|
|
Using the CiscoWorks NetView Interface
This chapter contains the following topics:
This section describes how the PCA is used to monitor and troubleshoot router activity via NetView. This process is completed by converting network traps and events into SNA Network Management Vector Transport (NMVT) or alerts.
Once you start the PCA using the SNM console Glyph menu command, PCA Start, PCA registers itself with the SNM event dispatcher to receive all the SNMP events and traps. There is no manual intervention required. Once the event or trap is received, it is converted to an NMVT and can be viewed on the NetView NPDA screen. See Figure 6-1.
For more details on the PCA, refer to the 7.0 SunLink SNA Peer-to-Peer Administrator's Guide.
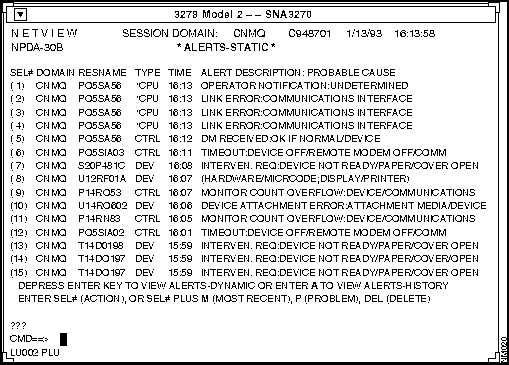
Figure 6-1 : Events Displayed in IBM NetView's NPDA Screen
PCA runs as a part of SunNet Manager (SNM). The SNM event logger receives events and traps and shares this data with the PCA.
The RUNCMD process allows you to perform certain system administration functions from the NetView console. For the RUNCMD process, the CiscoWorks NetView Interface shares the functionality of CiscoWorks with NetView. These RUNCMD commands are issued at the NetView console.
CiscoWorks NetView Interface receives RUNCMD requests from NetView operators and executes the commands on the local UNIX system. To execute the RUNCMD in the IBM NCCF facility, the IBM NetView operator has to edit the scope of command for their operators. Refer to the IBM manual, NetView Installation and Administration SC30-3476.
The following process describes the interaction between the NetView console and the CiscoWorks NetView Interface. The IBM NetView operator issues and displays the RUNCMD requests and receives output on the NetView Command Control Facility (NCCF).
The following conditions must be satisfied in order for the RUNCMD process to work:
You can invoke the RUNCMD commands from the CiscoWorks workstation. For example, entering netmenu at the UNIX prompt will display the available RUNCMD commands.
The sample show_if_ids RUNCMD file is available on Cisco Systems CiscoWorks FTP public area. This file displays the ifIndex for each interface. You can substitute any SQL queries to create different customized commands. The show_if_ids file is located in the CiscoWorks/sql directory. For instructions on obtaining this file using FTP, refer to "Obtaining Additional Information" in the CiscoWorks NetView Interface Installation and User Guide.
The following section describes the general syntax of the RUNCMD and lists the command options.
Before a NetView operator can request information via RUNCMD commands, the IBM system administrator must locally define the NetView operator's access rights for command requests. Contact your IBM system administrator and request this type of access. For more information on editing the scope of command, refer to the IBM document, NetView Installation and Administration SC30-3476.
Use the following syntax to specify RUNCMD requests:
The following list describes the command parameters of this syntax:
Table 6-1 describes the CiscoWorks-supported RUNCMD commands available with the CiscoWorks NetView Interface. These commands and their parameters are described in greater detail later in this chapter. For more information on adding your own commands to the RUNCMD file, refer to the next section, "Writing a Customized RUNCMD."
Table 6-1 : RUNCMD Command Descriptions
From the NetView console at the NCCF facility, the operator types in the RUNCMD string. The RUNCMD requires that you indicate the device, or service point, you are sending the RUNCMD to and a command string to pass to the service point. The RUNCMD commands are not case sensitive.
Figure 6-2 shows an example window of a RUNCMD request and the response from CiscoWorks.
