|
|
This chapter describes the interconnection facilities for the access cards that you can install in the LightStream 2020 multiservice ATM switch (LS2020 switch). These facilities are described in the following order:
Signal diagrams are provided for the I/O connectors and data cables described in this chapter. Figure 3-1 shows the conventions used in representing the signal paths in these diagrams.
Figure 3-1 : LS2020 Cable Signal Diagram Conventions
For those interface cables offered for sale by Cisco Systems, a table in the body of each applicable section contains the following information for your convenience:
You can populate the front of an LS2020 chassis with a variety of line cards, depending on your particular communications requirements. Correspondingly, you can populate the opposite slots in the rear of the LS2020 chassis with matching access cards.
Each line card/access card combination in a given slot of an LS2020 chassis constitutes an operational/functional entity referred to as an interface module.
Interface modules support specific kinds of data transfer services in an LS2020 network and provide the means of interconnection and communication among network devices. Each line card is connected to its corresponding access card through the LS2020 chassis midplane.
If you remove an access card from the midplane, service to the corresponding line card is disrupted.
Table 3-1 lists the types of interface modules available for use in an LS2020 switch, together with the applicable line card, associated access card, and the number of ports supported by each module.
Table 3-1 : LS2020 Interface Modules
| Interface Module Type | Line Card Type | Access Card/Number of ports |
|---|---|---|
| Serial modules:
First-generation Second-generation1 |
Low-speed card (LSC) Packet line card (PLC) |
Low-speed access card (LSAC) --- 8 ports Serial access card (SAC) --- 8 ports |
| T3/E3 modules:
First-generation Second-generation2 |
Medium-speed card (MSC) Cell line card (CLC) |
T3 medium-speed access card (MSAC) --- 2 ports E3 G.804 medium-speed access card (MSAC) --- 2 ports E3 PLCP medium-speed access card (MSAC) --- 2 ports (First-generation T3/E3 cards are no longer orderable) T3 access card (T3AC) --- 4 or 8 ports E3 access card (E3AC) --- 4 ports |
| Constant bit rate (CBR) modules | Packet line card (PLC) | T1 circuit emulation access card (CEMAC-T1) --- 8 ports
E1 circuit emulation access card (CEMAC-E1) --- 8 ports |
| OC-3 modules:
First-generation Second-generation Multimode |
Cell line card (CLC) |
OC-3c single-mode access card equipped with ST connectors (OC3AC-SM) --- 1 or 2 ports OC-3c single-mode access card equipped with SC connectors (OC3AC-SM) --- 1 or 2 ports OC-3c multimode access card equipped with SC connectors (OC3AC-MM) --- 1 or 2 ports |
| FDDI module | Packet line card (PLC) | FDDI access card (FAC) --- 2 ports |
| Ethernet module | Packet line card (PLC) | Ethernet access card (EAC) --- 8 ports |
| Fiber Ethernet module | Packet line card (PLC) | Fiber Ethernet access card (FEAC) --- 8 ports |
| 1. Upgrade option from first-generation, low-speed access card (LSAC)
2. Upgrade option from first-generation, medium-speed, two-port T3/E3 access cards (MSAC) |
||
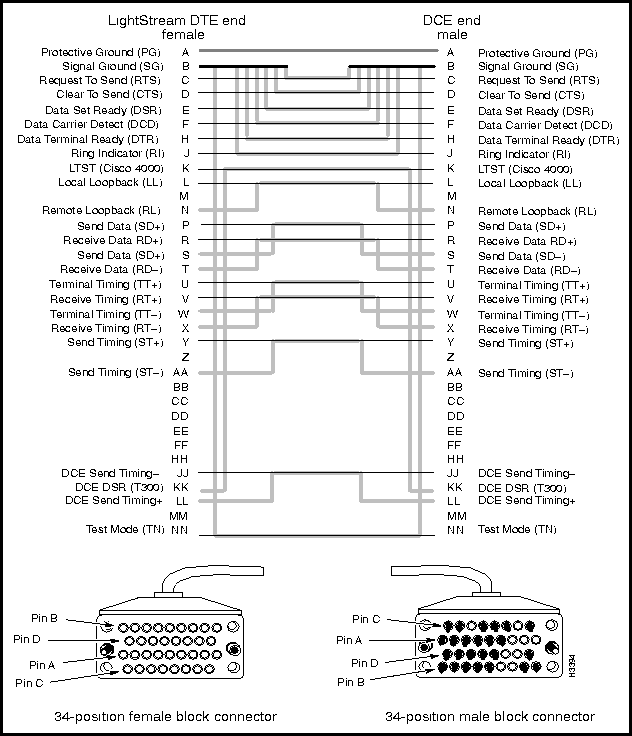
This section describes the connectors and cables for the X.21, RS-449, and V.35 interfaces for the serial access cards available for use with the LS2020 switch. Figure 3-2 shows the bulkhead view of these serial interface cards. Such cards are of two types:
Figure 3-2 : Low-Speed and Serial Access Cards
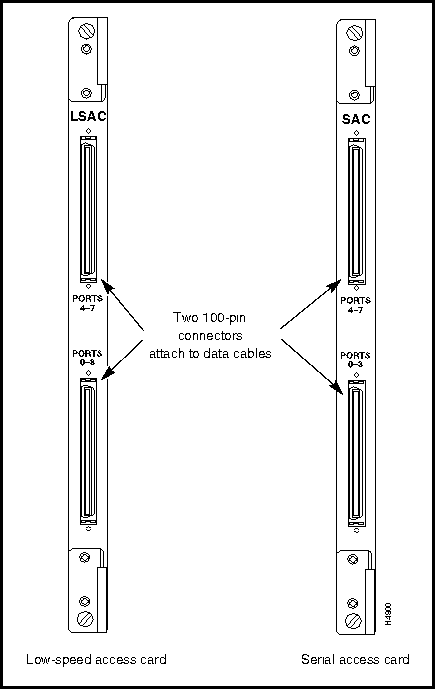
The low-speed access card (LSAC) and the serial access card (SAC) use the same types of connectors and cables for hookup. These interconnection facilities are described in the following order:
Figure 3-3 shows the X.21 fantail that you can use with either the low-speed access card (LSAC) or the serial access card (SAC).
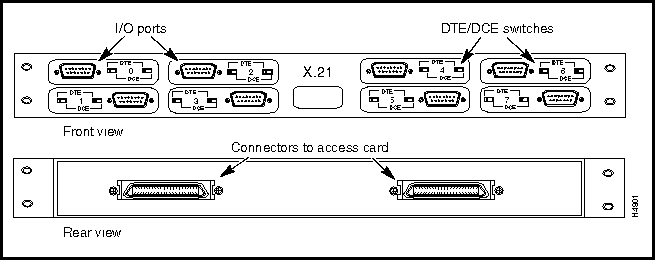
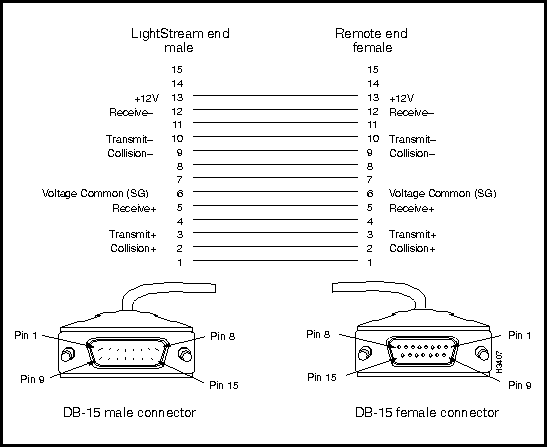
Figure 3-4 shows the pin assignments for the eight X.21 interface DB-15 connectors (I/O ports) present on the X.21 fantail.
Figure 3-4 : X.21 Interface DB-15 Connector Pin Assignments
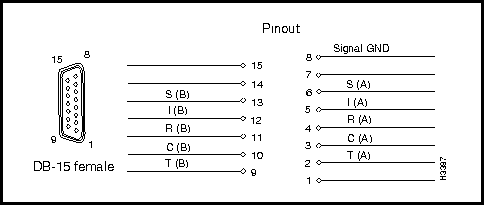
Interface connector type: DB-15 female
Connectors per fantail: eight (numbered 0 -- 7)
Figure 3-5 shows the RS-449 fantail that can be used with either the low-speed access card (LSAC) or the serial access card (SAC).
