|
|
LightStream 2020 MIB Reference
Network management systems that use the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) work with information stored in a Management Information Base (MIB). The MIB is a collection of variables known as MIB objects. The values of MIB objects help to govern the status and activities of LightStream 2020 multiservice ATM switch (LS2020 switch) software and hardware. The values of MIB objects are written by LS2020 operational software and by network management system (NMS) software, including the CLI. When NMS software displays the activities and status of the LS2020 node, it obtains them by reading the values of MIB objects.
The major branches of the MIB are themselves referred to as MIBs, such as the FDDI MIB, the Bridge MIB, and the SONET MIB. Most of these MIBs are public standards which are described in publicly available RFC documents.
This chapter
Figure 7-1 shows a high-level diagram of the MIB that is used to manage LS2020 switches. The high-level organization of the MIB is defined in RFC 1155, Structure of Management Information (SMI). (The full title is Structure and Identification of Management Information for TCP/IP-based Internets.) Public MIBs have been defined by various standards bodies to fit in this structure. There is also a place defined in it for private MIBs, such as the LS2020 private MIB.
Figure 7-1 : Overall MIB Structure
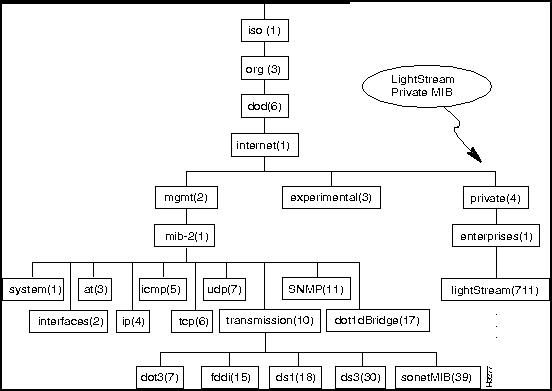
The MIB has a hierarchical tree structure:
Many of the objects shown in Figure 7-1 (that is, the branches rooted in those objects) are themselves referred to as MIBs. Outside of the private MIB branch, these are all standard MIBs. For information on some of the standard MIBs shown in Figure 7-1, refer to the following public-domain documents:
| MIB | Request for Comment (RFC) Document |
|---|---|
| MIB-II | RFC 1213 |
| Dot-3 Ethernet MIB | RFC 1398 |
| FDDI MIB | RFC 1512 |
| DS1 MIB | RFC 1406 |
| DS3 MIB | RFC 1233 |
| Dot-1 Bridge MIB | RFC 1493 |
| SONET MIB | RFC 1595 |
The LS2020 private MIB is in the private subtree (under the private object). This is the MIB that is described in the remainder of this chapter.
There are two ways to access a MIB, including the LS2020 private MIB:
These two methods are discussed in the following subsections. In addition, some network management applications include MIB browsing software that displays the descriptive text that is given in the definition of each MIB object under the heading "DESCRIPTION."
Displaying MIB Objects with CLI Commands
You can use CLI commands to view MIB object names and values.
| walksnmp | To learn the names of MIB variables in a subtree, specify the name of the object at the head of the subtree as the argument of the walksnmp command. This command displays all the branches and leaves below the specified point in the MIB.
cli>
walksnmp fddi
|
| browse | To step through the branches of the MIB tree one at a time, specify a branch as the argument of the browse command. (The default is the iso object.) When you reach the end of a branch, this command displays the values of leaves one at a time.
cli>
browse mib-2
|
| getsnmp | To display the value of a single MIB object at the end of a branch, specify an individual instance of a "leaf" as the argument of the getsnmp command.
cli>
getsnmp sysContact.0
|
The browse and walksnmp commands each display the set of objects in a specified branch of the MIB. The default for the browse command is the iso object at the root of the MIB; the walksnmp command has no default and requires an argument.
The getsnmp command displays an individual instance of a leaf object at the bottom of a branch. The MIB address in its argument must include an object identifier. See the subsections entitled "MIB Addresses" and "Object Identifiers."
The browse, walksnmp, getsnmp, getnextsnmp, and setsnmp commands are described in the chapter entitled "MIB Commands."
A MIB address identifies a particular MIB object by giving its location in the MIB.