Figure 6-2 : RUNCMD Request from NCCF Facility The following sections describe each RUNCMD command in greater detail and provides examples of these commands and resulting system output.
Use the cmpconf command to compare a given device's configuration file stored in Sybase with a current configuration on a Cisco device. This command generates output similar to the CiscoWorks Configuration Management application.
For more information on configuration management, refer to the CiscoWorks User Guide, Chapter 5, "Managing Cisco Device Configurations."
Where:
This command sends a response similar to the following to NetView:
Use the contacts command to retrieve emergency contact information including names, phone numbers, and addresses for an administrator of a Cisco device. This command retrieves this information from the CiscoWorks database (Sybase) and generates output similar to CiscoWorks Contacts application. For more information on the CiscoWorks Contacts application, refer to Chapter 3, in the section "Using Device Contacts" in the CiscoWorks User Guide.
Where:
This command sends a response similar to the following to NetView:
If there are no contacts in the database for this device, you receive the following message:
Use the getconf command to retrieve a Cisco router's configuration file.This command generates output similar to the CiscoWorks Configuration Management application.
Where:
This command sends a response similar to the following to NetView:
Use the ifstatus command to retrieve Cisco device's interface status. This command generates output similar to an SNM Quick Dump:cisco:ifstatus function for a requested interface. This command uses the SNM snm_cmd command, which queries on a given interface by name. Refer to the SunNet Manager 2.0 Reference Guide for more information on snm_cmd.
Where:
This command sends a response similar to the following to NetView:
Use the neticmp command alone or with other information.This command allows a quick comparison of cumulative ICMP activity and generates output similar to Show IP Traffic from the CiscoWorks Show Commands application.
Refer to the Router Products Configuration and Reference publication for a detailed description of the show ip traffic command.
Where:
This command sends a response similar to the following to NetView:
Use the netif command to access Cisco device interface information. This information includes the interface name, IP address, IP net mask designation, input packets and errors, and output packets and errors. This command generates output similar to Show Interface from the CiscoWorks Show Commands application.
Refer to the Router Products Configuration and Reference publication for a detailed description of the show interface command.
Where:
This command sends a response similar to the following to NetView:
Use the netmenu command to provide a list of available RUNCMD commands in the CiscoWorks NetView Interface.
In the following netmenu command statement, the NetView operator requests the list of RUNCMD commands.
The following response is sent to NetView:
Use the netroute command to display Cisco device routing table information. This command generates output similar to Show IP Route in the CiscoWorks Show Commands application.
Refer to the Router Products Configuration and Reference publication for a detailed description of the show ip route command.
Where:
This command sends a response similar to the following to NetView:
Use the netset command to change a Cisco device's interface status to up or down. This command uses the SNM snm_cmd.
Refer to the 7.0 SunLink SNA Peer-to-Peer Administrator's Guide for a detailed description of the snm_cmd command.
Where:
This command sends a response similar to the following to NetView:
Use the netstatus command to query Cisco device status information, including device uptime and software version. This command generates output similar to Show Version in the CiscoWorks Show Commands application.
Use this command to provide version information when you contact your technical support specialist. Refer to the Router Products Configuration and Reference publication for a detailed description of how to read the version data.
Refer to the Router Products Configuration and Reference publication for a detailed description of the show version command.
Where:
This command sends a response similar to the following to NetView:
Use the shomibvar command to show the value of specified Cisco group MIB variables from Cisco devices. A list of supported Cisco group MIB variables appears in Table 6-2. This table includes group MIBs from Software Release 8.1 through 9.1.
Where:
Table 6-2 : Supported Cisco Group MIB Variables for Use with shomibvar
This command sends a response similar to the following to NetView:
Use the showflash command to show the Flash memory data on a Cisco devices.
Refer to the Router Products Configuration and Reference publication for a detailed description of the show flash command.
Where:
The following is an example showflash command:
This command sends a response similar to the following to NetView:
Use the showif command to retrieve device interface information from the CiscoWorks database.
