|
|
Before the hardware installation of the ASM-CS can take place, certain prerequisites must be considered and implemented. This chapter includes information on the following pre-installation requirements:
To ensure general safety, follow these guidelines:
![]()
As stated previously, the successful installation of the ASM-CS should not require removing or replacing any printed circuit cards; however, if this becomes necessary, the following warning will appear at the beginning of any procedures requiring access to the ASM-CS interior.
Failure to observe this warning and act accordingly may increase the potential for shock hazard or electrocution. Before beginning a procedure that requires access to the ASM-CS interior, we strongly advise that you read through the entire procedure. If after reading the procedure, you have any doubts about your ability to perform any part, contact your service representative for information on how to proceed.
Following are basic guidelines for working near electricity:
Preventing Electrostatic Discharge Damage
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) damage, which occurs when electronic printed circuit cards are improperly handled, can result in complete or intermittent failures. ESD can impair electronic circuitry and equipment. Typically, the successful installation of the ASM-CS should not require handling any printed circuit cards; however, always follow ESD prevention procedures if removing and replacing cards becomes necessary.
Following are the guidelines for preventing ESD damage:
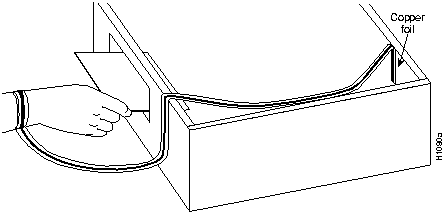
Step 1: Slip on an ESD wrist strap, ensuring that it makes good skin contact.
Step 2: Connect the strap to an unpainted chassis frame surface or another proper grounding point or surface to safely channel unwanted ESD voltages to ground (see Figure 2-1).
Figure 2-1 : Placement of ESD Wrist Strap Step 3: Use the ejectors to remove the card. Handle the card by its sides. Place the card on an antistatic surface or in a static shielding bag. To prevent further damage to the card by ESD voltages, defective cards must remain in the static shielding bag when they are returned for repair or replacement.
Step 4: Handling the new card by its edges only, insert it into the chassis. Avoid contact between the card and clothing. The wrist strap only protects the card from ESD voltages on the body; ESD voltages on clothing can still damage the card.
To preclude unintended shutdowns, the ASM-CS chassis must be properly installed and maintained.
The ASM-CS is designed to operate in a level, dry, clean, well-ventilated, and air-conditioned environment. The ASM-CS has an internal blower that pulls air through the card cage from left to right (with the chassis front facing you). If either the intake or exhaust vents are blocked in any way, this air-cooling function will be impaired, causing the ASM-CS to overheat. Excessive heat can damage the power supply and components.
If the ambient temperature of the air being drawn into the chassis is higher than desirable, the air temperature inside the chassis may also be too high. This condition can occur when the wiring closet or rack in which the chassis is mounted is not ventilated properly, when the exhaust of one chassis (or other electronic device) is placed so that it enters the air intake vent of the chassis, or when the chassis is the top unit in an unventilated rack. Precautions should be taken to avoid these conditions.
The following sections address the site environment requirements for the ASM-CS chassis.
The ASM-CS chassis can be used as a tabletop or rack-mounted system in a data processing or lab environment. Because the large cooling blower in the ASM-CS chassis is somewhat noisy (approximately 60 decibels), the chassis is intended for unattended or computer room use.
General environmental requirements for the ASM-CS chassis follow:
Table 2-1 provides the environmental design specifications for the ASM-CS.
Table 2-1 : Environmental Specifications
The proper location of the ASM-CS and the layout of your equipment rack or wiring closet are essential for successful system operation. Equipment placed too close together and inadequately ventilated can cause system malfunctions and shutdowns. In addition, chassis panels made inaccessible by poor equipment placement can make system maintenance difficult.
Read and follow the following precautions when planning your site layout and equipment locations; this will help avoid future equipment failures and reduce the likelihood of environmentally-caused shutdowns.
Use the installation checklist following to assist you with your installation, by allowing you to keep track of what was done, by whom, and when.
