|
|
The MGS chassis is a modular chassis incorporating a four-slot Multibus backplane, which can support up to three network interface cards and one processor card. External connections to the network are provided by interface appliques attached to the rear of the chassis. These appliques are connected internally to the appropriate interface card by way of ribbon cables. Figure 1-1 shows the front of the MGS chassis, and Figure 1-2 shows the MGS rear panel and appliques.
Figure 1-1 MGS Chassis---Front View

Figure 1-2 MGS Chassis---Rear-Panel View
The C chassis is a modular chassis incorporating a two-slot Multibus backplane, which can accommodate up to two separate processor and interface cards. The required presence of the processor card leaves one slot that can be used for a Multibus interface card in the C chassis. There are two models: the CGS router and the CPT protocol translator. Figure 1-3 shows the front of the CGS chassis. Except for the product name, the CPT chassis front panel is identical to the CGS chassis.
Figure 1-3 CGS Chassis---Front View
The CGS chassis can support a single multiport Ethernet, serial, or Token Ring interface card for external network connection. External connections to the network are provided by interface appliques attached to the rear of the chassis. These appliques are connected internally to the appropriate interface card by way of ribbon cables. Figure 1-4 shows the CGS rear panel and appliques.
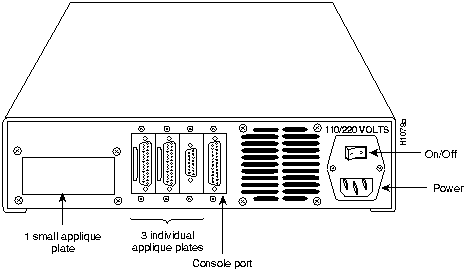
Figure 1-4 CGS Chassis Rear-Panel View
The CPT chassis can support a single multiport Ethernet or serial interface card for external network connection. The CPT chassis can only support one Ethernet interface port, but it will support up to two serial interfaces.
External connections to the network are provided by interface appliques attached to the rear of the CPT. These appliques are connected internally to the appropriate interface card by way of ribbon cables. Figure 1-5 shows the CPT rear panel and appliques.
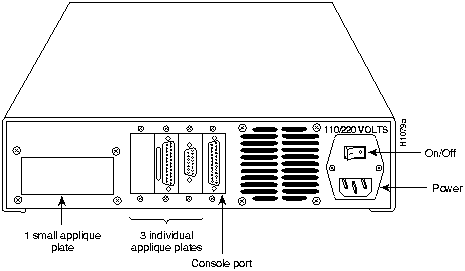
Figure 1-5 CPT Chassis---Rear-Panel View
Your responsibilities for bringing the MGS or C chassis on line will include installing the chassis (only the MGS can be installed in a rack), making external connections to various networks by way of appropriate interface cables, and using the configuration software routines specified in the appropriate getting started guide.
This publication applies to hardware installation only; it will take you through the installation up to, but not including, the configuration software routines.
The different models of the MGS and C chassis are identified by their size, card and interface capacity, configuration, physical characteristics, and specifications. These specific physical characteristics and specifications are noted in the following four tables.
Table 1-1 provides a summary of the physical specifications for the MGS chassis, and Table 1-2 describes the power and cooling specifications for the MGS chassis.
Table 1-1 MGS Chassis Physical Specifications
| Description | Physical Specifications |
|---|---|
| Multibus slots | 4-slot backplane (3 slots available due to processor card requirement) |
| Dimensions (H x W x D) | 5.25'' x 17.5'' x 20'' (13.33 cm x 44.45 cm x 50.8 cm) |
| Weight | 35 lb (15.9 kg) |
| Connectors | 2 small, 3 individual |
| Additional hardware | 19" rack-mount kit and optional slide-mount kit |
Table 1-2 MGS Chassis Power and Cooling Specifications
| Description | Power and Cooling Specifications |
|---|---|
| Power dissipation | 270W (918 Btu/hr) in the U.S.310W (1054 Btu/hr) in the U.K. |
| Input voltage and frequency | 120--240 VAC (U.S. only---autoranging), 50--60 Hz240 VAC (U.K. only---not autoranging), 50--60 Hz |
| Current rating | 2.3A @ 120 VAC (U.S.)1.2A @ 240 VAC (U.S. and U.K.) |
| Current and DC voltages available | U.S. 25A @ +5V; 2A @ -5V; 2.5A @ +12V; 2A @ -12VU.K. 20A @ +5V; 1A @ -5V; 2A @ +12V; 1A @ -12V |
| Cooling | 60 cfm(1) provided by two muffin fans |
| Fan noise | 45 dBa(2) |
Table 1-3 and Table 1-4 provide the specifications for the C chassis.