You can specify the address of a MIB object in a number of ways. For example, the following MIB addresses all refer to the same MIB object:
sysContact.0
1.3.6.1.2.1.1.4
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.4
org.6.1.2.1.1.4
dod.1.2.1.1.4
internet.2.1.1.4
mgmt.1.1.4
mib.1.4
system.4
To identify a single instance of a MIB object at the end of a branch, you specify the object name, followed by a numeric suffix known as an object identifier. The object name is separated by a dot from the object identifier.
If there is only a single instance of the given object, the identifier suffix for that instance is 0. For example, there is only one instance of the sysContact object, so its identifier is sysContact.0. The following command displays the name of the contact person for the target node:
cli> getsnmp sysContact.0
You can determine what object identifier is used to specify a single instance of a given MIB object by examining the definition of that object in the MIB. (They are also included in the descriptions of configurable attributes in the LightStream 2020 Configuration Guide.) The following section describes the process by which MIB objects are defined, using examples from the private MIB file. For more information about object identifiers in particular, see the subsections entitled "Object Identifiers in the MIB File," "How the ifIndex Value Specifies a Unique Port," and "Multiply-Indexed Objects."
Detailed descriptions of the objects in a MIB are given in the MIB file in which the MIB is defined. The definitions of a standard MIB are elaborated in somewhat greater detail in the RFC document that specifies the MIB (see the subsection entitled "Standard MIBs").
The location of the LS2020 private MIB file depends upon the system on which you are looking.
| If you are connected to ... | Look in this directory ... |
|---|---|
| an LS2020 node | /usr/app/base/etc/private_mib.asn |
| a Workstation running HP OpenView StreamView | /usr/OV/snmp_mibs/lightstream |
| a Workstation not running HP OpenView StreamView | /LightStream-2.1/mib/lightstream.asn |
Use a text display program to examine this file. For example, to view the file on an LS2020 switch with the more command, enter the following commands:
LSnode:2# cd /usr/app/base/etc LSnode:2# more private_mib.asn
To view the file with the vi editor, enter the following commands:
LSnode:2# cd /usr/app/base/etc LSnode:2# vi private_mib.asn
See the LightStream 2020 NP O/S Reference Manual for information about using the more command and the vi editor.
This section uses instances from the LS2020 private MIB to illustrate how MIB objects are defined. The MIB object names and their definitions in the private MIB file are compiled into the operational code on the node. The file is write protected. There are comments in the file which are not compiled into the code; each comment line is marked with two hyphens (
--
) before the comment text, usually in the left margin.
The beginning of the file includes
The definitions of the lsOther objects in the private MIB file serve here as simple examples of how objects are defined in the MIB:
-- lsOther is used to define varbinds in trap message
lsOther OBJECT IDENTIFIER ::= { lightStreamOIDs 2 }
lsTrapText OBJECT-TYPE
SYNTAX DisplayString
ACCESS not-accessible
STATUS mandatory
DESCRIPTION
"This is the OID of the free formatted string used in
enterprise specific traps to describe the event."
::= { lsOther 2 }
LsTrapName OBJECT-TYPE
SYNTAX DisplayString
ACCESS not-accessible
STATUS mandatory
DESCRIPTION
"The first object in an enterprise specific
trap that contains the trap level, trap name and time
the trap occurred."
::= { lsOther 3 }
These definitions have the following elements:
Variables Used in the SYNTAX Field
The variables that can be specified in the SYNTAX field are defined in three ways: by importation from a different MIB file, by global definition at the beginning of the given MIB file, or in an ad hoc way for each table defined in the given MIB file.