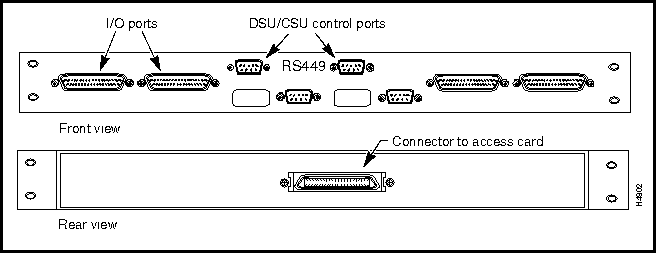
Figure 3-6 shows the pin assignments for the four RS-449 interface DB-37 connectors (I/O ports) present on the RS-449 fantail.
Figure 3-6 : RS-449 Interface DB-37 Connector Pin Assignments
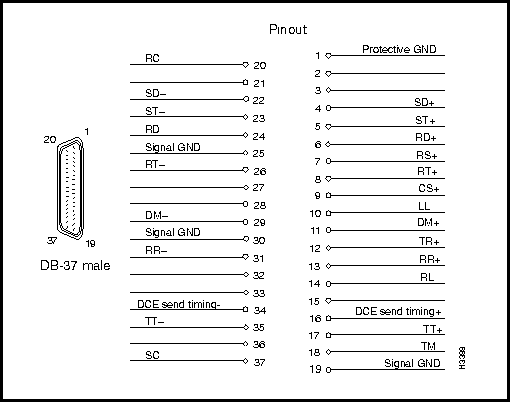
Interface connector type: DB-37 male
Connectors per fantail: four (numbered 0 -- 3)
Figure 3-7 shows the V.35 fantail that can be used with either the low-speed access card (LSAC) or the serial access card (SAC).
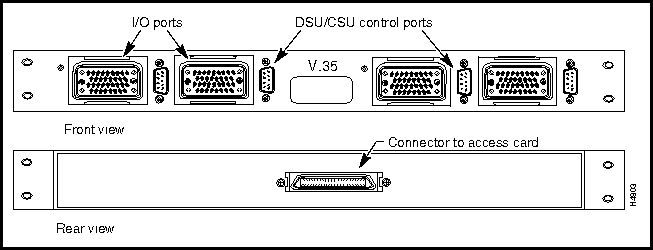
Figure 3-8 illustrates the pin assignments for the four V.35 interface ISO 2593 connectors (I/O ports) present on the V.35 fantail.
Figure 3-8 : V.35 Interface ISO 2593 Connector Pin Assignments
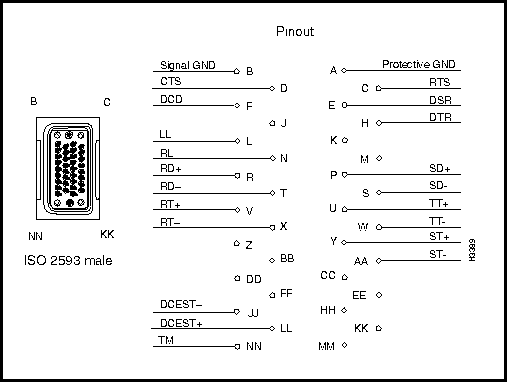
Interface connector type: ISO 2593 male (34-pin block type)
Connectors per fantail: four (numbered 0 -- 3)
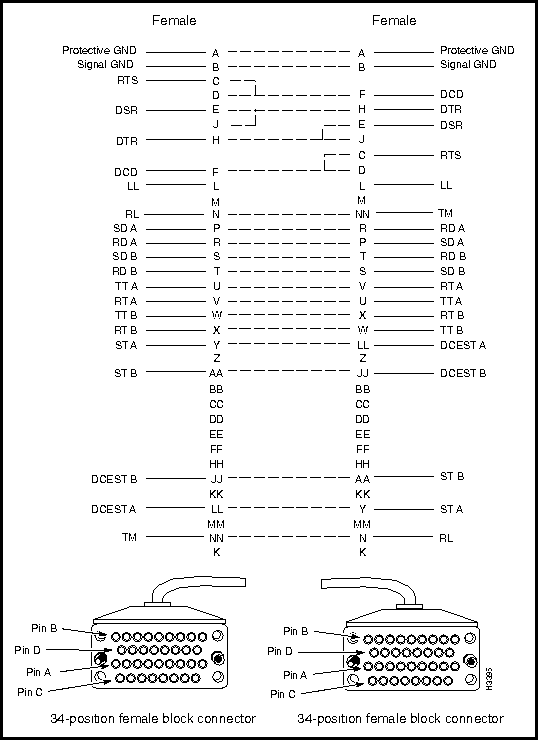
DSU/CSU Control Ports on RS-449 and V.35 Fantails
RS-232 DSU/CSU control ports are present on both the RS-449 and V.35 fantails. If you connect the control port to the craft port on a DSU/CSU device, you can use the csumon program to communicate remotely with the DSU/CSU from an LS2020 switch.
Figure 3-9 shows the pin assignments for the four RS-232 DSU/CSU control ports (DB-9 connectors) present on the RS-449 and V.35 fantail.
Figure 3-9 : RS-232 DSU/CSU Control Port (DB-9 Connector) Pin Assignments
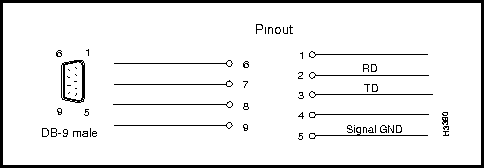
Interface connector type: DB-9 male
Connectors per fantail: four (numbered 0 -- 3)
This high-density, 100-pin fantail cable is used to interconnect the bulkhead of a low-speed access card (LSAC) or a serial access card (SAC) with the back of an X.21, RS-449, or V.35 fantail.
The data cable for an X.21, RS-449, or V.35 fantail can be ordered from Cisco Systems in any of three lengths. Select the appropriate order number from the following table.
| Manufacturing No. | Length | Order No. |
| 72-1117-01 | 4 feet (1.2 m) | L2020-CAB-F4= |
| 72-1118-01 | 8 feet (2.4 m) | L2020-CAB-F8= |
| 72-1119-01 | 12 feet (3.6 m) | L2020-CAB-F12= |
Two such data cables are required for the interconnection of an LSAC or SAC bulkhead to the rear of an X.21 fantail: one cable for ports 0 -- 3 on bulkhead, and another cable for ports 4 -- 7 on the bulkhead.
Only one such cable is required for the connection of an LSAC or SAC bulkhead to an RS-449 or V.35 fantail.
This cable is used to interconnect an X.21 fantail with an external X.21 device.
The X.21 interface cable can be ordered from Cisco Systems in any of three lengths. Select the appropriate order number from the following table.
| Manufacturing No. | Length | Order No. |
| 72-0991-01 | 30 feet (9.1 m) | LS-CAB-X21-TC30= |
| 72-0992-01 | 50 feet (15.2 m) | LS-CAB-X21-TC50= |
| 72-0993-01 | 100 feet (30.5 m) | LS-CAB-X21-TC100= |
Figure 3-10 is a signal diagram for the X.21 interface cable.
Figure 3-10 : X.21 Interface Cable Signal Diagram
RS-449 Interface Straight-Through Cable
This cable is used to interconnect an RS-449 fantail with an external RS-449 DCE device.
The RS-449 interface straight-through cable can be ordered from Cisco Systems in any of three lengths. Select the appropriate order number from the following table.
| Manufacturing No. | Length | Order No. |
| 72-1002-01 | 30 feet (9.1 m) | LS-CAB-RS4-TC30= |
| 72-1003-01 | 50 feet (15.2 m) | LS-CAB-RS4-TC50= |
| 72-1004-01 | 100 feet (30.5 m) | LS-CAB-RS4-TC100= |
Figure 3-11 is a signal diagram for the RS-449 interface straight-through cable.
Figure 3-11 : RS-449 Interface Straight-through Cable Signal Diagram
RS-449 Interface Crossover Cable
This cable is used to connect two LS2020 switches via their RS-449 fantail interfaces, or to interconnect an RS-449 fantail with an external RS-449 DTE device.
The RS-449 interface crossover cable can be ordered from Cisco Systems in any of four lengths. Select the appropriate order number from the following table.
| Manufacturing No. | Length | Order No. |
| 72-1008-01 | 8 feet (2.4 m) | LS-CAB-RS4-TT8= |
| 72-1005-01 | 30 feet (9.1 m) | LS-CAB-RS4-TT30= |
| 72-1006-01 | 50 feet (15.2 m) | LS-CAB-RS4-TT50= |
| 72-1007-01 | 100 feet (30.5 m) | LS-CAB-RS4-TT100= |
Figure 3-12 is a signal diagram for the RS-449 interface crossover cable.
