trap if it is not receiving valid STATUS_ENQUIRY messages or if an NNI is not receiving valid STATUS messages.
Verify that both the LS2020 port and edge equipment have compatible values for the net request interval and polling interval.
LCC_3023 "Frame Relay Port %d - LMI sequence number mismatch, expected %d received %d"
Some messages are being lost between the edge port and the host.
Verify that edge equipment can support the data rate being used.
LCC_3024 "Frame Relay Port %d - LMI reply is not for last enquiry, current %d last %d"
Some messages are being lost between the edge port and the host.
Verify that edge equipment can support the data rate being used.
Error Text
Definition
What to Do
No flow resources
The cardMaxVCs attribute is set too low.
Increase this value and reboot that line card.
No connect resources
The cardMaxVCs attribute is set too low.
Increase this value and reboot that line card.
Invalid connect request
The VC has illegal attributes set.
Review the bandwidth values in particular. A VC cannot have a MaxRate larger than the port. Also, certain combinations of parameters are illegal. If a VC uses "guaranteed" bandwidth, it is not allowed to have any excess bandwidth; the insured rate must equal the max rate.
Unknown destination
The local node is out of communication with the destination node.
Check to see if any trunks are down that are supposed to connect the nodes.
Not enough outbound
bandwidth
No path exists with sufficient bandwidth to support the VC.
Review the VC attributes. The Cells Required attribute shows how many cells worth of bandwidth are needed to carry that VC over a trunk.
No path
No path exists with sufficient bandwidth to support the VC.
Review the VC attributes. The Cells Required attribute shows how many cells worth of bandwidth are needed to carry that VC over a trunk.
Destination refused
connection
The remote end of the VC is refusing the connection.
Review the VC settings on the remote end point.
Not enough inbound
bandwidth
Not enough bandwidth exists on the source port for this VC.
Check the Cells Required attributes to determine the bandwidth required to carry that VC over the source port.
Check the Cells Available attribute to determine the bandwidth that has not been allocated to other VCs.
cli>
prompt:
cli>
show port <c.p> dlci <dlci#>
cli>
prompt:
cli>
walksnmp lsFrameRelayDlciStatTable
Name: frameRelayDlciStatPortIndex.3003.39 Value: 3003
Name: frameRelayDlciStatPortIndex.3003.40 Value: 3003
Name: frameRelayDlciStatPortIndex.3003.41 Value: 3003
Name: frameRelayDlciStatPortIndex.3003.42 Value: 3003
.
.
.
cli>
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()