In the definitions of the lsOther objects, the DisplayString variable was imported from a standard MIB for use in the SYNTAX fields of definitions in the LS2020 private MIB. Table 7-1 lists imported SYNTAX variables:
Table 7-1 : SYNTAX Variables That Are Imported from Standard MIBs
| SYNTAX Variable | Source | Object Type | Values |
|---|---|---|---|
| IpAddress | RFC 1155 (SMI) | Octet string | 32-bit IP address |
| Counter | RFC 1155 (SMI) | Integer | 0 -- 4,294,967,295;
Wraps to 0 when max is reached |
| Gauge | RFC 1155 (SMI) | Integer | 0 -- 4,294,967,295;
Latches at max attained value |
| TimeTicks | RFC 1155 (SMI) | Integer | Hundredths of a second |
| ifIndex | RFC 1213 (mib-2) | Integer | An interface ID |
| DisplayString | RFC 1213 (mib-2) | Octet string | A string of printable characters |
Other SYNTAX variables are globally defined at the beginning of the private MIB file as "text conventions" for use in many object definitions. Table 7-2 lists these variables:
Table 7-2 : Other Globally Defined SYNTAX Variables
| SYNTAX Variable | Object Type | Values |
|---|---|---|
| LightStreamStatus | Integer | 1 = enabled
2 = disabled |
| LightStreamValidation | Integer | 1 = valid
2 = invalid |
| LightStreamFilterAction | Integer | 1 = forward
2 = block |
| LightStreamUpToMaxAge | Integer | Range: 1 -- 3600 |
| LightStreamDLCI | Integer | A DLCI number |
| VCI | Integer | A VCI number |
In addition, a SYNTAX variable is defined for the objects that make up each table in the MIB. The definitions of MIB tables are presented in the following subsection.
When a set of MIB objects describe attributes of the same entity (such as a card or a port), they are defined as a table. All the objects in a table use the same object identifier (such as a card number or port number) as an index.
Figure 7-2 represents the outline of a typical MIB table, cardTable in the cardInfo branch of the MIB.
Figure 7-2 : An Example of a MIB Table
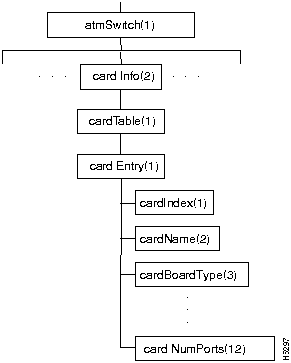
Five different kinds of objects are defined to make a table:
| The table object, that is, the name of the table itself. | |
| The table entry object. The actual table entries (Item 5) are instances of this object. | |
| The table entry structure object. This object is not shown in Figure 7-2 because it is not defined as a branch of any higher-level object; its function is only to provide structure for other objects. It specifies a list of objects (see Item 5). | |
|
The table index object, an integer. |
| The actual table entries. These are the objects enumerated for the table entry structure object (see Item 3). |
The definitions of these five different kinds of objects are interrelated:
cardTable OBJECT-TYPE
SYNTAX SEQUENCE OF CardEntry
ACCESS not-accessible
STATUS mandatory
DESCRIPTION
"Card specific information"
::= { cardInfo 1 }
cardEntry OBJECT-TYPE
SYNTAX CardEntry
ACCESS not-accessible
STATUS mandatory
DESCRIPTION
"An entry in the chassis card table. (1-n)"
INDEX { cardIndex }
::= { cardTable 1 }
CardEntry ::=
SEQUENCE {
cardIndex
INTEGER,
cardName
DisplayString (SIZE (0..255)),
cardBoardType
DisplayString (SIZE (0..255)),
cardLcSoftwareVersion
DisplayString (SIZE (0..255)),
cardLccSoftwareVersion
DisplayString (SIZE (0..255)),
cardPID
INTEGER,
cardMaxVCs
INTEGER,
cardOperStatus
INTEGER,
cardAdminStatus
INTEGER,
cardStatusWord
INTEGER,
cardConfigRegister
INTEGER,
cardNumPorts
INTEGER
}
cardIndex OBJECT-TYPE
SYNTAX INTEGER
ACCESS read-only
STATUS mandatory
DESCRIPTION
"Unique Index consisting of card number."
::= { cardEntry 1 }
cli>
getsnmp cardName.3
cardName OBJECT-TYPE
SYNTAX DisplayString (SIZE (0..255))
ACCESS read-write
STATUS mandatory
DESCRIPTION
"Name of Card
::= { cardEntry 2 }
cardNumPorts OBJECT-TYPE
SYNTAX INTEGER
ACCESS read-only
STATUS mandatory
DESCRIPTION
"Number of Ports available on this card."
