|
|
Cisco HyperSwitch A100 Software Configuration
This publication suggests a software configuration path for you to follow for the initial bring-up of the Cisco HyperSwitch A100 ATM switch in a minimum time.
![]()
These software configuration procedures are not a substitute for the Cisco HyperSwitch A100 User Guide, rather they are a guide for the expert user.
The initial software configuration procedures consist of the following:
Help with command syntax is available by entering a question mark at the system prompt.
For example:
> show pvc ? line All pvc set on specified line/VP detail PVC set on specified line/VP/VC
Refer to the Cisco HyperSwitch A100 User Guide for more information about commands.
This procedure describes connecting an EIA/TIA-232 cable from a console terminal to the HyperSwitch A100. To connect the cable, do the following:
Figure 1 Connecting a Console Terminal to a HyperSwitch A100
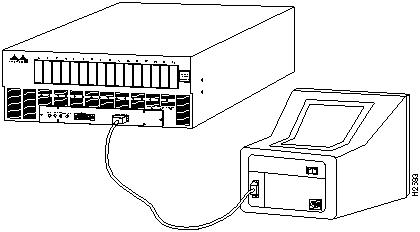
To set the HyperSwitch A100 and console terminal communications parameters, perform the following procedure:
Follow these steps when powering ON the HyperSwitch A100.
Cisco Systems, Inc. ATM HyperSwitch Software Version 1.2(0) Boot ROM Version K07 10 Sep 94 ATMSIG Version 1.2(0.4) Hardware Configuration: CPU Board : OK; Bus Convertor : OK; Switch Core : OK; Gateway PAD : OK; Slot 0: OC-3C(MMF) OK; Slot 1: Not Installed; Slot 2: Not Installed; Slot 3: Not Installed; Slot 4: Not Installed; Slot 5: Not Installed; Slot 6: 100M-TAXI OK; Slot 7: Not Installed; Slot 8: Not Installed; Slot 9: Not Installed; Slot10: Not Installed; Slot11: Not Installed; Slot12: Not Installed; Slot13: Not Installed; Slot14: Not Installed; Slot15: OC-3C(MMF) OK; System Initialization finished. >
> show version Software Version 1.2(0) Boot ROM Version K07 10 Sep 94 ATMSIG Version 1.2(0.4) >
> show status CPU :(Normal) SwitchCore :(Normal) Bus Interface :(Normal) FAN :(Normal) GWPAD :(Normal) Line0 :(Normal) Line1 :(NA) Line2 :(NA) Line3 :(NA) Line4 :(NA) Line5 :(NA) Line6 :(Normal) Line7 :(NA) Line8 :(NA) Line9 :(NA) Line10 :(NA) Line11 :(NA) Line12 :(NA) Line13 :(NA) Line14 :(NA) Line15 :(Normal)
Follow this procedure to enter the privileged mode.
passwd=c> enable passwd=c> Input password: ********
passwd=c#
The following procedures step you through an example of an initial configuration of the HyperSwitch A100.
Perform the following to set the local host name, IP address, and IP mask for the Ethernet port.
passwd=c# set local a100 99.99.10.10 255.255.255.0 a100#
The following sections contain examples of creating and deleting switched virtual circuits (SVCs). All of these examples are based on creating connections between two ATM hosts or routers, one connected to port 0 on the HyperSwitch A100 and the other ATM host or router connected to port 7 on the HyperSwitch A100.
Perform the following steps to add SVC routes.
a100# route add AA12345678 nsap 0 SVC route has been added. a100# route add BB12345678 nsap 1 SVC route has been added.
a100# show route
Destination Type 1st_Choice 2nd_Choice
AA12345678 XXXXXXXXXX XXXXXXXXXX XXXXXXXXXX NSAP 0 -
BB12345678 XXXXXXXXXX XXXXXXXXXX XXXXXXXXXX NSAP 7 -
a100# show svc 0
Line Number : 1
Uni/Bi Guaranteed/Best Effort Mbps LN VPI VCI LN VPI VCI
1 Best Effort 0.0 0 0 128 7 0 129
SVC route entries may be deleted one at a time or all at once with the following commands.