Where:
This command sends a response similar to the following to NetView:
The standard output response includes the interfaces that are active and their address.
Use the tracepath command to display a network path as a series of network hops. This command uses the CiscoWorks Path Tool application in ASCII output.
Where:
This command sends a response similar to the following to NetView:
In addition to the standard RUNCMD commands provided by the CiscoWorks NetView Interface, you can add customized commands. These customized commands format CiscoWorks output as UNIX standard output to the NetView console.
The following are examples of why you might write a customized command:
To write your own customized command statement, perform the following steps:
Step 1: Create an executable shell program containing the command request that generates a response as UNIX standard output.
Step 2: Place the shell program in a directory where your PATH statement can locate it.
Step 3: Create a directory named $NMSROOT/temp/custom_cmds to store any customized RUNCMDs you create.
Step 4: To add this directory to your path, edit your .cshrc file and add the $NMSROOT/temp/custom_cmds directory to the path.
Use the RUNCMD statement you have written just as you would any other RUNCMD command at the NetView console. There are no limits to the number of customized RUNCMDs you can create. Just be aware of your system memory limitations.
This document includes a sample of a customized RUNCMD commands. This sample customized RUNCMD collects interface data on a device or devices you specify.
You can edit this sample script and rename it if you want to extend the list of customized commands you have at your disposal.
Sample Customized RUNCMD for Collecting Interface Data
This section contains a sample customized RUNCMD designed to display the ifIndex value for each interface on a device. The RUNCMD name is show_if_ids.
The important part of the show_if_ids script is the Structured Query Language (SQL). SQL is a high-level language for the Sybase relational database. The SQL statement in the script contains the following statements:
The following list describes what function each line performs in the previous SQL statement:
For more information on SQL and Sybase, refer to your Sybase documentation set (Transact-SQL User's Guide and System Administration Guide).
Running the show_if_ids command
Use the following syntax to request your customized RUNCMD:
Where:
The following is an example show_if_ids command:
This command sends a response similar to the following to NetView:
Sample show-if-ids RUNCMD Script
The following is the customized script for show_if_ids command. You can substitute other MIB variables and parameters to create different customized commands.
To run your own customized command statement, specify your RUNCMD syntax at the NetView console.
The following response is sent to NetView:
Creating a Customized Event Table for PCA
This section contains a sample CiscoWorks event table for the SNM Protocol Conversion Application (PCA). Edit the event table to reflect this custom table.
For detailed information on event table format, refer to the 7.0 SunLink SNA Peer-to-Peer Administrator's Guide.
Copyright 1988-1996 © Cisco Systems Inc.
![]()
Command
Command Parameters
When to Use
cmpconf1
device user password
To compare a device's configuration file with the one in the CiscoWorks database.
contacts
device
To retrieve available contact information on a device from the CiscoWorks database if that device goes down.
getconf1
device community user password
To retrieve a Cisco router's configuration file.
ifstatus
device.domain interface
To query a Cisco device's interface status.
neticmp
device.domain community
To show a device's ICMP information.
netif
device.domain community
To access interface activity to assess potential problem areas, such as error rate inconsistencies or threshold, packet volume thresholds, or underutilization of a circuit.
netmenu
None
To access a list of available RUNCMDs provided by the CiscoWorks NetView Interface.
netroute
device.domain community
To review the current status of network destination nodes and interface traffic.
netset
device.domain interface_name2 up/down
To set a devices interface up or down.
netstatus
device community
To query a remote device's status information including device uptime and software version. Provide this version information when you contact your technical support specialist.
shomibvar
device.domain variable_name
To show the value of specified Cisco MIB variables from Cisco devices.
showflash
device.domain community
To retrieve Flash memory data on a Cisco device.
showif
device user password
To retrieve the interface information of a Cisco device from the CiscoWorks database.
tracepath
source destination
To display a network path as a series of network hops.
1 cmpconf and getconf use the community string from the Sybase database, which should be RW (ReadWrite) accessible.