::= { cardEntry 12 }
Object Identifiers in the MIB File
To use a CLI command to address a single instance of an object defined in a MIB table, you must know the object identifier for that instance. (This requirement was discussed earlier, in the section entitled "Displaying MIB Objects with CLI Commands.")
This section describes the different kinds of object identifiers that may be specified in the definitions of tables.
How Object Identifiers Are Specified
In the MIB file, the object identifier for table entries is identified in the INDEX field of the definition of the table entry object. The entry in this field specifies the structure of table entries. The object identifier is defined as the table index object (Items 2 and 4 in the section entitled "Tables in the MIB File"). For example, under the cardTable object, the definition of cardEntry (the table entry object) includes the following INDEX specification:
INDEX { cardIndex }
In the same example, the cardIndex object is defined as an integer, specified as the card number:
cardIndex OBJECT-TYPE
SYNTAX INTEGER
ACCESS read-only
STATUS mandatory
DESCRIPTION
"Unique Index consisting of card number."
::= { cardEntry 1 }
Because of this INDEX specification in the definition of the table entry object, every entry in the table has the same object identifier. In this example, the index is the number of the particular card whose MIB object values are being set or read. For instance, the value of cardName.3 is the name of Card 3.
How the ifIndex Value Specifies a Unique Port
In working with CLI commands, you may become accustomed to specifying a unique port number (a port on a specified card) in the format c.p, where c is the card (slot) number and p is the number of a port on that card. However, when you use the getsnmp, getnextsnmp, or setsnmp command with a MIB object that is indexed by port number as its argument, you must specify the object identifier in a more complex format. In this format, the card number, the port number, and the port type are all represented by a single integer. This integer is the value of the ifIndex object. (The ifIndex object is defined in the MIB-II MIB, RFC 1213.)
The definition of the portInfoTable object can be used to illustrate how the ifIndex value specifies a unique port. the portInfoTable object organizes information about ports (interfaces) in much the same way as the cardTable object organizes card attributes. The index object in the portInfo table is an ifIndex value, defined as follows:
portInfoIndex OBJECT-TYPE
SYNTAX INTEGER
ACCESS read-only
STATUS mandatory
DESCRIPTION
"This is the ifIndex value of the corresponding
ifEntry. See comments above."
::= { portInfoEntry 1 }
Where the description text in this definition says "see comments above," it refers to comments at the beginning of the private MIB file. These comments describe the algorithm for defining the ifIndex value for a port. This algorithm can be expressed in the following formula:
The variables in this formula are as follows:
| c | The card number, an integer in the range 1 -- 11. A number in the range 1 -- 10 is the number of the physical slot in which the card resides. The number 11 represents the logical interface for the LS2020 ATM network. | |
| p | The port number on the card, an integer in the range 0 -- 7.
If c is 11 (the logical interface for the LS2020 ATM network), p must be 4. |
|
| t | An offset indicating the card type. This is an arbitrary numeric value assigned to each type of card. The values of t are as follows: | |
| 100
200 0 |
Ethernet or Fiber Ethernet
FDDI Other |
|
You can abbreviate this formula in the format ctp. For example, the MIB object that stores the alias or name for Port 3 on Card 4 is portInfoName.3104 for an Ethernet port, portInfoName.3204 for an FDDI port, or portInfoName.3004 for a port on any other type of card.
Some objects are indexed by more than one number. For example, a DLCI must be specified not only by a DLCI number but also by an ifIndex value identifying a port, and a multicast group is a list of member ports, each of which must be specified not only by its ifIndex value, but also by a chassis ID and a multicast group ID. The several parts of a complex object identifier are dot-separated integers.
For example, the output of the command getsnmp frCktInfoLclLMI.4002.16 in the following example tells us that the local LMI state of the frame relay circuit on DLCI 16, Port 4, Card 2 is inactive. (In the next section, you will see how to determine that the integer 2 here means that the local LMI state is inactive.)
cli> getsnmp frCktInfoLclLMI.4002.16 Name: frCktInfoLclLMI.4002.16 Value: 2 cli>
The double index 4002.16 means that this frCktInfoLclLMI object is indexed first by ifIndex value 4002 (Card 4, Type 0, Port 2) and then by DLCI number 16.