Figure 3-12 : RS-449 Interface Crossover Cable Signal Diagram
V.35 Interface Straight-Through Cable
This cable is used to interconnect a V.35 fantail with an external V.35 DCE device.
The V.35 interface straight-through cable can be ordered from Cisco Systems in any of three lengths. Select the appropriate order number from the following table.
| Manufacturing No. | Length | Order No. |
| 72-1009-01 | 30 feet (9.1 m) | LS-CAB-V35-TC30= |
| 72-1010-01 | 50 feet (15.2 m) | LS-CAB-V35-TC50= |
| 72-1011-01 | 100 feet (30.5 m) | LS-CAB-V35-TC100= |
Figure 3-13 is a signal diagram for the V.35 interface straight-through cable.
Figure 3-13 : V.35 Interface Straight-through Cable Signal Diagram
V.35 Interface Crossover Cable
This cable is used to connect two LS2020 switches via their V.35 fantail interfaces, or to interconnect a V.35 fantail with an external V.35 DTE device.
The V.35 interface crossover cable can be ordered from Cisco Systems in any of four lengths. Select the appropriate order number from the following table.
| Manufacturing No. | Length | Order No. |
| 72-0997-01 | 8 feet (2.4 m) | LS-CAB-V35-TT8= |
| 72-0994-01 | 30 feet (9.1 m) | LS-CAB-V35-TT30= |
| 72-0995-01 | 50 feet (15.2 m) | LS-CAB-V35-TT50= |
| 72-0996-01 | 100 feet (30.5 m) | LS-CAB-V35-TT100= |
Figure 3-14 is a signal diagram for the V.35 interface crossover cable.
Figure 3-14 : V.35 Interface Crossover Cable Signal Diagram
This section describes the connectors and cables for the TE/E3 access cards. These facilities are discussed in the following order:
Connectors on T3/E3 Medium-Speed Access Cards
Figure 3-15 shows the T3/E3, two-port medium-speed access card (MSAC). The MSAC is a first-generation card that is available in three versions:
Although three different versions of the MSAC are available, the bulkheads of these cards are identical in appearance (see Figure 3-15) and use the same cables for interconnection purposes.
Figure 3-15 : T3/E3 Medium-speed Access Card (2-Port)
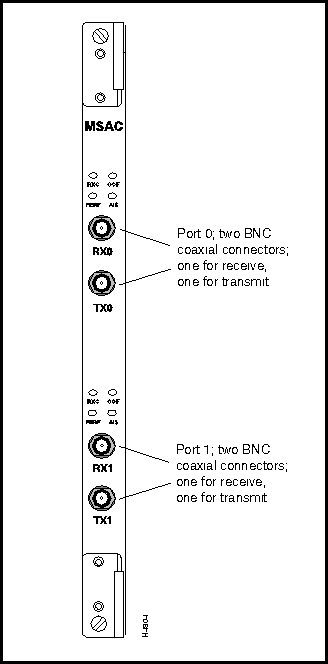
Interface connector type: 75-ohm coaxial BNC jack
Connectors per MSAC card: four (two receive channels and two transmit channels)
Coaxial Cable (75-Ohm) for T3/E3 Applications
Figure 3-16 shows the coaxial cable available for use in making interconnections for 75-ohm T3/E3 interface applications.
Figure 3-16 : T3/E3 75-ohm Coaxial Cable
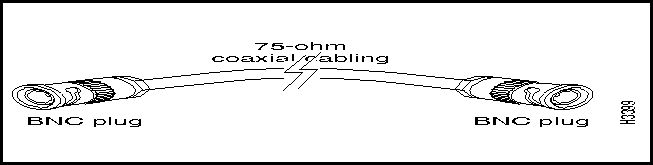
The 75-ohm coaxial cable can be used for the following purposes:
The 75-0hm coaxial cable for T3/E3 applications can be ordered from Cisco Systems in any of four lengths. Select the appropriate order number from the following table.
| Manufacturing No. | Length | Order No. |
| 72-0998-01 | 3 feet (0.9 m) | LS-CAB-T3-CX3= |
| 72-0399-01 | 25 feet (7.6 m) | LS-CAB-T3-CX25= |
| 72-1000-01 | 50 feet (15.2 m) | LS-CAB-T3-CX50= |
| 72-1001-01 | 100 feet (30.5 m) | LS-CAB-T3-CX100= |
Connectors on T3/E3 Access Cards
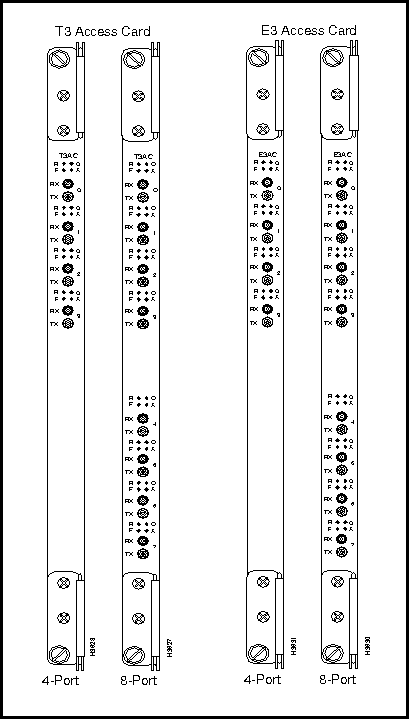
Figure 3-17 shows the T3/E3 access cards (T3AC/E3AC). These are second-generation ATM interfaces that operate in conjunction with cell line cards (CLCs).
The T3 access cards are available in either 4-port or 8-port versions, while the E3 access card is available only in a 4-port version, as shown in Figure 3-17.
Figure 3-17 : T3/E3 Medium-Speed Access Cards
T3/E3 Fantail and Cable Harness
Figure 3-18 shows the T3/E3 fantail (dressing panel) containing 16 BNC connectors for 75-ohm hookup to external devices. Also shown is the cable harness that provides the means for direct connection between the back of the T3/E3 fantail and the SMB connectors on a T3AC or E3AC access card.
Figure 3-18 : T3/E3 Fantail and Cable Harness
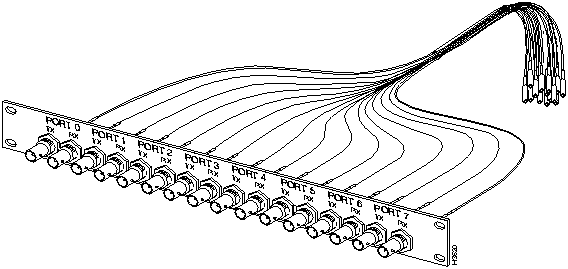
Interface connector type: SMB connectors on the access card bulkhead and the rear of the T3/E3 fantail; BNC connectors on the front of the T3/E3 fantail (see Figure 3-18).
Connectors per access card: 8 or 16 SMB connectors on the access card bulkhead, depending on the number of ports on the card (either 4 or 8). Each port has one receive connector and one transmit connector.
The T3/E3 fantail (dressing panel) and the T3/E3 cable harness (in both 4- and 8-port versions) are available as separate items for interconnecting patch panels or T3/E3 fantails to T3AC or E3AC access cards, as appropriate.
