|
|
Troubleshooting Cisco 700 Series Routers
Each of the Cisco 700 series routers is thoroughly tested before it is shipped from the factory. Although it is unlikely that the router will exhibit any problems, if your Cisco 700 series router appears to have any operating problems, read this chapter to identify the problem.
The following sections describe troubleshooting particular kinds of problems:
The Cisco 750 series routers have a set of 11 to 14 (depending on the model) LEDs on the front panel. The Cisco 760 series routers have a set of 12 to 14 LEDs on the front panel. In addition to indicating operation status, these LEDs indicate problems that might occur during the power-on process.
Figure 8-1 illustrates the LEDs that appear on the Cisco 750 series routers.
Figure 8-1 : Cisco 750 Series Front Panel LEDs (Cisco 753 Shown)
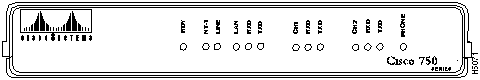
See Table 8-1 for a list of Cisco 750 series model numbers that do not have one or more of the LEDs shown in Figure 8-1.
Table 8-1 : Cisco 750 Series LEDs
| Model | LEDs Not Included |
|---|---|
| Cisco 751 | NT-1, Phone |
| Cisco 752 | Phone |
Figure 8-2 illustrates the LEDs that appear on the Cisco 760 series routers.
Figure 8-2 : Cisco 760 Series Front Panel LEDs (Cisco 766 Shown)

This section describes the functions of the Cisco 700 series routers' LEDs.
The front panel LEDs display the activity status of the router as connections are made and as packets are sent and received.
Table 8-2 lists the LEDs and their functions.
Table 8-2 : Front Panel LED Functions
| LED | Function |
|---|---|
| RDY (Cisco 750 Series)RD (Cisco 760 Series) | Indicates the router's operating status. Lights when power is supplied to the router and when the router completes its self-test procedure and begins operating. |
| NT1 (Cisco 752, Cisco 753, Cisco 762 and Cisco 766 only) |
|
| LINE | Lit (unblinking) indicates synchronization between the NT-1 S interface and the ISDN terminal device(s). Also indicates framing between the router and the ISDN switch. |
| LAN | Lights when packets are sent to or received from the Ethernet within the last minute. |
| LAN RXD | Blinks when packets are received from the Ethernet. |
| LAN TXD | Blinks when packets are sent to the Ethernet. |
| CH1 | Blinks when a call is being connected on the first ISDN B channel. After the call is established, the LED remains lit without blinking. |
| CH1 RXD | Blinks when packets are received from the first ISDN B channel. |
| CH1 TXD | Blinks when packets are sent on the first ISDN B channel. |
| CH2 | Blinks when a call is being connected on the second ISDN B channel. After the call is established, the LED remains lit without blinking. |
| CH2 RXD | Blinks when packets are received from the second ISDN B channel. |
| CH2 TXD | Blinks when packets are sent on the second ISDN B channel. |
| PHONE(Cisco 753 only) |
|
| PH 1PH 2(Cisco 765 and Cisco 766 only) |
|
There is one LED on the router's rear panel: the LINK LED. The LINK LED remains lit when the router is configured to function as an Ethernet hub or when the router is connected to an Ethernet hub.
The front panel LEDs can be used for diagnostic purposes. When the router is powered on, it performs a series of self-tests. After these tests are completed, any operational problem is represented by a combination of lit and unlit LEDs.
Table 8-3 lists the combinations of lit and unlit LEDs and their significance.
Table 8-3 : LED Error Messages
| RDY | NT1 | LINE | CH1 | CH2 | Test Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| On | Blinking several times per second | See Note1 | Internal NT1 is unable to synchronize with the ISDN switch | ||
| On | Blinking one time per second | Internal NT1 is synchronized with the ISDN switch, but is unable to synchronize with the ISDN terminal devices | |||
| On | Waiting for software | ||||
| On | On | On | On | Processor inactive | |
| Processor self-test error | |||||
| On | EPROM2 checksum error | ||||
| On | RAM3 error | ||||
| On | On | Flash memory error | |||
| On | On | HDLC4 packet chip error | |||
| On | On | Configuration port error | |||
| On | On | On | ISDN interface chip error |
The following conditions are often caused by router configuration problems:
If the router calls itself, check that the number configured with the set number command is not the same number configured with the set directory number command.
ISDN supports two separate logical data channels on the same physical line. If these two numbers are the same, the router might attempt to call itself when on-demand dialing is enabled or if the user issues the call command.
Terminal Identifier or SPID Problems
Either of the following two messages received on your terminal might indicate a SPID configuration problem:
Channel Not Available Facility Not SubscribedCheck for the following conditions:
If outgoing calls are unsuccessful, check the following conditions:
If an outgoing call is initially successful and then rejected, check for the following conditions:
If you have problems connecting to the 10BaseT Ethernet network, check the node/hub configuration. On the Cisco 750 series routers, this configuration is set by moving a set of five jumpers inside the chassis. On the Cisco 760 series routers, this configuration is set with a switch labeled HUB/NODE on the rear panel. For more information, refer to the appendix "Configuring Cisco 750 Series Routers to Operate as an Ethernet Hub."
Software load errors can occur when downloading new software. If an error occurs during a software download, a combination of blinking LEDs will indicate the problem. An error code will also be displayed on the terminal.
Table 8-4 lists the combination of blinking LEDs that indicate an error, along with the error code and a description of the error.
Table 8-4 : LED Error Messages---Software Download
| Blinking LED | Error Code | Description of Error |
|---|---|---|
| Line CH 2 |
E-1 | A framing, parity, or overflow error occurred during software download, usually because of an incorrect data rate or configuration port setting. Check the data rate and configuration port settings. |
| CH 1 | E-2 | A colon did not occur at the beginning of a line in the new software image file. Either the software image file is corrupted, or some characters were entered before the download started. Start the software load process again. If the same error occurs, contact Cisco for a new software image file. |
| Line CH 1 |
E-3 | One line in the software image file has a bad checksum, usually because of a temporary line error. Start the software download process again. |
| Line CH 1 CH 2 |
E-5 | The software image file has a bad or missing checksum. Start the software load process again. If the same error occurs, contact Cisco for a new software image file. |
|
|
Copyright 1988-1996 © Cisco Systems Inc.