|
|
Installing Line Cards in the CDDI/FDDI Workgroup Concentrator
Product Numbers: WS-C1521=, WS-C1524=, WS-C1531=, and WS-C1533=
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) can damage equipment and impair electrical circuitry. It occurs when electronic components are improperly handled and can result in complete or intermittent failures. Always follow ESD-prevention procedures when removing and replacing components. Ensure that the chassis is electrically connected to earth ground using an ESD mat or a ground wire. Wear an ESD wrist strap, ensuring that it makes good skin contact. Connect the clip to an unpainted chassis frame surface to safely channel unwanted ESD voltages to ground. To properly guard against ESD damage and shocks, the wrist strap and cord must operate effectively. If no wrist strap is available, ground yourself by touching the metal part of the chassis.
![]()
This publication includes the procedures required to install Copper Distributed Data Interface/multilevel transmission (CDDI/MLT-3) and Fiber Distributed Data Interface (FDDI) line cards in the Workgroup Concentrator models that use these cards. The equal sign (=) appended to the product numbers designates parts as spares. The line cards provide master (M) and slave (S) ports.
The following sections are included:
Following are the cabling requirements for the line cards.
The multimode FDDI connectors on the concentrator accept 62.5/125-micron or 50/125-micron multimode fiber with standard FDDI media interface connectors (MICs). The single-mode connectors accept 8.7 to 10/125-micron single-mode fiber with standard FDDI ST-type connectors. Table 1 lists FDDI distance specifications and Figure 1 and Figure 2 illustrate single-mode and multimode connectors, respectively.
Table 1 FDDI Maximum Transmission Distances
| Transceiver Type | Max.imum Distance Between Stations |
|---|---|
| Single-mode | 18.6 miles (up to 30 km) |
| Multimode | 1.2 miles (up to 2 km) |
![]()
Figure 1 Single-Mode FDDI Interface Connector---ST Type
Figure 2 Multimode FDDI Interface Connector---MIC Type
Check all existing cables for conformance with CDDI/MLT-3 distance requirements and . Following are cable and distance specifications:
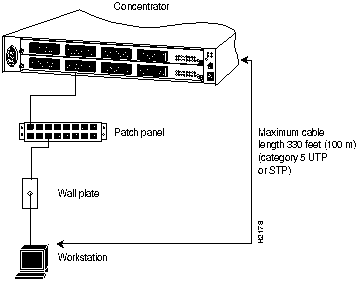
Figure 3 Category 5 UTP and STP Distance Requirement
When you plan your CDDI installation, remember the following:
Figure 4 shows the pinout for the CDDI/MLT-3 concentrator and adapter ports for M and S ports.
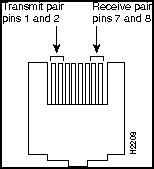
Figure 4 CDDI Concentrator Port Pin Arrangement
Following are pinouts and cabling requirements for CDDI UTP wiring. Table 2 lists the pinout used for the CDDI/MLT-3 transmit and receive pairs.
| Pin | Signal | Pin | Signal |
| 1 | TX+ | 5 | -- |
| 2 | TX-- | 6 | -- |
| 3 | -- | 7 | RX+ |
| 4 | -- | 8 | RX-- |
The EIA/TIA 568B wiring scheme is recommended and is listed in Table 3.
Table 3 EIA/TIA-568B RJ-45 Wiring Scheme
| Pin | Pair | Color | Pin | Pair | Color |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | White/orange | 5 | 1 | White/blue |
| 2 | 2 | Orange | 6 | 3 | Green |
| 3 | 3 | White/green | 7 | 4 | White/brown |
| 4 | 1 | Blue | 8 | 4 | Brown |
Figure 5 shows examples of modular cross-connect cables used for CDDI/MLT-3 connections between various devices using the CDDI-FDDI translator.
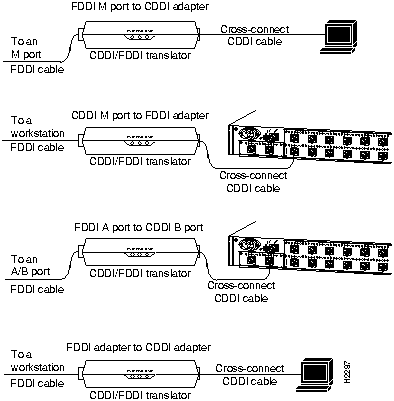
Figure 5 CDDI/MLT-3 Connections Using Cross-Connect Cable
The line cards are options that provide up to 16 CDDI/LT-3 or FDDI ports. The line cards support a single media access control (MAC), dual attachhment station (DAS) with dual homing configuration for FDDI (can also be used as a single attachment station [SAS]). The line card slots also accept a CDDI/MLT-3 card for UTP and STP connections. The following procedures describe how to install and remove port and line cards.
![]()
To add ports to the concentrator, use the optional line cards, which are shown in Figure 6. The following line-card models are available:
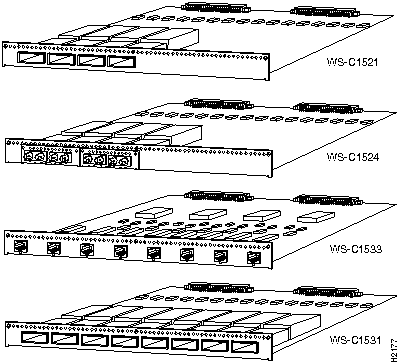
Figure 6 CDDI and FDDI Line Cards
Following is the procedure for installing a line card:
![]()
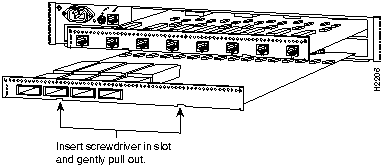
Figure 7 Installing or Removing Line Cards---WS-C1521 Shown
Following is the procedure for removing a line card:
![]()


|
|
Copyright 1988-1995 © Cisco Systems Inc.