Use the following table for ordering information for the T3/E3 fantail (dressing panel).
| Manufacturing No. | Order No. |
| 700-00605-01 | LS2020-T3E3-FT= |
The T3 cable harness can be ordered from Cisco Systems in any of three lengths. Use the following table for ordering information.
| Manufacturing No. | Ports | Length | Order No. |
| 72-1097-01 | 4 | 4 feet (1.2 m) | LS-CAB-4T3-4B= |
| 72-1098-01 | 4 | 8 feet (2.4 m) | LS-CAB-4T3-8B= |
| 72-1099-01 | 4 | 12 feet (3.6 m) | LS-CAB-4T3-12B= |
| 72-1061-01 | 8 | 4 feet (1.2 m) | LS-CAB-8T3-4B= |
| 72-1062-01 | 8 | 8 feet (2.4 m) | LS-CAB-8T3-8B= |
| 72-1063-01 | 8 | 12 feet (3.6 m) | LS-CAB-8T3-12B= |
The E3 cable harness can be ordered from Cisco Systems in any of three lengths. Use the following table for ordering information.
| Manufacturing No. | Ports | Length | Order No. |
| 72-1097-01 | 4 | 4 feet (1.2 m) | LS-CAB-4E3-4B= |
| 72-1098-01 | 4 | 8 feet (2.4 m) | LS-CAB-4E3-8B= |
| 72-1099-01 | 4 | 12 feet (3.6 m) | LS-CAB-4E3-12B= |
| 72-1061-01 | 8 | 4 feet (1.2 m) | LS-CAB-8E3-4B= |
| 72-1062-01 | 8 | 8 feet (2.4 m) | LS-CAB-8E3-8B= |
| 72-1063-01 | 8 | 12 feet (3.6 m) | LS-CAB-8E3-12B= |
The circuit emulation access card (CEMAC) is available in two versions:
Figure 3-19 shows the bulkhead views of the T1 and E1 CEMAC cards. These cards are identical in appearance, except for the identifying "T1" or "E1" nomenclature at the bottom of the bulkhead.
The E1 CEMAC contains user-settable, on-board jumpers that are configured initially at the factory for 120-ohm operation without a fantail.
If you wish to configure the E1 CEMAC for 75-ohm operation with an E1 fantail, you must set these on-board jumpers accordingly. For detailed information about setting these jumpers, see the LightStream 2020 Hardware Reference & Troubleshooting Guide.
Figure 3-19 : T1/E1 CEMAC Cards
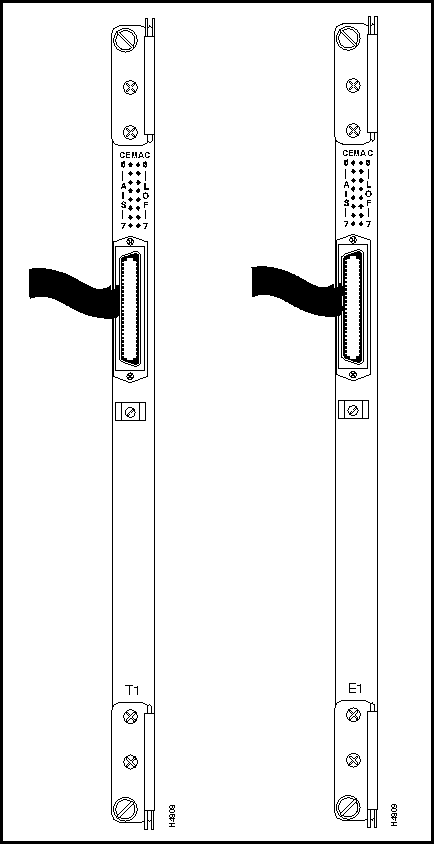
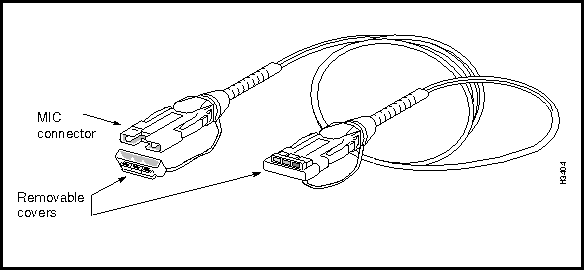
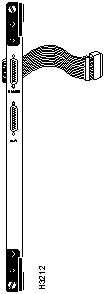
Figure 3-20 shows a component side view of the CEMAC card, together with its bulkhead connector and associated fantail cable.
To attach the fantail cable to the CEMAC card, seat the cable firmly in the bulkhead connector, secure the cable to the connector with the Velcro strip, and, optionally, add a cable tie to hold the cable to the bulkhead. These steps are illustrated in Figure 3-20.
Figure 3-20 : Securing CEMAC Cable to Bulkhead Connector
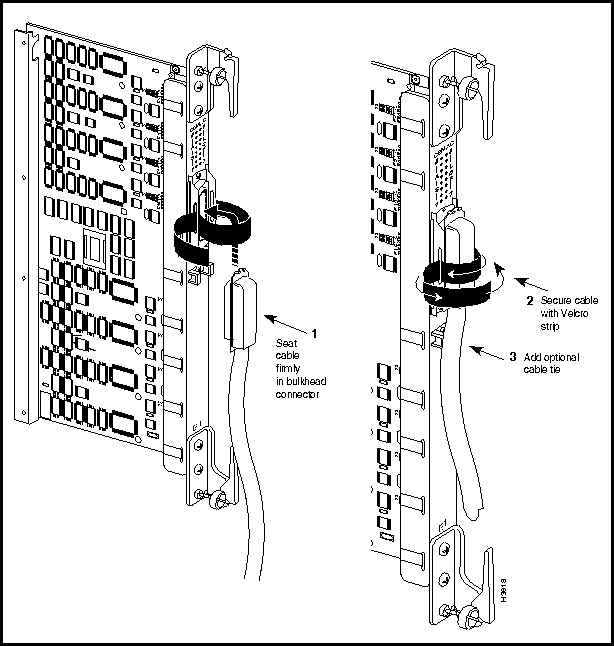
Table 3-2 shows the pin assignments common to the T1 and E1 CEMAC bulkhead connectors. The information in this table has been extracted from Figure 10 of American National Standard T1.403-1989. The T1/E1 CEMAC bulkhead connector is a standard RJ48 connector.
Table 3-2 : T1/E1 CEMAC Bulkhead Connector Pin Assignments
|
Port |
Receive | Transmit | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tip | Ring | Tip | Ring | |
| 0 | 26 | 1 | 39 | 14 |
| 1 | 27 | 2 | 40 | 15 |
| 2 | 28 | 3 | 41 | 16 |
| 3 | 29 | 4 | 42 | 17 |
| 4 | 30 | 5 | 43 | 18 |
| 5 | 31 | 6 | 44 | 19 |
| 6 | 32 | 7 | 45 | 20 |
| 7 | 33 | 8 | 46 | 21 |
| 8 -- not used | 34 | 9 | 47 | 22 |
| 9 -- not used | 35 | 10 | 48 | 23 |
| 10 -- not used | 36 | 11 | 49 | 24 |
| 11 -- not used | 37 | 12 | 50 | 25 |
E1 Fantail (for 75-ohm CEMAC Applications)
When you use an E1 CEMAC in the 75-ohm mode, you must also use an E1 fantail and cable for interconnection with the bulkhead connector on the card. The fantail supports up to 12 ports. Figure 3-21 shows the E1 CEMAC fantail; Figure 3-22 shows the fantail cable.
To provide full compatibility with G.703 E1 interfaces, an E1 CEMAC fantail is available in either of two versions: one equipped exclusively with 12 BNC connectors, or one equipped exclusively with 12 SMZ connectors. For convenience, Figure 3-21 illustrates both types of connectors on the E1 CEMAC fantail.
When you interconnect the 8-port E1 CEMAC card to an E1 fantail using a fantail cable (see Figure 3-22), only the first eight transmit and receive ports (TX0 -- TX7 and RX0 -- RX7) on the fantail are used.
Figure 3-21 : E1 Fantail for 75-ohm CEMAC Applications
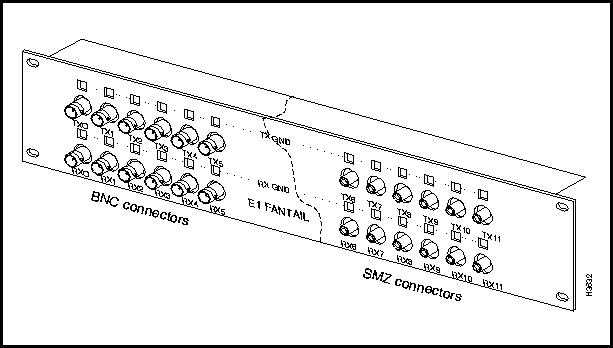
Refer to the LightStream 2020 Hardware Reference & Troubleshooting Guide for information about configuring the TX GND and RX GND jumpers on the E1 fantail.
E1 Fantail Cable (for CEMAC Card)
A 50-pin cable is used to connect the bulkhead connector on the E1 CEMAC card and the back of the E1 fantail. This cable, illustrated in Figure 3-22, supports up to 12 ports.