2 The domain and interface_name must be spelled out. For example, device_1.cisco.com ethernet0. This device must also have a Write community string defined on the SNM Properties sheet for snm_cmd to work properly.
![]()
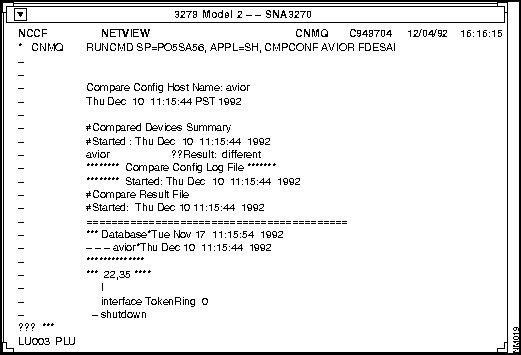
RUNCMD sp=CISCONV,appl=sh,cmpconf
device user password
The following is an example cmpconf
command:
RUNCMD sp=CISCONV,appl=sh,cmpconf device_1 nms beta
Compare Config Host Name: device_1
Thu Mar 11 11:15:44 PST 1993
#Compared Devices Summary
#Started : Thu Dec 10 11:14:44 1992
device_1 //Result: different
******** Compare Config Log File ********
******** Started : Thu Dec 10 11:15:44 1992
#Compare Result File
#Started : Thu Dec 10 11:15:44 1992
===================================================
*** Database*Tue Nov 17 11:18:49 1992
--- device_1*Thu Dec 10 11:15:54 1992
****************
*** 22,35 ****
|
interface TokenRing 0
no ip address
- shutdown
...
...
...
clockrate 4000000
|
interface Ethernet 1
***************
*** 64, 69 ****
--- 63, 69 ----
snmp-server community
snmp-server community poppaa RW
snmp-server community public RO
+ snmp-server host 131.108.60.82 public
hostname device_1
|
RUNCMD sp=CISCONV,appl=sh,contacts
device
The following is an example contacts
command:
RUNCMD sp=CISCONV,appl=sh,contacts device_1
Host Name: device_1
Thu Mar 11 11:01:55 PST 1993
Joe Newman
123 First Street
Mytown, CA
USA, 94025
email: jnewman
(415) 455-0000
Scarlet Utara
333 Second Street
Brettown, MI 89999
e-mail: stara
Host Name: device_1
Thu Dec 10 11:01:55 PST 1992
No contacts found for device_1
RUNCMD sp=CISCONV,appl=sh,getconf
device community user password
The following is an example getconf
command:
RUNCMD sp=CISCONV,appl=sh,getconf device_1 public nms beta
View Config Host Name: device_1
Wed Feb 3 17:00:22 PST 1993
******** Get Config Log File ********
******** Started : Wed Feb 3 17:00:27 1993
version 9.1
!
hostname sloth
!
enable-password xxxx
!
boot network sloth-confg 131.108.1.111
boot network sloth-confg 131.108.13.111
boot system sloth-system 131.108.13.111
boot system sloth-system 131.108.1.111
!
exception dump 131.108.13.111
...
...
interface Ethernet 1
ip address 131.108.42.8 255.255.255.0
delay 100000
appletalk cable-range 4042-4042 4042.8
appletalk zone Engineering
!
interface Serial 1
no ip address
!
...
...
RUNCMD sp=CISCONV,appl=sh,ifstatus
device.
domain interface
The following is an example ifstatus
command:
RUNCMD sp=CISCONV,appl=sh,ifstatus device_1.cisco.com ethernet0
Host Name: device_1
- Thu Feb 4 11:35:13 PST 1993
-
- Success: timestamp = 728854522.138995
- netmgt_schema: cisco
- ifIndex: 2
- ifDescr: Ethernet0
- ifType: 6
- ifMtu: 1500
- ifSpeed: 10000000
- ifPhysAddress: 00000c02084e
- ifAdminStatus: 1
- ifOperStatus: 1
- ifLastChange: 8176413
- ifSpecific: 0.0
- (End of row)
(End of report)
-
- (Last report from agent)
-
- Status: Up = 1
- Down = 2
RUNCMD sp=CISCONV,appl=sh,neticmp
device.
