|
|
Overview of CiscoSecure UNIX Server Software
Security is an increasingly important aspect of the growth and proliferation of LANs and WANs. You want to provide easy access to information on your network but you also want to prevent access by unauthorized personnel. CiscoSecure UNIX Server software is designed to help ensure the security of your network and track the activity of people who successfully connect to your network. CiscoSecure UNIX Server software uses the Terminal Access Controller Access Control System (TACACS)+ protocol to provide this network security and tracking.
TACACS+ uses Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting (AAA) to provide network security and enable you to control access to your network from a central location. (See the sections "Authentication," "Authorization," and "Accounting" later in this chapter.) Each facet of AAA significantly contributes to the overall security of your network, as follows:
AAA within a client/server architecture (in which transaction responsibilities are divided into two parts: client [front end] and server [back end]) allows you to store all security information in a single, centralized database instead of distributing the information around the network in many different devices. You can use CiscoSecure UNIX Server software to make changes to the database that administers security on your network on a few security servers instead of making changes to every network access server (NAS) in your network.
Using CiscoSecure UNIX Server software, you can expand your network to accommodate more users and provide more services without overburdening system administrators with security issues. As new users are added, system administrators can make a small number of changes in a few places and still ensure network security.
Features of CiscoSecure UNIX Server Software
The AAA features of CiscoSecure UNIX Server software satisfy most access security requirements. CiscoSecure UNIX Server software uses Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP), which provides a reliable connection between the client and server, an important feature for guaranteed network security and accountability. CiscoSecure UNIX Server software has the following features:
CiscoSecure UNIX Server software is comprised of two components: a daemon (long-running) server and a graphical user interface (GUI). The daemon relies on two files for its operation, a control file defining all system-wide parameters and an Authentication and Authorization (AA) database file that contains information about the users of your network. The GUI is used to maintain the user AA database.
Using the CiscoSecure UNIX Server software saves memory in all the access devices and eliminates the need to update every network access server when new users are added, authorization is modified, or users change their passwords.
CiscoSecure UNIX Server and the Network Access Server
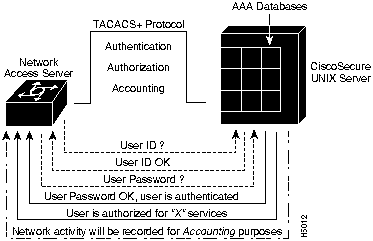
The CiscoSecure UNIX Server software does the actual work of verifying AAA, and responds to the network access server for access requests by users outside the LAN. Using the TACACS+ protocol, the network access server sends authentication requests to the CiscoSecure server, which then verifies the user password and returns a success or failure response to the network access server.
When the user has been authenticated, a set of session attributes can be sent to the network access server to provide additional security. These attributes can include per-user access lists, specific services that can be used, and session timeout values.
Figure 1-1 illustrates a scenario in which the process of AAA is performed by the network access server and the CiscoSecure server.
Figure 1-1 : TACACS+ Protocol from Network Access Server to CiscoSecure server
CiscoSecure UNIX Server Graphical User Interface
The GUI enables you to modify the authorization and authentication parameters of any group or user on your network. Users may be assigned to groups that have a set of common configuration parameters. The parameters of each user may then be further modified to reflect the differences between each user. The GUI provides a point-and-click interface to administer the user database. (See the chapter "CiscoSecure UNIX Server Graphical User Interface.")
Three Keys to Network Security
Reliability and security are key concerns in managing networks. When you implement security features, you need to have the following information available:
The AAA features of CiscoSecure UNIX Server software help you to monitor and control this information.
Authentication allows network managers to bar intruders from their networks. Simple authentication methods use a database of usernames and passwords, while more complex methods use one-time passwords.
CiscoSecure UNIX Server software uses the TACACS+ protocol to accept usernames or password information sent to a network access server by different protocols such as the AppleTalk Remote Access protocol (ARA protocol), Serial Line Internet Protocol (SLIP), Password Authentication Protocol (PAP), Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol (CHAP), and standard Telnet. This broad protocol support allows network administrators the flexibility to define the same or different usernames and passwords for different protocols. CiscoSecure UNIX Server software supports the following password management features:
Authorization allows network managers to limit which network services are available to each user. Authorization also helps restrict the exposure of the internal network to outside callers and simplifies the view of the network.
Authorization allows mobile users to connect to the closest local connection and still have the same access privileges they would have if they were directly connected to their local networks. You can also use authorization to specify which commands a new system administrator can issue on specific network devices.
The CiscoSecure UNIX Server software also supports the following features:
System administrators may need to bill departments or customers for connection time or resources used on the network (for example, bytes transferred). Accounting tracks this kind of information. You can also use accounting to track suspicious connection attempts into the network.
Because CiscoSecure UNIX Server software uses TCP/IP, its accounting information database receives reliable accounting information, providing a secure and complete accounting log. The accounting portion of AAA contains the following information:
The billing information includes connect time, user ID, connection location, amount of data transferred, start time, and stop time.
The following features are also supported:
Operation of CiscoSecure UNIX Server Software
CiscoSecure UNIX Server software uses a control file and a set of AA database files containing user and group configuration information. At startup, the server reads the control file, which contains parameters that tailor the server's operation, lists the files in the AA database, and a list of NAS-specific parameters (such as encryption key and NAS name). The AA database is then read into memory where it is stored in a way that minimizes memory storage and retrieval time, both of which are important for optimum performance of the server with large numbers of users.
Modifications to the control file or AA database can be made at any time, after which the server is instructed to reload. During a reload operation, the previous version of the control file and AA database are used to continue servicing user requests, providing nonstop operation to users. The standard UNIX signal mechanism is used to inform the server of changes to these files. When a signal is sent, the server rereads the files and builds a new internal AA database. While this occurs, AAA requests continue to be serviced based on the previous AA database, making the transition from the previous AA database to the new one completely transparent.
User password changes are recorded in a log file, which can be integrated with an existing AA database by running CiscoSecure UNIX Server software with the -u flag. This preserves user password changes over system reboots. (See the chapter "Using CiscoSecure UNIX Server Software.")
Another file, the accounting database, is where all accounting information is stored. The CiscoSecure UNIX server checks this file periodically and re-creates it if the previous file has been moved to a new filename. No accounting transactions are lost during this process.
CiscoSecure UNIX Server software is licensed according to the number of network access server ports; in addition, you must acquire a license key from Cisco Systems in order to enable the product. (See Step 6 in the section "Installing CiscoSecure UNIX Server Software" in the chapter "Getting Started with CiscoSecure UNIX Server Software.") The key authorizes a specific number of network access server ports to be recognized and multiple keys may be used to increase the number of licensed ports. (See the section "Licensing" in the chapter "Using CiscoSecure UNIX Server Software.") In addition, you can use a backup server license to allow sites to run fully redundant systems to facilitate a check-and-balance system of security and accounting service.
|
|
Copyright 1988-1996 © Cisco Systems Inc.