The E1 fantail cable for a CEMAC card can be ordered from Cisco Systems in any of three lengths. Select the appropriate order number from the following table.
| Manufacturing No. | Length | Order No. |
| 72-1094-01 | 4 feet (1.2 m) | LS-CAB-8E1-4B= |
| 72-1095-01 | 8 feet (2.4 m) | LS-CAB-8E1-8B= |
| 72-1096-01 | 12 feet (3.6 m) | LS-CAB-8E1-12B= |
Figure 3-22 : E1 Fantail Cable
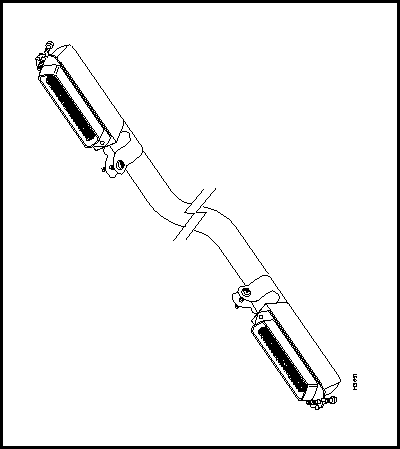
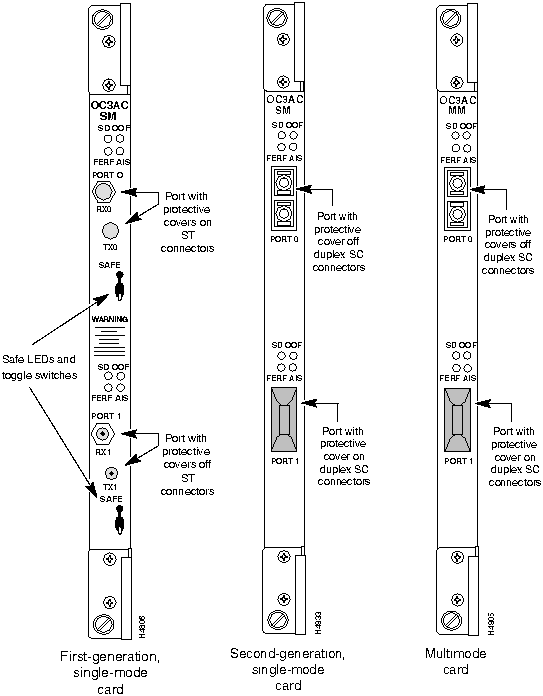
Figure 3-23 shows a bulkhead view of the following versions of the OC-3c access cards:
As shown in Figure 3-23, the bulkhead view of the second-generation, single-mode OC-3c card is identical to that of the multimode card, except that the former contains the nomenclature "OC3AC SM" at the top of its bulkhead.
The cables for the OC-3c access cards are described in separate sections below.
Figure 3-23 : OC-3c Access Cards Multimode interface connector type: SC
Connectors per multimode access card: four (2 connectors per port; 2 ports, numbered 0 and 1)
Single-mode interface connector type: ST (SC connectors for second-generation, single-mode card)
Connectors per single-mode access card: four (2 connectors per port; 2 ports, numbered 0 and 1)
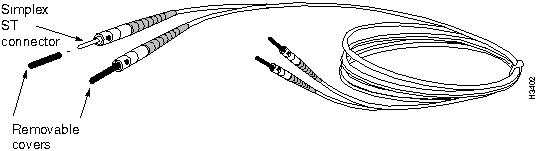
Single-Mode OC-3c Cable (ST Connectors)
A single-mode OC-3c cable with simplex ST connectors is used to connect a first-generation, single mode OC-3c access card to a single-mode OC-3c interface. Cisco Systems does not provide this cable; it is readily available from other sources.
The single-mode OC-3c interface operates at a wavelength of 1300 nanometers.
Single-mode cables with ST connectors should conform to the following specifications:
Standard: EIA class IVa
Cabling: 8.3 micron core with a maximum attenuation at 1300 nanometers of .3 dB/km. Optical path loss should not exceed 12 dB.
Maximum path length (all cables in a connection from end to end): 22 km
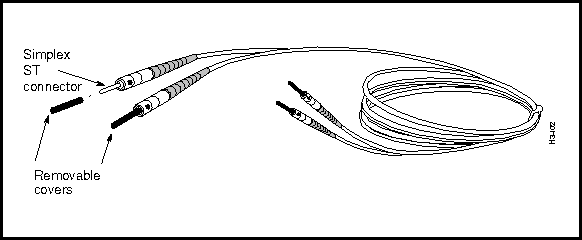
Figure 3-24 shows the cable used with the first-generation, single-mode OC-3c access card. This cable is equipped with simplex ST connectors.
Figure 3-24 : Single-Mode OC-3c Cable with ST Connectors Single-Mode OC-3c Cable (SC Connectors)
A single-mode OC-3c cable with SC connectors is used to connect a second-generation, single-mode OC-3c access card to a single-mode OC-3c interface. Cisco Systems does not provide this cable; it is readily available from other sources.
The single-mode OC-3c cable equipped with SC connectors is similar in appearance to the multimode OC-3c cable shown in Figure 3-26. However, the optical characteristics of the single-mode cable are different.
The single-mode OC-3c interface operates at a wavelength of 1300 nanometers.
The single-mode SC cables should conform to the following specifications:
Standard: EIA class IVa
Cabling: 8.3 micron core.
The path loss characteristics and maximum cable lengths for the single-mode OC-3c access card equipped with duplex SC connectors are discussed in the following section.
Estimating Transmit Distances for Single-Mode OC-3c SC Transceivers
The Intermediate Reach (IR) transceiver used in the single-mode OC-3c access card equipped with duplex SC connectors has the power characteristics outlined in the table below.
The maximum distance over which a single-mode fiber-optic signal can be transmitted reliably by the IR transceiver depends on two factors:
The supplier of the fiber-optic cable that you purchase for use with the single-mode OC-3c access card should be able to provide you with the path loss characteristics of the cable. With this information, you can use the maximum path loss value in the following table to determine whether or not the IR transceiver will meet your end-to-end optical transmission requirements.
The maximum path loss value of 16.0 dBm is based on an assumed margin of 0 dB. This 16.0 dBm value is based on the transceiver's minimum optical input sensitivity and minimum optical output power. Hence, this value constitutes a "worst-case" path loss characteristic.
If you know the path loss characteristics of your selected fiber-optic cable and the number of splices contained in the end-to-end fiber-optic link, you can make a rough determination as to whether the single-mode IR transceiver will meet your optical transmission needs. Such a determination, however, must be based on the assumption that the optical attenuation characteristics of the cable are the same across all cable segments (or splices) in the entire end-to-end link.
In general, acceptable quality fiber-optic cable has a path loss characteristic of .3 dB/km or less. A path loss characteristic of .45 dB/km is considered quite poor.
If your overall fiber-optic link consists of link segments with different loss characteristics, you should regard each link as having the path loss characteristic of the worst link in determining aggregate attenuation losses.
Connector manufacturers specify the performance of a connector by measuring its "insertion loss." In calculating insertion loss, power flowing through a fiber-optic cable is measured. Next, the cable is cut in half and a connector is affixed. Power at the end of the cable is again measured. The difference in these two measurements are used to calculate the insertion loss.
This method eliminates losses caused by variations in cable diameters when cables from different vendors are spliced together. Typical insertion loss values range from .1 dB to .6 dB, depending on the quality and type of connector. In any case, you are advised to use a very conservative path loss value of 1 dB/km for fiber-optic links composed of multiple vendor or fiber types.
For the IR transceiver used in the single-mode OC-3c access card, consult either Table 3-3 or Table 3-4 to determine the maximum allowed cable lengths (in kilometers), given specific assumptions about the number of splices contained in the end-to-end link and the loss characteristics of each splice.
Table 3-3 shows the maximum cable lengths for end-to-end connections that incur a loss of .5 dB/splice.
Table 3-3 : IR Transceiver Range (.5 dB loss/splice)
Table 3-4 shows the maximum cable lengths for end-to-end connections that incur a loss of 1.0 dB/splice.
Table 3-4 : IR Transceiver Range (1.0 dB loss/splice)
Path Loss Conclusions and Assumptions
You can ascertain whether the single-mode OC-3c access card equipped with SC connectors will meet your optical transmission requirements by determining the overall path loss of your fiber-optic link and comparing this value against the following baseline:
If you cannot determine the overall path loss of your fiber-optic link, you must assume that the maximum transmit distance of the IR transceiver is no more than 50 km.