Table 1-3 C Chassis Physical Specifications
| Description | Physical Specifications |
|---|---|
| Multibus slots | 2-slot backplane (1 slot available due to processor card requirement) |
| Dimension (H x W x D) | 3.5'' x 15'' x 18'' (8.89 cm x 38.1 cm x 45.72 cm) |
| Weight | 15 lb (6.81 kg) |
| Connectors | 1 small, 3 individual |
Table 1-4 C Chassis Power and Cooling Specifications
| Description | Power and Cooling Specifications |
|---|---|
| Power dissipation | 230W (782 Btu/hr) in the U.S.270W (918 Btu/hr) in the U.K. |
| Input voltage and frequency | 120--240 VAC (U.S. only---autoranging), 50--60 Hz240 VAC (U.K. only---not autoranging), 50--60 Hz |
| Current rating | 2.3 A @ 120 VAC (U.S.)1.2A @ 240 VAC (U.S. and U.K.) |
| Current and DC voltages available | U.S. 25A @ +5V; 2A @ -5V; 2.5A @ +12V; 2A @ -12VU.K. 20A @ +5V; 1A @ -5V; 2A @ +12V; 1A @ -12V |
| Cooling | 30 cfm(1) provided by one muffin fan |
| Fan noise | 46 dBa(2) |
This section provides an overview of the following cards that can be used in the MGS and C chassis:
The processor card is the supervisor that contains and executes most of the programs that control the system. Table 1-5 lists the specifications for the central processing unit (CPU) cards that can be used in the MGS and C chassis.
Table 1-5 Processor Card Specifications
| Processor Card | Description |
|---|---|
| CSC/4 | 25-MHz clock speed MC68EC040 microprocessorand 16 MB of RAM |
| CSC/3 | 30-MHz clock speed MC68020 microprocessor and 4 MB of RAM |
Memory cards provide long-term, nonvolatile random-access memory (NVRAM) storage for configuration and data. Table 1-6 lists the memory cards available for the MGS and C chassis.
Table 1-6 Memory Card Specifications
| Memory Card | Description |
|---|---|
| CSC-MC | 32-KB NVRAM applique card that installs on the bottom of the chassis; no slot required. Requires a NVRAM connection to the CSC-MCI, CSC-1R, or CSC-2R(1) card. |
| CSC-MC+ | Optional memory card with a combination of 4 MB of Flash memory and 32 KB of NVRAM.Allows remote loading and storage of multiple software images. Installs on the bottom of the chassis; no slot required. Requires a NVRAM connection to the CSC-MCI, CSC-1R, or CSC-2R1 cards. |
| CSC-MT | Combination Multibus memory and NVRAM card that can be used in the MGS chassis only.Provides 48 KB of Multibus memory (for bus master cards) and 32 KB of NVRAM. Occupies one chassis slot in the MGS, leaving two slots available. |
Network interface cards connect the chassis to one or more networks. Table 1-7 describes the various network interface cards available for the MGS and C chassis and gives the chassis limitations for Token Ring interface cards.