Interpreting Integer Values of MIB Objects
To interpret the value of a MIB object, refer to the definition of the object. In the last example in the preceding section, the value of the frCktInfoLclLMI.4002.16 object was displayed as 2. To interpret this value, examine the private MIB file and read the description text for frCktInfoLclLMI in the private_mib.asn MIB file. The definition of this object is as follows:
frCktInfoLclLMI OBJECT-TYPE
SYNTAX INTEGER {
active(1),
inactive(2)
}
ACCESS read-only
STATUS mandatory
DESCRIPTION
"This variable indicates the local LMI
state of the circuit."
::= { frCktInfo
The syntax field in this definition specifies that the value 2 means "inactive."
Major Branches of the Private MIB
The high-level structure of the LS2020 private MIB is shown in Figure 7-3.
Figure 7-3 : Structure of the LS2020 Private MIB
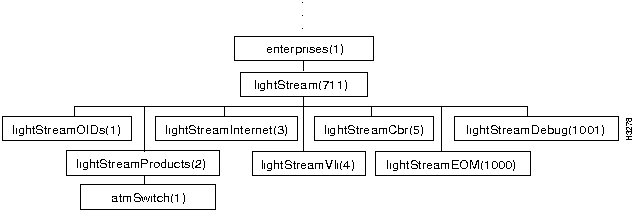
The major branches of the private MIB are described in the following sections:
Three objects shown in Figure 7-3 are not major branches of the MIB:
| lightStreamOIDs | Miscellaneous object identifiers |
| lightStreamEOM | The end-of-MIB mark |
| lightStreamDebug | MIB objects used for debugging |
Figure 7-4 shows the atmSwitch subtree, which comprises most of the LS2020 private MIB.
Figure 7-4 : The atmSwitch Subtree
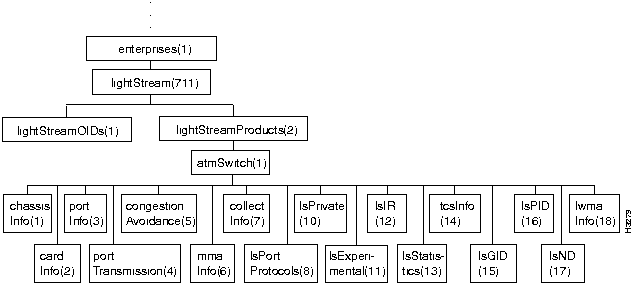
The branches of the atmSwitch subtree are described in the following sections:
Figure 7-5 shows the chassisInfo branch of the atmSwitch subtree.
Figure 7-5 : The chassisInfo Branch
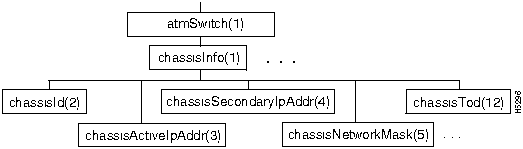
Figure 7-6 shows the cardInfo branch of the atmSwitch subtree.
Figure 7-6 : The cardInfo Branch
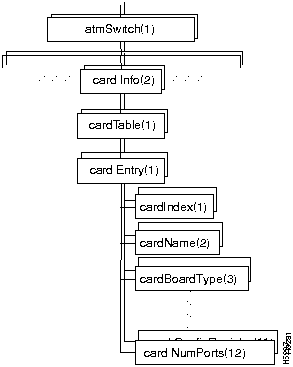
Figure 7-7 shows the portInfo branch of the atmSwitch subtree.
Figure 7-7 : The portInfo Branch
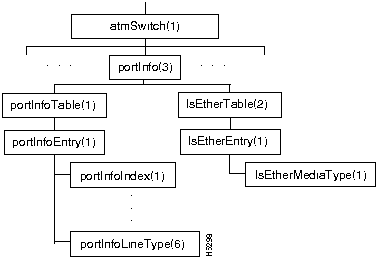
There are two tables in the portInfo branch, portInfoTable, in which each table entry contains information about one port on a card, and lsEtherTable, whose only entry is the lsEtherMediaType object.
Figure 7-8 shows the portTransmission branch of the atmSwitch subtree.