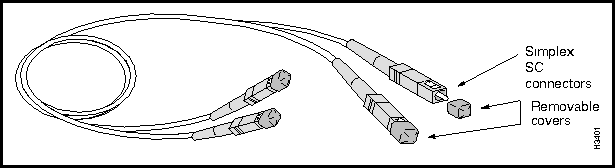
The transceivers on the second-generation, single-mode OC-3c access card are equipped with duplex SC connectors (see Figure 3-23). Note that you can attach either simplex or duplex SC optical cables to these bulkhead connectors.
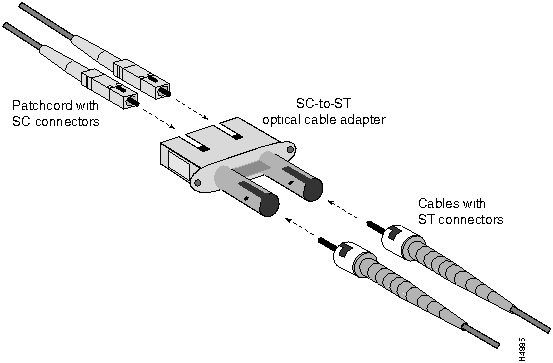
Also, using an SC-to-ST optical cable adapter (see Figure 3-25), you can interconnect cables from a second-generation, single-mode access card with another OC-3c device equipped with ST connectors.
Figure 3-25 : SC-to-ST Optical Cable Adapter The following components are required for interconnecting the second-generation OC-3c access card equipped with SC connectors to another fiber optic device equipped with ST connectors:
Suggested patchcord vendors are listed in the following table.
This adapter is available from the vendor indicated in the following table.
Multimode OC-3c Cable (SC Connectors)
This cable is used to connect a multimode OC-3c access card to another multimode OC-3c interface.
Cisco Systems does not provide this cable; it is widely available from other sources.
The OC-3c interface operates at a wavelength of 1300 nanometers.
A multimode OC-3c cable with SC connectors should conform to the following specifications:
Standard: ISO/IEC 9314-3
Cabling: 62.5 micron core with an optical loss of 0 -- 9 dB, or 50 micron core with an optical loss of 7 dB. You should not mix 62.5 and 50 micron cables in the same fiber-optic link.
Maximum path length (all cables in a connection from end to end): 2 km
Figure 3-26 shows an OC-3c multimode cable equipped with simplex SC connectors.
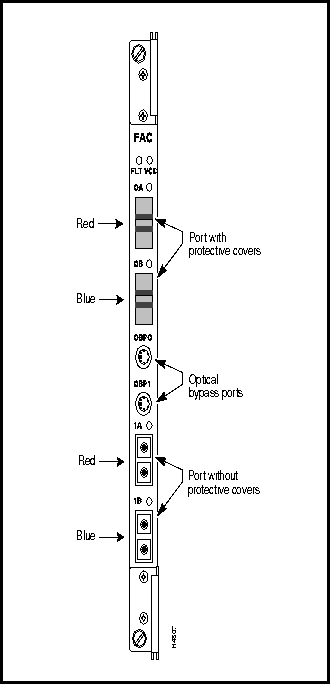
Figure 3-26 : Multimode OC-3c Cable with SC Connectors Figure 3-27 shows the bulkhead view of an FDDI access card (FAC).
Figure 3-27 : FDDI Access Card Interface connector type: media interface connector (MIC); two MIC connectors per port, one for transmit and one for receive
Connectors per access card: four, one labeled A (red) and one labeled B (blue) for each of two ports. The MIC connectors are keyed to ensure proper cable connections to the access card.
This cable is used to connect a multimode FDDI access card to another FDDI device. Cisco Systems does not provide this cable; it is widely available from other sources.
The FDDI interface operates at a wavelength of 1300 nanometers.
FDDI cables should conform to the following specifications:
Cabling: 62.5 micron core, graded-index fiber with an optical loss of 11 dB and a maximum cable attenuation of 1.5 dB/km at 1300 nanometers.
Maximum path length (all cables in a connection from end to end): 2 km
Figure 3-28 shows a physical representation of the FDDI cable.
Ethernet Connectors and Cables
This section describes the bulkhead connectors and cables for the Ethernet access card (EAC).
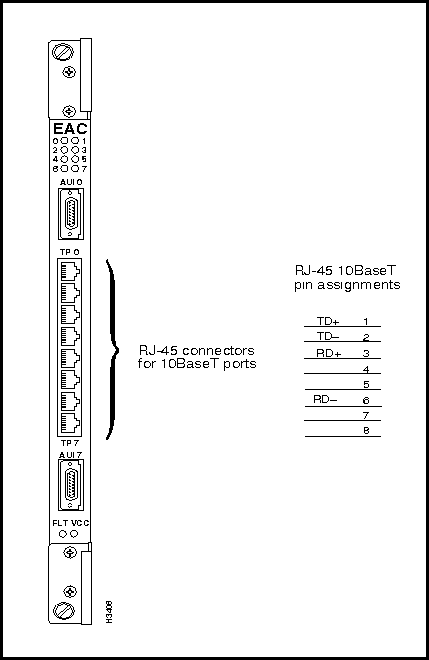
Figure 3-29 shows the bulkhead view of the Ethernet access card, which includes eight RJ-45 connectors and two attachment unit interface (AUI) DB-15 connectors. The RJ-45 connectors are used for the twisted pair Ethernet (10BaseT) ports.
Figure 3-29 : Ethernet Access Card and RJ-45 Connector Pin Assignments Ethernet Access Card 10BaseT (RJ-45) Connectors
Figure 3-29 shows the RJ-45 connectors and their pin assignments on the Ethernet access card. These connectors are used for Ethernet twisted pair (10BaseT) ports.
Cables for Ethernet Access Card RJ-45 Connectors
The cables used with the RJ-45 ports on the Ethernet access cards are described in the following sections.
Ethernet 10BaseT Straight-Through Cable
This cable is used for the following purposes:
Cisco Systems does not provide this cable; it is widely available from other sources.
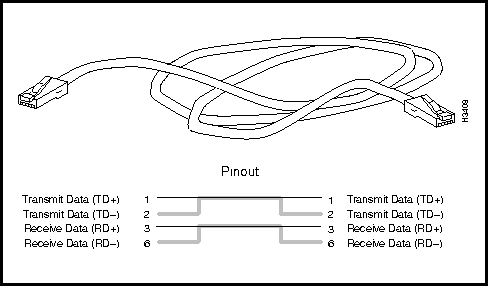
Figure 3-30 shows a physical representation of the Ethernet 10BaseT (twisted pair) straight-through cable and provides a schematic diagram of its pin assignments.
Figure 3-30 : Ethernet 10BaseT Straight-Through Cable and Pin Assignments Ethernet 10BaseT Crossover Cable
This cable is used to directly connect an Ethernet access card to another device on the Ethernet, such as a workstation.
Cisco Systems does not provide this cable; it is widely available from other sources.
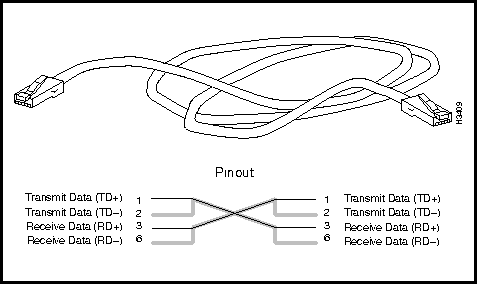
Figure 3-31 shows a physical representation of the Ethernet 10BaseT (twisted pair) crossover cable and provides a schematic diagram of its pin assignments.
Figure 3-31 : Ethernet 10BaseT Crossover Cable and Pin Assignments Ethernet Access Card AUI Connectors
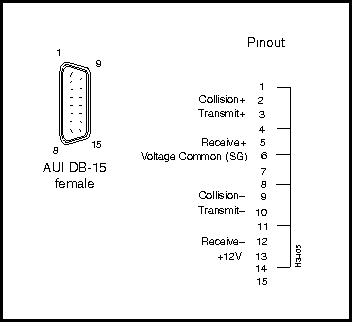
Figure 3-32 shows the pin assignments for the two 15-pin Ethernet AUI connectors on the Ethernet access card. The top AUI connector is for port 0, and the bottom connector is for port 7.
Figure 3-32 : Ethernet Access Card AUI Port (DB-15) Connector and Pin Assignments The AUI DB-15 connector pin assignments shown in Figure 3-32 apply to the following access cards:
Ethernet Access Card AUI Port Cable
This cable connects an AUI port on the Ethernet access card to an Ethernet 10Base2, 10Base5, or 10BaseFL transceiver. This cable also works with the Ethernet (E-NET) port on the network processor access card (NPAC).