Table 1-7 Network Interface Card Specifications
| Interface Card | Description |
|---|---|
| CSC-1R | MGS only---Single-port Token Ring interface card. 4- or 16-Mbps rate is user-selectable by way of software. |
| CSC-2R | MGS, CGS only---Dual-port Token Ring interface card.4- or 16-Mbps rate for each port is user-selectable by way of software. |
| CSC-MCI | Up to 2 Ethernet and 2 synchronous serial interface ports. Transmission rates up to 4 Mbps for serial and 10 Mbps for Ethernet.Serial ports configurable as DCE or DTE(1), Ethernet as Version 1 or 2. |
| CSC-R16M | MGS only---Single-port Token Ring interface card. 4- or 16-Mbps rate is user-selectable by way of a jumper. |
| CSC-SCI(2) | 4 synchronous serial interface ports.Transmission rates up to 4 Mbps for each port. Ports can be configured as DCE or DTE. |
The following sections discuss the card and port limitations for the MGS and C chassis models.
Table 1-8 provides a list of the card and port types (and the quantities of each) that can be installed in the MGS and CGS chassis.
Table 1-8 Card and Port Limits for the MGS and CGS Chassis
| Maximum No. of Ports | MaximumNo. of Cards | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Card Type | Interface/Port Type | MGS | CGS | MGS | CGS |
| CSC/3 or CSC/4(one or the other required) | ConsoleAuxiliary | 11 | 11 | 1-- | 1-- |
| CSC-1R | Token Ring | 3 | -- | 3 | -- |
| CSC-2R | Token Ring | 6 | 2 | 3 | 1 |
| CSC-MCI-2E2T or 2E2S | Ethernet and serial (any type) | 44 | 22 | 2-- | 1-- |
| CSC-MCI-1E1T or 1E1S | Ethernetand serial (any type) | 33 | 11 | 3-- | 1-- |
| CSC-MCI-2E | Ethernet | 6 | 2 | 3 | 1 |
| CSC-MCI-2S or 2T | Serial (not RS-449) | 6 | 2 | 3 | 1 |
| CSC-MCI-2S or 2T | RS-449 | 4 | 2(1) | 2 | 1 |
| CSC-R16M | Token Ring | 3 | -- | 3 | -- |
| CSC-SCI-4S or 4T(2) | RS-232 (and SDLC)or HD V.35 | 8 | -- | 2 | -- |
| CSC-SCI-4S or 4T1 | RS-449 | 4 | -- | 1 | -- |
The CPT chassis can support only one Ethernet interface, but it will support up to two serial interfaces. Token Ring interfaces cannot be used in the CPT chassis. The types and number of interface cards that can be used in the CPT chassis are listed in Table 1-9. The ports attach to the network by way of rear-panel appliques.
Table 1-9 Card and Port Limits for the CPT Chassis
| Card Type | Interface/Port Type | Maximum No. of Ports | Maximum No. of Cards |
|---|---|---|---|
| CSC-MCI |
Ethernet and serial(any type of serial)(1) | 1E1S, 1E1T, 1E2S, 1E2T, or 1E1S1T | 1 |
| CSC-MCI | Serial only | 2S or 2T | 1 |
External network connections to the MGS and C chassis are provided through a variety of rear-panel connector plates and appliques. Table 1-10 lists the available connector plates, their relative sizes, the maximum number of appliques per plate, and where the appliques can be positioned on the rear panel of the MGS or C chassis. Plates are listed from left to right when facing the rear panel of the MGS or C chassis. (See Figure 1-2, Figure 1-4, and Figure 1-5.)
Table 1-10 MGS and C Chassis Connector Plates
| MGS Chassis | C Chassis | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Connectors | Small Plate 1 | Small Plate 2 | Individual Plates |
Small Plate | Individual Plates |
| Token Ring(1) | 4 | 4 | 3 | 22 | 2(2) |
| Ethernet(3) | 4 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 2 |
| 10BaseT | 4 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 2 |
| RS-232 (and SDLC) | 4 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
3 |
| RS-449 | 2 | 2 | -- | 2(4) | -- |
| HD V.35 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 3 |
| X.21 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 3 |
| G.703 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 3 |
|
|
Copyright 1988-1995 © Cisco Systems Inc.