Figure 7-8 : The portTransmission Branch
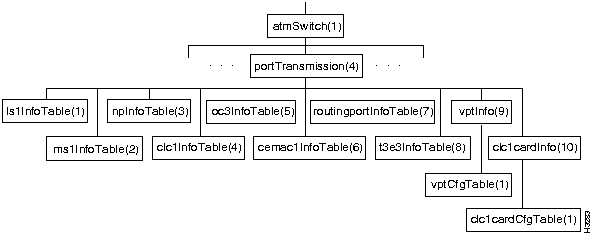
The objects in the portTransmission branch include a number of MIB object tables: one for each card type, one for cell routing information (controlling cell delay variation), and one for virtual path trunking. Each entry of a table for a card type (such as ls1InfoEntry, ms1InfoEntry, or npInfoEntry) contains information about a port on a card.
Figure 7-9 shows the objects in the congestionAvoidance branch of the atmSwitch subtree.
Figure 7-9 : The congestionAvoidance Branch
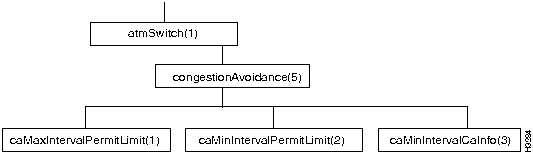
Figure 7-10 shows the mmaInfo branch of the atmSwitch subtree.
Figure 7-10 : The mmaInfo Branch
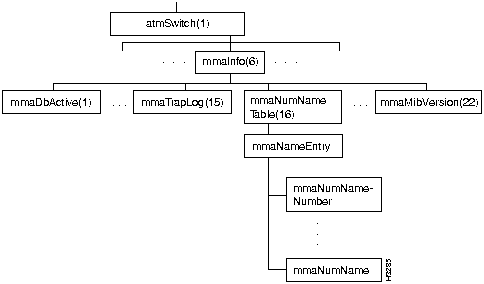
The mmaInfo branch contains one table, mmaNumNameTable.
Figure 7-11 shows the collectInfo branch of the atmSwitch subtree.
Figure 7-11 : The collectInfo Branch
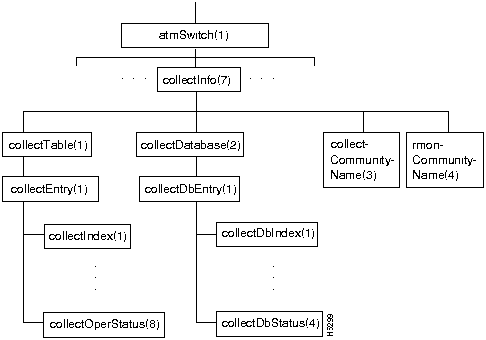
The collectInfo branch contains two tables:
Each row of each table contains information about a collection that has been defined. The collectInfo branch also contains the collectCommunityName and rmonCommunityName objects (the latter not currently used).
Figure 7-12 shows the lsPortProtocols branch of the atmSwitch subtree.
Figure 7-12 : The lsPortProtocols Branch
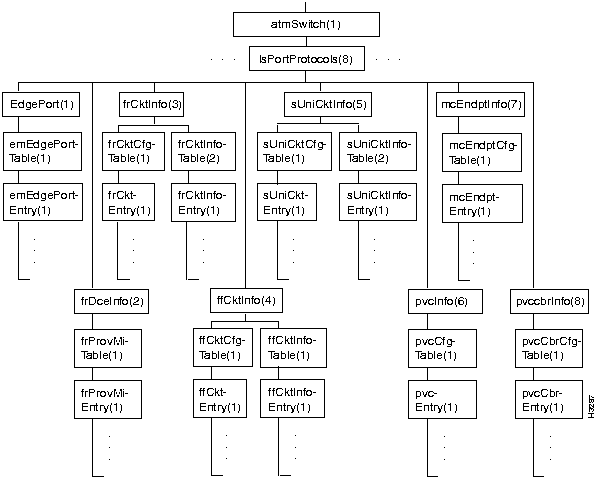
The lsPortProtocols branch includes a number of tables containing information about the various services available on an LS2020 network.
The lsPrivate branch of the atmSwitch subtree (atmSwitch.10) is reserved for use in later releases. It is currently empty.