Cisco Systems does not provide this cable; it is widely available from other sources.
Figure 3-33 shows a schematic diagram of the Ethernet access card AUI cable.
Figure 3-33 : Ethernet AUI Cable and Pin Assignments Fiber Ethernet Connectors and Cables
This section describes the fiber Ethernet access card (FEAC) connectors and associated data cable.
Fiber Ethernet Access Card Connectors
Figure 3-34 shows the bulkhead view of the fiber Ethernet access card (FEAC).
Figure 3-34 : Fiber Ethernet Access Card Fiber Ethernet Multimode Cable
This cable is used to connect a multimode fiber (10Base-FL) Ethernet access card to another fiber Ethernet device.
Cisco Systems does not provide this cable; it is widely available from other sources.
The fiber Ethernet interface operates at a wavelength of 850 nanometers.
Multimode fiber Ethernet cables should conform to the following specifications:
Standard: ISO/IEC 9314-3
Maximum path length (all cables in a connection from end to end): 2 km
Cabling: 62.5 micron core with an optical loss of 0 -- 9 dB, or 50 micron core with an optical loss of 7 dB. You should not mix 62.5 and 50 micron cables in a single fiber optic link.
Figure 3-35 illustrates the multimode fiber Ethernet access card cable equipped with ST connectors.
Figure 3-35 : Multimode Fiber Ethernet Cable with ST Connectors Console/Modem Assembly Connectors and Cables
Figure 3-36 shows the bulkhead view of the console/modem assembly located in the rear of the LS2020 chassis.
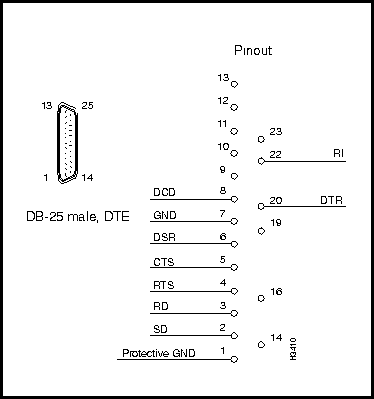
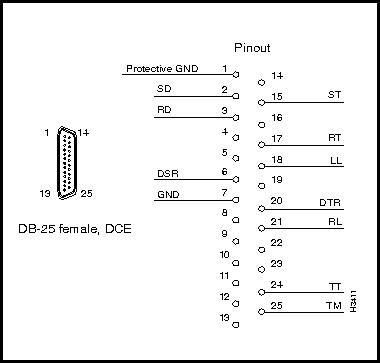
Figure 3-36 : Console/Modem Assembly Figure 3-37 shows the pin assignments of the RS-232 modem port (DB-25 connector). This port is labeled MODEM on the bulkhead of the console/modem assembly located in the rear of the LS2020 chassis (see Figure 3-36).
Figure 3-37 : RS-232 Modem Port (DB-25) Connector and Pin Assignments Figure 3-38 shows the pin assignments of the RS-232 console port (DB-25 connector). This port is labelled CNSL on the bulkhead of the console/modem assembly located in the rear of the LS2020 chassis (see Figure 3-36).
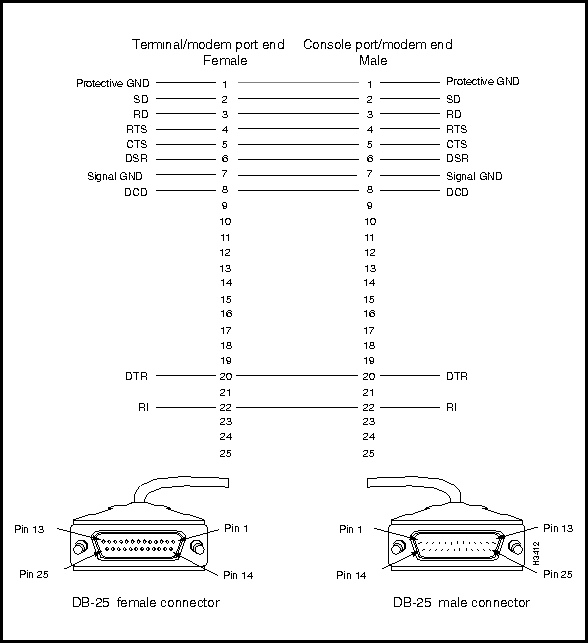
Figure 3-38 : RS-232 Console Port (DB-25) Connector and Pin Assignments This cable is used to connect the console or modem port on the LS2020 console/modem assembly to an external console or modem.
Cisco Systems does not provide this cable; it is widely available from other sources.
Figure 3-39 shows the DB-25 connectors associated with the RS-232 straight-through data cable and provides a schematic diagram of the pin assignments for the cable.
Figure 3-39 : RS-232 Straight-Through Data Cable Connector and Pin Assignments BITS Interface (on Release 2 Switch Card)
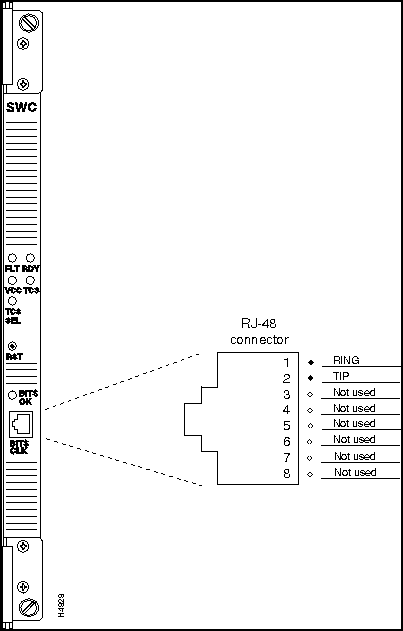
The Release 2 switch card incorporates a building-integrated timing source (BITS) interface for constant bit rate (CBR) applications. The BITS interface is a receive-only T1 line that extracts only the clock signal from a T1 line (data is discarded).
The clock signals provide a highly stable time reference for use in an LS2020 chassis or within the network. Figure 3-40 shows the bulkhead view of the Release 2 switch card and defines the pin assignments of the RJ48 connector for the BITS CLK port.
Figure 3-40 : Release 2 Switch Card BITS Interface and RJ-48 Connector Pin Assignments Country Kits and Power Cordsets
AC-Powered LightStream 2020 Systems
A variety of power cordsets is available for AC-powered LS2020 switches. These cordsets are available either with new system orders or as spare parts. This section provides information that will enable you to choose the proper cordset for your LS2020 site.
If you are specifying a cordset as part of a new system order, refer to the LS2020 price list or the Products Catalog and order the appropriate country power kit. Doing so ensures that you will also receive the appropriate labels and instructions for the country of destination.
If you want to check the cordset included in a specific country power kit, refer to Table 3-5, which cross-references cordset product numbers and country power kit models.
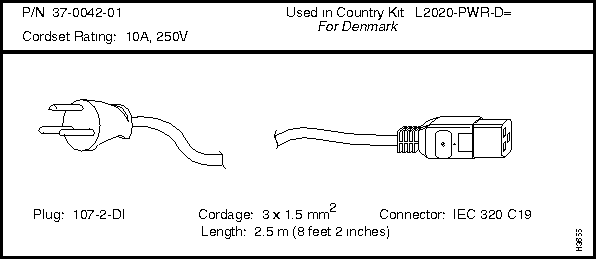
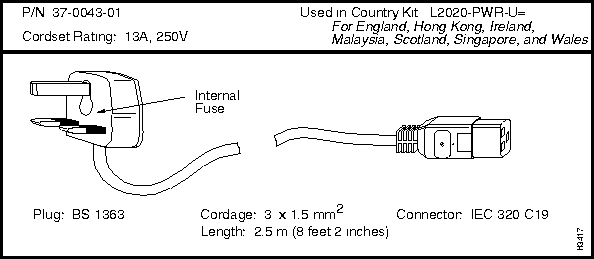
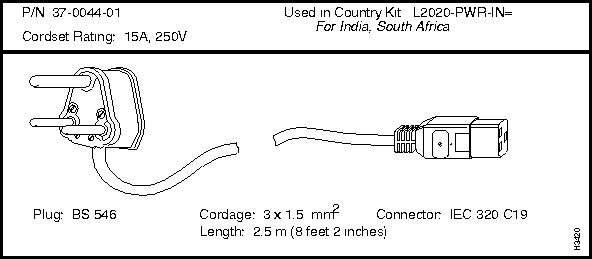
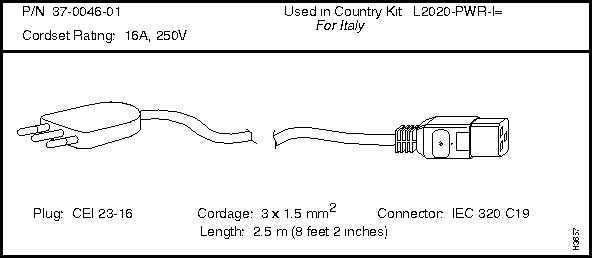
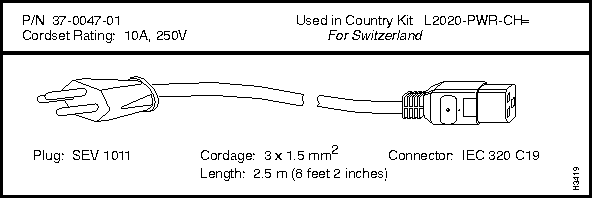
If you need to order a replacement cordset that is not part of a country power kit, you must reference the cordset's part number. This part number (P/N) appears above each cordset illustrated in the section below entitled "LightStream 2020 AC Power Cordsets."
