|
|
This chapter provides an overview of the workgroup CDDI/FDDI EISA PC adapters for EISA (Extended Industry Standard Architecture) PCs, information about the hardware and software required to run the EISA PC adapters, and unpacking information.
Workgroup high-performance CDDI/FDDI EISA PC adapters connect workstations and servers to CDDI or FDDI networks. The adapters provide a single attachment or dual attachment connection that is fully compliant with SMT (station management) Revision 6.2 (the FDDI station management specification).
The workgroup EISA PC adapters ensure high performance by maximizing data throughput and minimizing network overhead on the host processor. Downloadable firmware permits convenient upgrades and eliminates the need to swap PROM chips.
Workgroup EISA PC adapters feature a highly integrated design and several high-performance features to ease internal data flow and minimize overhead imposed on the host processor. To maximize throughput, EISA PC adapters support 32-bit wide EISA burst-data transfers. Bus mastering via two specially designed direct memory access (DMA) channels and an onboard SMT processor minimize host processor intervention.
EISA PC adapters incorporate SMT Revision 6.2. The adapter firmware is downloadable to enable you to easily update SMT versions.
Figure 1-1 shows the CDDI/FDDI EISA PC adapters.
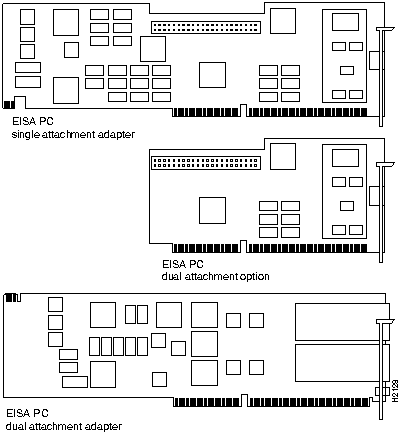
Figure 1-1 : Workgroup CDDI/FDDI EISA PC Adapters
The workgroup CDDI and FDDI EISA PC adapters are available for single attachment and dual attachment configurations.
Single attachment EISA PC adapters can connect to another station or to a concentrator, which in turn can connect to the dual ring of an FDDI network. A single attachment configuration consists of a single attachment adapter with an FDDI or CDDI port. The single attachment adapter is an S (slave) port. The workstation FDDI interface has one PMD (physical medium dependent) PHY (Physical), one MAC (media access control), and one SMT (station management).
The dual attachment configuration consists of either of the following:
A workstation with the dual attachment configuration connects directly to the primary and secondary rings of an FDDI network. The workstation FDDI interface has two PMDs, two PHYs, one MAC, and one SMT.
Figure 1-2 and Figure 1-3 show how single attachment stations and dual attachment stations are connected.
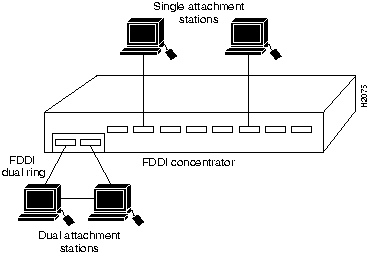
Figure 1-2 : Single Attachment and Dual Attachment Stations
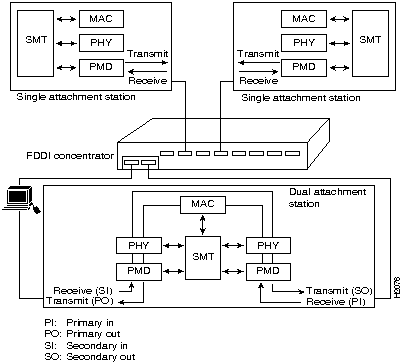
Figure 1-3 : Single Attachment and Dual Attachment Stations
You also can connect a dual attachment station in the redundant configuration called dual homing. Figure 1-4 is an example of a dual homing configuration A dual attachment station is connected to two concentrators that are connected to the dual ring. Port A on the station is the backup connection that only becomes active if the primary connection (Port B) fails.
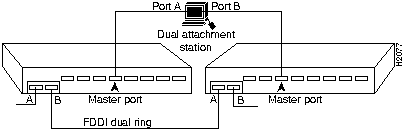
Each EISA PC adapter has two LED indicators on the faceplate for easy monitoring of the adapter internal status and the FDDI link. The FDDI dual attachment option adapter also has a connector for an optical bypass switch, while the FDDI dual attachment adapter has a connector for a bypass switch cable adapter. The LEDs and connector are shown in Figure 1-5.
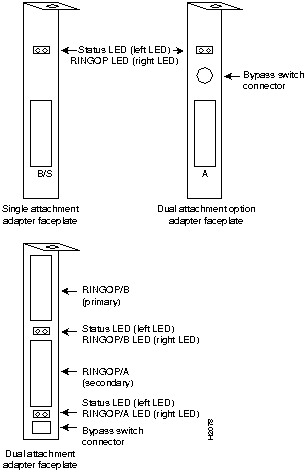
Figure 1-5 : Workgroup EISA PC Adapter Faceplates
The adapter LEDs descriptions follow:
The dual attachment FDDI adapter and optional dual attachment adapter have a connector for an optical bypass switch. When activated, a bypass switch removes a nonfunctioning dual attachment adapter from the ring. The 6-pin mini-DIN connector, used on the optional dual attachment adapter and bypass switch connector cable adapter, is compatible with most optical bypass switches. (For more information, see Appendix D, "Optical Bypass Switch Connector Pinout Information.")
Your EISA PC system must meet the following hardware requirements:
Your EISA PC system must meet the following software requirements:
Workgroup EISA PC Adapter Package
Upon receipt of your workgroup EISA PC adapter package, do the following:
Copyright 1988-1996 © Cisco Systems Inc.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()