domain community
The following is an example neticmp
command:
RUNCMD sp=CISCONV,appl=sh,neticmp device_1.cisco.com poppaa
Host Name: device_1
Fri Mar 5 8:05:44 PST 1993
IP Statistics:
Rcvd:*746280 total, 587748 local destination
*0 header errors, 0 address errors
*0 security failures
Flags: 0 reassembled, 0 reassembly failures
*0 fragmented, 0 couldn't fragment
Sent:*558947 generated, 158531 forwarded
*0 no route
ICMP Statistics:
Rcvd:*0errors, 0 redirects, 12 unreachable, 10 echo
*14 echo reply, 0 mask requests, 0 mask replies, 0 quench
*0 parameter problem, 0 timestamps, 0 timestamp replies
*0 time exceeded
Sent:*0 errors, 0 redirects, 0 unreachable, 25 echo
*10 echo reply, 0 mask requests, 0 mask replies, 0 quench
*0 parameter problem, 0 timestamps, 0 timestamp replies
*0 time exceeded
UDP Statistics:
Rcvd:*3821 total, 0 errors, 24 no port
Sent:*529650 total
TCP Statistics:
Rcvd:*3821 total, 0 errors
Sent:*2492 total
EGP Statistics:
Rcvd:*0 total, 0 errors
Sent:*0 total, 0 errors
RUNCMD sp=CISCONV,appl=sh,netif
device.
domain community
The following is an example netif
command:
RUNCMD sp=CISCONV,appl=sh,netif device_1.cisco.com poppaa
Host Name: device_1
Fri Mar 5 10:51:46 PST 1993
TokenRing0 is administratively down, line protocol down
Hardware is 16/4 Token Ring, address is 0000.0000.0000
MTU is 8136 bytes, BW 16000 Kbit, DLY 630 usec, rely 255/255, load 1/255
Encapsulation SNAP, keepalive is set
Last input never, output never, output hang never
Output queue 0, 0 drops, input queue 0 drops
Five minute input rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
Five minute output rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
0 packets input, 0 bytes, 0 no buffer
Received 0 broadcasts, 0 runts, 0 giants
0 input errors, 0 CRC, 0 frame, 0 overrun, 0 ignored, 0 aborts
0 packets output, 0 bytes
0 output errors, 0 collisions, 0 interface resets, 0 restarts
Ethernet0 is up, line protocol down
Hardware is MCI Ethernet, address is 0000.0c02.084e
MTU is 1500 bytes, BW 10000 Kbit, DLY 1000 usec, rely 255/255, load 1/255
Encapsulation ARPA, keepalive is set
Last input never, output 0:00:07, output hang never
Output queue 0, 0 drops, input queue 0 drops
Five minute input rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
Five minute output rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
0 packets input, 0 bytes, 0 no buffer
Received 0 broadcasts, 0 runts, 0 giants
0 input errors, 0 CRC, 0 frame, 0 overrun, 0 ignored, 0 aborts
23511 packets output, 2757693 bytes
0 output errors, 0 collisions, 23104 interface resets, 0 restarts
RUNCMD sp=CISCONV,appl=sh,netmenu
RUNCMD sp=CISCONV,appl=sh,netmenu
The CiscoWorks RUNCMD commands
.. ..
|| ||
|| ||
|||| ||||
..:||||||:...:||||||:..