DC-Powered LightStream 2020 Systems
A DC-powered system does not use a detachable power cord. Instead, a 48 VDC power source must be permanently wired to a DC power tray in the LS2020 chassis. This work should be done only by a licensed electrician or otherwise qualified individual.
A DC power kit is available (order number L2020-PWR-DC=) that provides the necessary attachment hardware (screws, nutclips, and washers) for installing a DC power tray in an LS2020 rack.
For instructions on wiring a DC-powered system, see the LightStream 2020 Installation Guide.
LightStream 2020 AC Power Cordsets
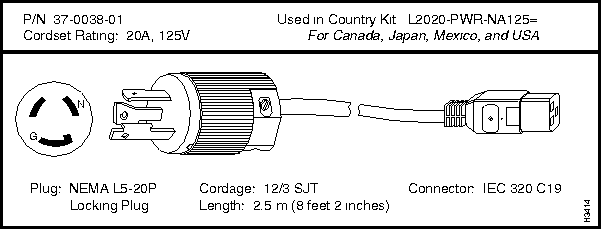
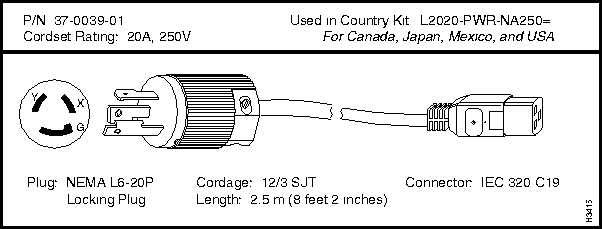
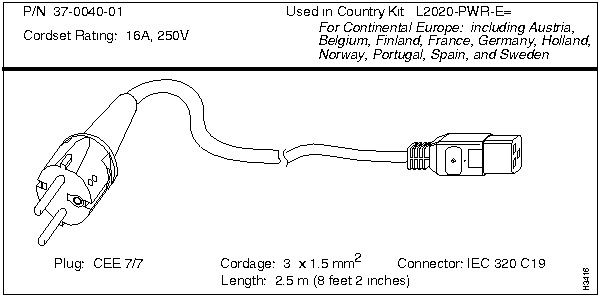
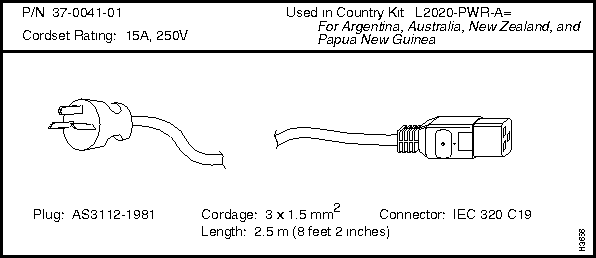
Each LS2020 AC power tray is equipped with one recessed male power inlet. The power connectors conform to IEC Standard 320 C20 and require cordsets with an IEC 320 C19 female connector. (All cordsets offered by Cisco Systems for the LS2020 switch have IEC 320 C19 female connectors.)
Each AC country power kit consists of a plastic bag containing a country-specific AC power cordset and sufficient attachment hardware for use in the 12 mounting slots in an LS2020 rack.
Table 3-5 summarizes the specifications of the AC power cordsets. The table lists the country of use, the cordset rating, its plug type, its manufacturing part number, and the country power kit order number for each cordset.
Following Table 3-5 is a series of illustrations summarizing the specifications of all the power cordsets available for the LS2020 switch. These summaries are arranged according to the cordset manufacturing part number.
Table 3-5 : Specifications for LightStream 2020 AC Power Cordsets
Copyright 1988-1996 © Cisco Systems Inc.
Transmit Power
Receive Power
Minimum: -15 dBm
Maximum: -8 dBm
Minimum: -31 dBm
Maximum: -8 dBm
Transceiver Type
Maximum Path Loss
Intermediate Reach (IR)
16.0 dBm
Fiber Loss
(dB/km)
2 Splices
(1.0 dB loss)
4 Splices
(2.0 dB loss)
6 Splices
(3.0 dB loss)
8 Splices
(4.0 dB loss)
.30
50.00 km
46.67 km
43.33 km
40.00 km
.35
42.86 km
40.00 km
37.14 km
34.29 km
.40
37.50 km
35.00 km
32.50 km
30.00 km
.45
33.33 km
31.11 km
28.89 km
26.67 km
Fiber Loss
(dB/km)
2 Splices
(2.0 dB loss)
4 Splices
(4.0 dB loss)
6 Splices
(6.0 dB loss)
8 Splices
(8.0 dB loss)
.30
46.67 km
40.00 km
33.33 km
26.67 km
.35
40.00 km
34.29 km
28.57 km
22.86 km
.40
35.00 km
30.00 km
25.00 km
20.00 km
.45
31.11 km
26.67 km
22.22 km
17.78 km
Vendor
Part Number
Quantity Required
3M
ADADA-MK 0001
Two (simplex)
AMP
503627-1
One (duplex)
Vendor
Part Number
Quantity Required
AMP
503137-5
One (duplex)

Country of Use
Cordset Rating
Plug Type
Mfg. Part
Number
Country Power Kit
Order Number
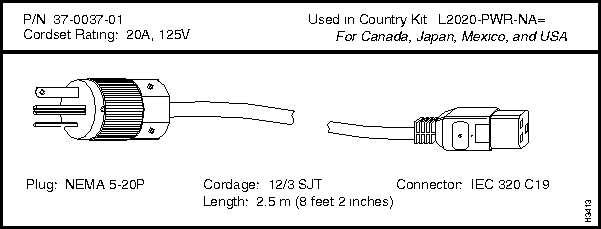
Canada, Mexico, Japan, and USA
125V @ 20A
NEMA 5-20P
37-0037-01
L2020-PWR-NA=
Canada, Mexico, Japan, and USA
125V @ 20A
NEMA L5-20P
37-0038-01
L2020-PWR-NA125=
Canada, Mexico, Japan, and USA
250V @ 20A
NEMA L6-20P
37-0039-01
L2020-PWR-NA250=
Continental Europe, including Austria, Belgium, Finland, France, Germany, Holland, Norway, Portugal, Spain, and Sweden
250V @ 16A
CEE 7/7
37-0040-01
L2020-PWR-E=
Argentina, Australia, New Zealand, and Papua New Guinea
250V @ 15A
AS3112-1981
37-0041-01
L2020-PWR-A=
Denmark
250V @ 10A
107-2-DI
37-0042-01
L2020-PWR-D=
England, Hong Kong, Ireland, Malaysia, Scotland, Singapore, and Wales
250V @ 13A
BS 1363
37-0043-01
L2020-PWR-U=
India and South Africa
250V @ 15A
BS 546
37-0044-01
L2020-PWR-IN=
Israel
250V @ 16A
SI 32
37-0045-01
L2020-PWR-IS=
Italy
250V @ 16A
CEI 23-16
37-0046-01
L2020-PWR-I=
Switzerland
250V @ 10A
SEV 1011
37-0047-01
L2020-PWR-CH=

![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()