Figure 7-13 shows portions of the lsExperimental branch of the atmSwitch subtree.
Figure 7-13 : The lsExperimental Branch
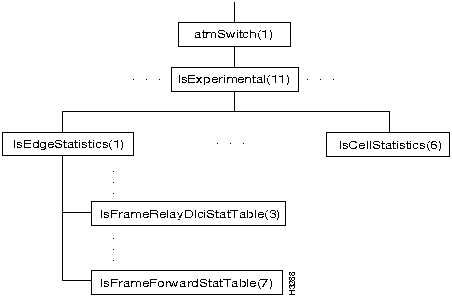
The lsExperimental branch contains objects that can be used by Cisco Systems to provide advanced support functions and analysis of network performance. This branch is little used. Three tables in this branch contain MIB objects that are used to collect cell statistics and to collect statistics on edge cards for frame relay and frame forwarding. These tables are
To obtain the statistical information associated with these MIB objects, use the getsnmp command.
Figure 7-14 shows the internal routing (lsIR) branch of the atmSwitch subtree.
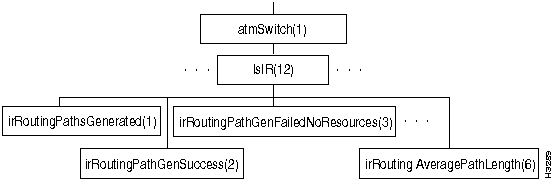
The lsIR branch contains objects pertaining to internal routing.
The lsStatistics branch of the atmSwitch subtree (atmSwitch.13) is currently empty. It will be used for objects (presently in the lsExperimental branch) that the LS2020 uses to analyze network performance.
Figure 7-15 shows the tcsInfo branch of the atmSwitch subtree.
Figure 7-15 : The tcsInfo Branch
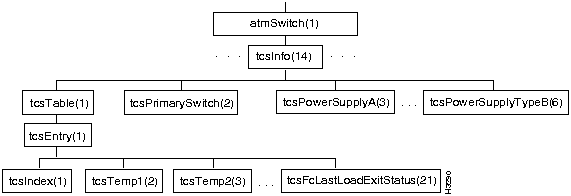
The tcsInfo branch contains objects pertaining to the test and control system (TCS).
Figure 7-16 shows the lsGID branch of the atmSwitch subtree.
Figure 7-16 : The lsGID Branch
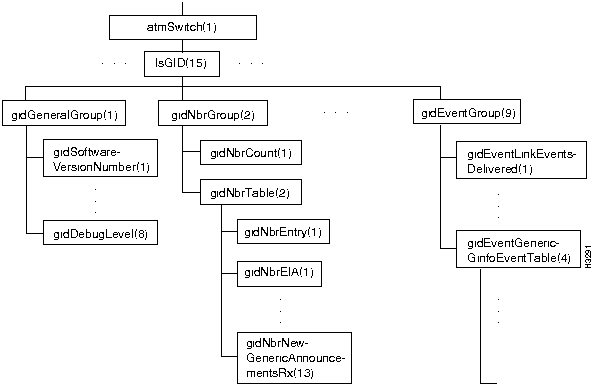
The lsGID branch contains objects pertaining to the global information distribution (GID) system.
Figure 7-17 shows the lsPID branch of the atmSwitch subtree.
Figure 7-17 : The lsPID Branch
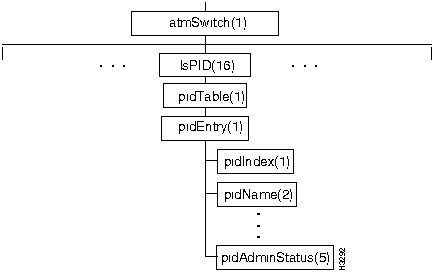
The lsPID branch contains objects that are concerned with operating system processes.
Figure 7-18 shows the lsND branch of the atmSwitch subtree.
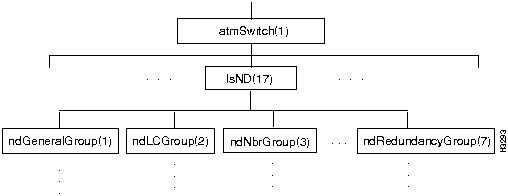
The lsND branch contains objects that pertain to neighborhood discovery.