For command syntax type: command help
COMMAND USAGE
cmpconf Compare configuration on the device with
the configuration on database
contacts Get the sysadmin contact name for a router
getconf Request configuration for a router
ifstatus Retrieve a given Interface status
neticmp View IP Routing Statistics for a router
netif View Interface Detail Status of a router
netmenu View CiscoWorks NetView Interface RUNCMDs
netroute View routing table of a router
netset Set a router interface up or down
netstatus View software version running on a router
shomibvar Retrieve MIB variable information
showflash Shows Flash memory data on a Cisco device.
showif View Interface name and Protocol Address
tracepath Request a path from Device A to a Device B
RUNCMD sp=CISCONV,appl=sh,netroute
device.
domain community
The following is an example netroute
command:
RUNCMD sp=CISCONV,appl=sh,netroute device_1.cisco.com poppaa
Host Name: device_1.cisco.com
Fri Mar 5 11:01:04 PST 1993
Codes: I - IGRP derived, R - RIP derived, H - HELLO derived
C - connected, S - static, E - EGP derived, B - BGP derived
i - IS-IS derived, O - OSPF derived
* - candidate default route
Gateway of last resort is 150.136.10.162
I Net 0.0.0.0 [8859] via 150.136.10.162, 76 sec, Ethernet1
I Net 11.0.0.0 [1673] via 150.136.10.162, 70 sec, Ethernet1
I Net 100.0.0.0 [1636] via 150.136.10.162, 70 sec, Ethernet1
I Net 128.18.0.0 [9049] via 150.136.10.162, 70 sec, Ethernet1
I Net 130.33.0.0 [10949] via 150.136.10.162, 70 sec, Ethernet1
I Net 130.93.0.0 [183044] via 150.136.10.162, 71 sec, Ethernet1
I Net 130.107.0.0 [10949] via 150.136.10.162, 71 sec, Ethernet1
I Net 131.108.0.0 [1373] via 150.136.10.162, 71 sec, Ethernet1
I Net 131.119.0.0 [8949] via 150.136.10.162, 71 sec, Ethernet1
I Net 132.249.0.0 [11149] via 150.136.10.162, 71 sec, Ethernet1
I Net 134.156.0.0 [8949] via 150.136.10.162, 71 sec, Ethernet1
I Net 134.163.0.0 [8949] via 150.136.10.162, 71 sec, Ethernet1
I Net 138.55.0.0 [8949] via 150.136.10.162, 71 sec, Ethernet1
...
...
C Net 150.136.0.0 is subnetted (mask is 255.255.255.0)
I 150.136.1.0 is possibly down, routing via 150.136.10.162, Ethernet1
C 150.136.10.0 is directly connected, Ethernet1
I 150.136.11.0 [8586] via 150.136.17.164, 17 sec, Fddi0
I 150.136.15.0 [1163] via 150.136.10.162, 72 sec, Ethernet1
C 150.136.17.0 is directly connected, Fddi0
I 150.136.19.0 [180581] via 150.136.17.164, 18 sec, Fddi0
RUNCMD sp=CISCONV,appl=sh,netset
device.
domain interface_name {up|down}
The following is an example netset
command:
RUNCMD sp=CISCONV,appl=sh,netset device_1.cisco.com ethernet0 up
Host Name: device_1
Thu Feb 4 11:41:01 PST 1993
Success: timestamp = 728854869.509537
Request succeeded.
RUNCMD sp=CISCONV,appl=sh,netstatus
device community
The following is an example netstatus
command:
RUNCMD sp=CISCONV,appl=sh,netstatus device_1 poppaa
Host Name: device_1
Fri Mar 5 16:02:02 PST 1993
GS Software (GS3-BFX), Version 9.0(1), SOFTWARE fc4
Copyright (c) 1986-1992 by cisco Systems, Inc.
Compiled Mon 11-May-92 12:13 by block
System Bootstrap, Version 4.5(1), SOFTWARE
Copyright (c) 1986-1992 by cisco Systems
device_1 uptime is 4 days, 7 hours, 10 minutes, 9 seconds
System restarted by power-on
Running default software
CSC3 (68020) processor with 4096K bytes of memory.
X.25 Software.
Bridging Software.