Make a copy of this checklist and mark your entries as each procedure is completed. Include a copy of the checklist for each system in your site log along with your records for the
Installation Checklist
for
__________________________________________________________
ASM-CS chassis name: ________________________________
ASM-CS chassis serial number: __________________________
A site log provides a historical record of all actions relevant to the ASM-CS system. Keep the site log in a common place near the chassis where anyone who performs tasks has access to it. Site log entries might include the following:
Following are the tools and equipment required to attach the rack-mount kit and install the chassis:
Network Connection Preparation
When setting up your system, you must consider a number of factors related to the cabling required for your connections. When using RS-232 connections, be aware of the distance limitations for signaling; electromagnetic interference may also be a factor. For telco connections, there are a variety of modular connectors from which to choose. Each of these cabling considerations is described in the following sections.
A variety of similar signaling schemes use the name RS-232. The following scheme, which is used in all modular and fixed-configuration products, is sufficient to control most modems and hardware flow control schemes. This scheme provides six signals per line, two of them outputs:
The line drivers are supplied with bipolar 12-volt power; an open output signal will be near +12 or -12 volts. The Receive Data input has a 10-kilo ohm resistor to the -12-volt supply that helps prevent open lines from ringing and causing spurious input to the communication server. An open Receive Data line will be near -7 volts, but can vary from -6 to -10 volts depending on temperature and component variation.
As with all signaling systems, RS-232 signals can travel a limited distance at any given baud rate; generally, the slower the data rate, the greater the distance. Table 2-2 shows the standard relationship between bit rate and distance.
Table 2-2 : IEEE Standard RS-232C Speed Versus Distance
When wires are run for any significant distance in an electromagnetic field, interference can occur between the field and the signals on the wires. This fact has two implications for the construction of terminal plant wiring:
If you use unsheilded twisted-pair (UTP) cables in your plant wiring with a good distribution of grounding conductors, the plant wiring is unlikely to emit radio interference. When exceeding the distances listed in Table 2-2, use a high-quality twisted-pair cable with one ground conductor for each data signal.
If wires exceed the distances in Table 2-2, or if wires pass between buildings, give special consideration to the effect of a lightning strike in your vicinity. The electromagnetic pulse (EMP) caused by lightning or other high-energy phenomena can easily couple enough energy into unshielded conductors to destroy electronic devices. If you have had problems of this sort in the past, you may want to consult experts in electrical surge suppression and shielding.
Most data centers cannot resolve the infrequent but potentially catastrophic problems just described without pulse meters and other special equipment. These problems can cost a great deal of time to identify and resolve, so take precautions to avoid these problems by providing a properly grounded and shielded environment, with special attention to issues of electrical surge suppression.
Console and Auxiliary Port Connection Considerations
You must adjust the baud rate of your terminal to match the ASM-CS console port default baud rate of 9600, 8 data bits, no parity, and 2 stop bits. Consult your terminal's documentation for this wiring specification. The console cable you received with the ASM-CS meets these requirements. If necessary, refer to Appendix A "Cabling Specifications" for the console port and auxiliary port wiring scheme required to connect the ASM-CS to a console terminal.
Terminal Wiring Considerations
The following sections contain considerations that may be helpful when planning modular wiring systems.
Three types of small connectors used on telephone sets are also used to construct terminal plant wiring:
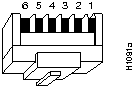
Generally, you can use the medium-sized connector with four contacts to connect a device that does not need modem control signals. You must use the medium-sized connector with six contacts to connect a device that needs modem control signals, or to provide optional modem control. Figure 2-2 shows a male six-position connector jack from the front, its non-cable end. When this connector is used to carry only four signals, positions 1 and 6 are not used.
Figure 2-2 : Six-Position Modular Jack---Front View Appendix C lists the usual correspondence between inside plant (wall-box) wiring and the modular-plug pin numbers in Figure 2-2. When you first use modular equipment from a particular manufacturer, check that the wire colors match the color code in Appendix C. Occasional variations are possible. For example, a manufacturer may substitute a slate-grey wire for a white wire or may reverse the order of the wires in the wire pairs.