Figure 7-19 shows the lwmaInfo branch of the atmSwitch subtree.
Figure 7-19 : The lwmaInfo Branch
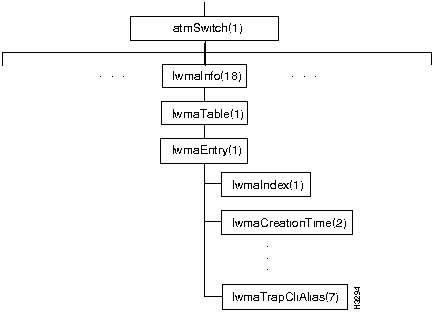
The lwmaInfo branch contains objects that pertain to the lightweight management agent (LWMA), which links application processes to the LS2020 network management system.
Figure 7-20 shows the lightStreamBridge and lightStreamLanPort branches in the lightStreamInternet subtree of the LS2020 private MIB. (The lightStreamInternet object is defined near the beginning of the MIB file.)
Figure 7-20 : The lightStreamInternet Subtree
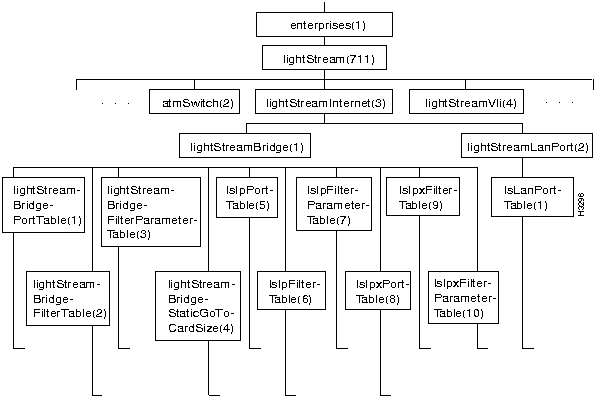
The lightStreamBridge branch contains objects that pertain to bridging, and the lightStreamLanPort branch contains objects that define port attributes required for LAN ports.
Figure 7-21 shows the lightStreamVli subtree in the LS2020 private MIB. (The lightStreamVli object is defined near the beginning of the MIB file.)
Figure 7-21 : The lightStreamVLI Subtree
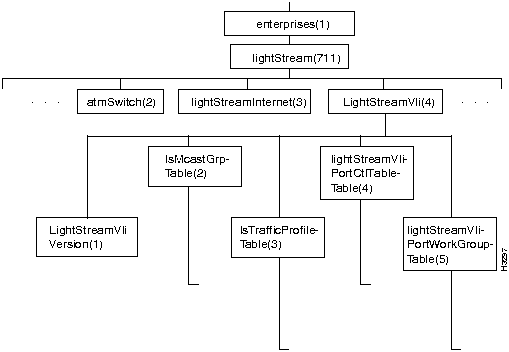
The lightStreamVli subtree contains objects that pertain to virtual LAN internetworking (VLI).
Figure 7-22 shows the lightStreamCbr subtree in the LS2020 private MIB. It contains one table, lsNtCfgTable, and a number of other objects relating to constant bit rate traffic.
Figure 7-22 : The lightStreamCbr Subtree
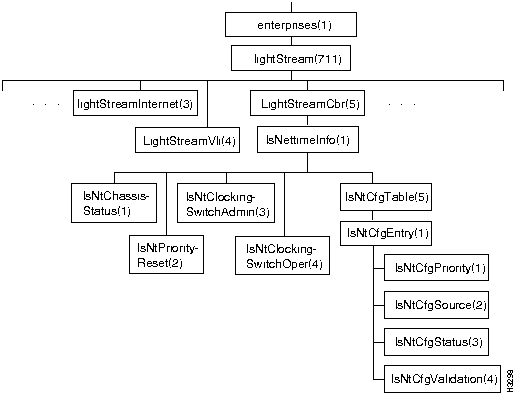
The lightStreamCbr subtree contains objects that pertain to constant bit rate traffic.
|
|
Copyright 1988-1996 © Cisco Systems Inc.