2 Ethernet/IEEE 802.3 interface.
1 Token Ring/IEEE 802.5 interface.
2 Serial network interface.
RUNCMD sp=CISCONV,appl=sh,shomibvar
device.
domain variable_name
Supported Group Variables
appletalk
appletalkProtocols
decnet
egp
fddi-number
icmp
interfaces
ipStatus
ip
lflash
lip
lsystemGeneral
lsystemSecurity
lsystemEnv
lsystemEnvTemp
lsystemEnvVoltage
lsystemMemory
lsystemContacts
lsystemBuffers
lsystemSmbuffers
lsystemMdbuffers
lsystemBgbuffers
lsystemLgbuffers
lsystemHgbuffers
lsystemNetconfig
lsystemCPUload
lts
novell
snmp
snmpStatus
system
tcp
transmission
udp
vines
xns
The following is an example shomibvar
command:
RUNCMD sp=CISCONV,appl=sh,shomibvar device_1.cisco.com ipAddrTable
Host Name: device_1.cisco.com
Fri Mar 5 16:17:58 PST 1993
Success: timestamp = 723514679.361930
netmgt_schema: snmp-mibII
netmgt_table_key: 1
ifIndex: 1
ifDescr: TokenRing0
...
...
ifSpecific: 0.0
(End of row)
ifType: 6
ifMtu: 1500
ifSpeed: 10000000
ifPhysAddress: 00000c0207f2
ifAdminStatus: 1
ifOperStatus: 1
ifLastChange: 1164
ifSpecific: 0.0
(End of row)
netmgt_table_key: 3
ifIndex: 3
ifDescr: Serial0
ifType: 22
ifMtu: 1500
ifSpeed: 1544000
ifPhysAddress: 00000c0207f2
ifAdminStatus: 1
ifOperStatus: 2
ifLastChange: 20205014
ifSpecific: 0.0
(End of row)
...
...
(End of report)
(Last report from agent)
RUNCMD sp=CISCONV,appl=sh,showflash
device.
domain community
RUNCMD sp=CISCONV,appl=sh,showflash polaris.cisco.com poppaa
showflash enterprise.cisco.com
Host Name: enterprise
Fri Jan 15 13:53:41 PST 1993
4096K bytes of flash memory.
Flash VPP dip is not installed.
file length name
0 2018552 gs3-k.91-2.2
[2175624/4194304 bytes free]
RUNCMD sp=CISCONV,appl=sh,showif
device.
domain community
The following is an example showif
command:
RUNCMD sp=CISCONV,appl=sh,showif device_1.cisco.com poppaa
interface name protocol addr
Ethernet0 131.108.42.85
Ethernet1 131.108.55.1
RUNCMD sp=CISCONV,appl=sh,tracepath
source destination
The following is an example tracepath
command:
RUNCMD sp=CISCONV,appl=sh,tracepath 192.31.8.239 131.108.2.57
Path from rmodule-ss2 to park
Thu Mar 11 14:42:11 PST 1993
Thu Mar 11 14:42:13 1993
Starting path discovery...
Hop #0: rmodule-ss2: out le0
Hop #1: debitt.CISCO.COM: in Ethernet3, out Fddi0
Hop #2: devo.cisco.com: in Fddi0, out Ethernet3
Hop #3: jazzy.CISCO.COM: in Ethernet0, out Ethernet3
Hop #4: Park: in Ethernet0
Path discovery complete.