Using a standard modular cord between two standard modular connectors reverses the sense of the wire pairs. As a result, the signal attached to pin 3 at one female jack is connected to pin 4 at the other end. Similarly, the signal attached to pin 1 at one female jack is connected to pin 6 at the other end.
Network Connection Considerations
You may need some of the following data communication equipment to complete your server installation. Your installation needs depend on many factors, including the interfaces you plan to use, as explained below.
Before unpacking the ASM-CS, determine where it will be installed. If its final installation site will not be ready for some time, keep the ASM-CS in the box in which it was shipped to prevent accidental damage. After you have chosen the site, proceed with the unpacking procedure.
Following is the procedure for unpacking the ASM-CS:
Step 1: Make certain the box containing the ASM-CS is upright.
Step 2: Make certain the areas where the ASM-CS will be unpacked and placed (even temporarily) are clear of debris.
Step 3: Remove any loose cables or material that could impede the removal of the ASM-CS and set these aside. Do not remove the packing material.
Step 4: Instead of trying to lift the heavy chassis out of the box, you can lift the much lighter box from around the chassis by proceeding as follows: carefully turn the box over so that the opened top of the box is now the bottom. Ensure that the four box flaps are away from the box opening.
Step 5: Carefully lift the box from around the chassis and packing material. It may be necessary to cut open the bottom of the box (the bottom can be taped up later) to hold down the chassis and packing material through the box.
Step 6: Carefully remove the chassis from the packing material enclosing it.
Step 7: Once the chassis is removed, place it out of the way and set the packing material and box aside.
Table 2-3 lists all of the components that are included in the ASM-CS.
Table 2-3 : ASM-CS Chassis Component Descriptions
Copyright 1988-1996 © Cisco Systems Inc.
![]()
![]()
Design Specifications
Description
Minimum
Maximum
Ambient temperature, operating
32°F (0°C)
104°F (40°C)
Ambient temperature,
nonoperating and storage
-6°F (-40°C)
167°F (75°C)
Ambient humidity, operating
5% RH,
noncondensing
95% RH,
noncondensing
Ambient humidity,
nonoperating and storage
5% RH,
noncondensing
95% RH,
noncondensing
Altitude, operating
-500 ft (-150 m)
10,000 ft (3050 m)
Altitude, nonoperating
-1000 ft (-305 m)
30,000 ft (9150 m)
Vibration, operating
5--500 Hz, 0.5 G (0.1 oct./min.)
Vibration, nonoperating
5--100 Hz, 1 G (0.1 oct./min.)
100--500 Hz, 1.5 G (0.2 oct./min.)
500--1000 Hz, 1.5 G (0.2 oct./min.)
ASM-CS.
Task
Verified by
Date
Installation checklist copied
Background information placed in site log
Required tools available
Additional equipment available
Environmental specifications verified
Power voltages verified
Installation site pre-power check completed
Date ASM-CS received
ASM-CS documentation received
Chassis components verified
Software version verified
Initial electrical connections established
ASCII terminal attached to console port
Signal distance limits verified
Startup sequence steps completed
Initial system operation verified
Baud Rate
Distance (Feet)
Distance (Meters)
2400
200
60
4800
100
30
9600
50
15
19200
25
7.6
38400
12
3.7
56000
8.6
2.6
![]()
Component
Description
Chassis buses
9-slot multibus backplane.
Processor cards
CSC/3 (or the optional CSC/4) processor.
Interface cards
Up to seven asynchronous interface cards (CSC-16) and one Ethernet, synchronous serial, or Token Ring interface.
System memory
CSC-MC NVRAM card
(or the optional CSC-MC+ Flash memory NVRAM card ).
External connectors
Mounting plates with connectors for attachment to various types of networks.
Accessories
Rack-mount kit that includes screws and two flanges for mounting the chassis in a standard 19-inch rack.
Power supplies
MAS-11 110 VAC or MAS-11B 240 VAC power supply
In the U.K., the MAS-26 240 VAC power supply is required.
Documentation
Communication Server Configuration and Reference, Getting Started Guide, ASM-CS Hardware Installation and Maintenance Manual, Internetworking Technology Terms and Acronyms, Cisco MIB User Quick Reference, System Error Messages, and Communication Server Quick Reference publications.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()