Table of Contents
Preparing for Installation
Preparing for Installation
Before you install the workgroup EISA adapter, please read this chapter carefully.
Follow these guidelines to ensure general safety:
Warning Keep the equipment area clear and dust-free during and after installation.
- When you remove the PC or workstation cover, put it in a safe place.
- Keep tools away from walk areas where you and others could fall over them.
- Do not wear loose clothing that could get caught in the equipment. Fasten your tie or scarf and roll up your sleeves.
- Wear safety glasses when working under any conditions that might be hazardous to your eyes.
- Do not perform any action that could create a potential hazard to people or make the equipment unsafe.
Follow these guidelines when working on equipment powered by electricity.
Warning Before working on equipment that is connected to power lines, remove jewelry (including rings, necklaces, and watches). Metal objects will heat up when connected to power and ground and can cause serious burns or weld the metal object to the terminals.
- Locate the emergency power-off switch for the room in which you are working. Then, if an electrical accident occurs, you can act quickly to turn off the power.
- Before working on the system, turn off the power.
- Disconnect all power before doing the following:
- Installing or removing an adapter
- Working near power supplies
- Performing a software upgrade
- Do not work alone if potentially hazardous conditions exist.
- Never assume that power is disconnected from a circuit. Always check.
- Look carefully for possible hazards in your work area, such as moist floors, ungrounded power extension cables, and missing safety grounds.
- If an electrical accident occurs, proceed as follows:
- Use caution; do not become a victim yourself.
- Turn off power to the system.
- If possible, send another person to get medical aid. Otherwise, assess the condition of the victim and then call for help.
- Determine if the person needs rescue breathing or external cardiac compressions, then take appropriate action.
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) can damage equipment and impair electrical circuitry. It occurs when electronic components are improperly handled and can result in complete or intermittent failures.
Always follow ESD-prevention procedures when removing and replacing components. Ensure that the chassis is electrically connected to earth ground. Wear an ESD-preventive wrist strap, ensuring that it makes good skin contact. Connect the clip to an unpainted surface of the chassis frame to safely channel unwanted ESD voltages to ground. To properly guard against ESD damage and shocks, the wrist strap and cord must operate effectively. If no wrist strap is available, ground yourself by touching the metal part of the chassis.
Warning For safety, periodically check the resistance value of the antistatic strap, which should be between 1 and 10 meg ohms (Mohms).
Following are the site requirements for installation.
Choose a clean, dust free, (preferably) air-conditioned location. Avoid direct sunlight, heat sources, or areas with high levels of electromagnetic interference (EMI).
Because the adapter faceplate LEDs provide information you may need to monitor, make the rear of the PC or workstation accessible and leave sufficient clearance for cabling and service.
The source electrical outlet should be installed near the PC or workstation, easily accessible, and properly grounded. Power should come from a building branch circuit. Use a maximum breaker current rating of 20A for 110V or 8A for 230V. Note the power consumption ratings of each unit before you connect to a power source.
Following are the cabling requirements for installation. For pinouts of the CDDI cabling, refer to the appendix "Cabling and Pinout Information."
The multimode FDDI connectors on the workgroup EISA adapter accept 62.5/125-micron or 50/125-micron multimode fiber, with standard FDDI media interface connector (MIC)-type connectors.
Table 2-1 lists FDDI maximum transmission distances, and Figure 2-1 illustrates a multimode FDDI connector.
Table 2-1 FDDI Maximum Transmission Distances
| Multimode |
1.2 miles (up to 2 km) |
Warning Invisible laser radiation may be emitted from the aperture ports of the single-mode FDDI card when no cable is connected. Avoid exposure and do not stare into open apertures.
Figure 2-1 Multimode FDDI Interface Connector---MIC Type
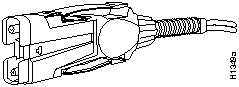
Check all existing cables for conformance with CDDI/multilevel transmission (MLT-3) distance requirements and to ensure that you have the proper connectors (modular RJ-45). See the appendix "Cabling and Pinout Information" for detailed cable usage.
Following are cable and distance specifications:
- Data-grade unshielded twisted-pair (UTP)
- Electronics Industries Association/Telecommunications Industry Association (EIA/TIA)--568 category 5, data-grade cable is recommended for CDDI installations. The total length of data-grade UTP cable from the adapter or media attachment unit (MAU) to the switch must not exceed 330 feet (100.6 meters), including patch cords and cross-connect jumpers.
- Shielded twisted-pair (STP) wiring
- Use IBM Type 1 STP wiring for your CDDI installation. The total length of STP cable measured from the adapter or MAU to the switch cannot exceed 330 feet (100.6 meters).
Note You must use high-performance, category 5, data-grade, modular cables for external connections.
When you plan your CDDI installation, remember the following:
- Do not use bridge taps.
- Do not use protection coils.
- Do not share services (such as voice and data) on the same cable. CDDI uses two of the four pairs in the twisted-pair cable. The remaining two pairs cannot be used for other applications.
- Do not exceed the maximum cable length for UTP and STP of 330 feet (100.6 meters).
To install the workgroup EISA adapter, you need the following tools and supplies:
- A flat-blade screwdriver
- ESD-preventive wrist strap (recommended)
- EISA adapter driver software media
Copyright 1988-1995
©
Cisco Systems Inc.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