Thu Mar 11 14:42:21 1993
select interface_name 'Interface Name', interface_id ifIndex
from interfaces, devices
where interfaces.device_id = devices.device_id
and devices.device_name = '$DEVICE'
order by interface_name
select interface_name 'Interface Name', interface_id ifIndex
from interfaces, devices
where interfaces.device_id = devices.device_id
and devices.device_name = '$DEVICE'
order by interface_name
RUNCMD sp=CISCONV, appl=sh, show_if_ids nms beta device_1
select interface_name 'Interface Name', interface_id ifIndex
List of interfaces and their ids (ifIndex) for gordy
Interface Name ifIndex
-------------------------------- -------
Ethernet0 1
Ethernet1 3
Ethernet10 16
Ethernet11 17
Ethernet12 18
Ethernet13 19
Ethernet14 20
Ethernet15 21
Ethernet2 5
Ethernet3 7
Ethernet4 9
Ethernet5 10
Ethernet6 11
Ethernet7 12
Ethernet8 13
Ethernet9 14
Fddi0 15
Fddi1 22
Serial0 2
Serial1 4
Serial2 6
Serial3 8
#!/bin/sh
#
# show_if_ids: Sample shell script to demonstrate joining two tables
#
# usage: show_if_ids <user_name> <password> <device_name>
#
#~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
~~~~~
#
# Function Definitions
#
#~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
~~~~~
#
# Function to display usage information
#
usage()
{
echo "usage: $0 <user_name> <password> <device_name>"
exit 1
}
#
# Function the check the SYBASE env variable
#
checkenv()
{
if [ $SYBASE = "" ]; then
echo "$0: The SYBASE environment variable is not set"
exit 1
fi
}
#~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
~~~~~
#
# Start of script
#
#~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
~~~~~
#
# Check the command line and environment
#
if [ $# != 3 ]; then
usage
fi
checkenv
#
# Get the command line arguments
#
USER=$1
PASSWORD=$2
DEVICE=$3
#
# Display a title for the output
#
echo
echo "List of interfaces and their ids (ifIndex) for $DEVICE"
echo
#
# Execute the SQL to retrieve the information
#
$SYBASE/bin/isql -U$USER -P$PASSWORD <<EOF
set nocount on
go
/* Get the list of interfaces and ids from the interfaces table.
* Note that a join is required with the devices table so that the
* device can be looked up by name
*/
select interface_name 'Interface Name', interface_id ifIndex
from interfaces, devices
where interfaces.device_id = devices.device_id
and devices.device_name = '$DEVICE'
order by interface_name
go
exit
EOF
RUNCMD sp=CISCONV,appl=unix,custcmd
parameters
SAMPLE CUSTOMIZED OUTPUT APPEARS HERE
SAMPLE CUSTOMIZED OUTPUT APPEARS HERE
SAMPLE CUSTOMIZED OUTPUT APPEARS HERE
SAMPLE CUSTOMIZED OUTPUT APPEARS HERE
SAMPLE CUSTOMIZED OUTPUT APPEARS HERE
# Event Table Example
###################################
# Using the Default Translation Subvectors
###################################
hostperf data "cpu%" <= 90 ; # Specific Event
hostperf data intr ; # Any event with intr attribute
-hostperf data intr -< ; # Except when relop is -<
hostif if/le0 qlen +> 10 ; # "if" table entry = le0
layers udp * +> * ; # Any of udp's attributes
layers udp * -> * ; # Any of udp's attributes
###################################
# Using User defined subvectors #
###################################
hostmem mbuf "mbufused" >= 10 : GA = 3320(01) CU = 0700 PC = 2050;
* : GA = 4012(01) PC = 4002 UC = 4002 / 00b2 + E0 "'RUNCMD SP=PUTR0800,AP
PL=SH,F
REECPU <NODE>'"; # Events not specified will
# translate with these 3 SV.
hostperf data "cpu%" < 99 :
GA = 3320(01)
CU = 0700
PC = 2050; #
###################
# Entry STARTS here :
###################
hostif if/le0 qlen < 5 : # Event Reporting X.25 Alert 6
GA = 3320(01) # Generic Alert SV
PC = 2050, 2008, 2006 # Probable Causes SV
FC = 20D1,2006 + # Failure Causes SV with
01 "expired", # 3 qualifiers
02 "retry",
03 "settings"
/3302, 3107, 32d0 +# Recommended Actions that
# Go with the Failure Causes SV
01 "called", # Having
02 "calling", # 3 Qualifiers
03 "Local"
SV(52) == # LCS SV superseding the one
# in Machine table if any
"060702010101";
###################
# And ENDS here
###################
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()