Enter route ? to determine the command syntax.
a100# route delete ?
<Destination> Destination Address
Type:NSAP Max:40char (0-9,A-F,X)
Type:E.164 Max:16char (0-9,X)
<Type> Type NSAP or E.164
a100#
To delete one route entry, enter the route delete command, as in the following example:
a100# route delete aa12345678 nsap SVC route has been deleted.
To delete the entire routing table, enter the route flush command, as in the following example:
a100# route flush SVC routing table has been flushed. a100#
The following is an example of how to create a PVC between an ATM host or router connected to port 0 on the HyperSwitch A100 and the ATM host or router connected to port 7 on the HyperSwitch A100. This example will establish a bidirectional best effort PVC between VPI/VCI 0/10 on port 0 to VPI/VCI 0/10 on port 7.
For example:
a100# pvc establish 1 1 0 0 0 10 512 1 7 0 10 512 1 ***Bi direction Best Effort Connection has been established. Low : 0, 0, 10, 512,1 High : 7, 0, 10, 512,1
The following examples show the available parameters of the pvc ? and pvc establish ? commands.
For example:
a100# pvc ? establish Establish PVC delete Delete PVC,line/VPI/VCI are required. add Add endpoint to existing uni-direction PVC remove Remove endpoint from existing uni-direction PVC a100#
For example:
a100# pvc establish ? <Direction> Direction of connection Uni(0),Bi(1) or Multicast(2) <Traffic> Traffic type Guaranteed(0) or Best Effort(1) <Throughput> Throughput 0-155(Mbps) <LowLine> Low line number 0-15 <LowVP> Low VPI 0-4095 <LowVC> Low VCI 0-4095 <LowUPVP> Low UPVP 0-512 <LowCOOP> Low COOP 1:Discard violated cells 0:Pass violated cells <HighLine> High line number 0-15 <HighVP> High VPI 0-4095 <HighVC> High VCI 0-4095 <HighUPVP> High UPVP 0-512 <HighCOOP> High COOP 1:Discard violated cells 0:Pass violated cells
To display PVC information, enter the show pvc line or show pvc detail command as in the following example:
a100# show pvc detail 0 0 10
Direction of Connection:Bi
Traffic Type:Best Effort
Throughput :0Mbps
Low Line Number, VPI, VCI , UPVP,COOP:
0 , 0, 10, 512, 1
High Line Number, VPI, VCI , UPVP,COOP:
7 , 0, 10, 512, 1
a100#
Enter the show pvc line ? and show pvc detail ? to determine further command options, as in the following examples:
a100#sh pvc line ? <Line> Line number 0-15 <VPI> VPI 0-4095 a100# a100#sh pvc detail ? <Line> Line number 0-15 <VPI> VPI 0-4095 <VCI> VCI 0-4095 a100#.
To save configuration changes, enter the save command, as follows:
a100# save Now Data saving ! Please do NOT push reset button till the "save" is complete........ System data has been saved. a100#
Connect one HyperSwitch A100 to another HyperSwitch A100 by designating one HyperSwitch A100 as the slave (the user side of the UNI). The following example sets port 7 to slave mode for connecting to another HyperSwitch A100.
a100# show atmsig Line Number M/S T303 T308 T309 T310 T313 T316 T317 T322 T398 T399 0 Master 4 30 90 10 4 120 60 4 4 14 7 Master 4 30 90 10 4 120 60 4 4 14 a100# set svcline 7 suspend SVC status of the Line Interface 7 : Suspended a100# set atmsig 7 slave 4 30 90 10 4 120 60 4 4 14 a100# set svcline 7 resume SVC status of the Line Interface 0 : Resumed a100# show atmsig Line Number M/S T303 T308 T309 T310 T313 T316 T317 T322 T398 T399 0 Master 4 30 90 10 4 120 60 4 4 14 7 Slave 4 30 90 10 4 120 60 4 4 14 a100#
Enter the save command to save the configuration change.
Refer to the Cisco HyperSwitch A100 User Guide for additional command information.


|
|
Copyright 1988-1995 © Cisco Systems Inc.