|
|
August 7, 1996
This document supplements the Cisco IOS Release 11.1 documentation set with new and changed commands that support the Cisco AS5200. Cisco IOS Release 11.1(474) supports the AS5200. This document discusses the software requirements for the AS5200 and also provides configuration tasks and command reference documentation for the new features available on the AS5200. It is divided into the following sections:
Use this document in conjunction with the Release Notes for Cisco IOS Release 11.1 and the Cisco IOS Release 11.1 configuration guide and command reference publications, specifically the Configuration Fundamentals Configuration Guide, Configuration Fundamentals Command Reference, Access Services Configuration Guide, Access Services Command Reference, and the Debug Command Reference. In addition, the 12-Port Modem AT Command Set and Register Summary publication, part of the AS5200 documentation set, is also referenced in this update.
Cisco IOS Release 11.1(474) supports the following platform:
Refer to "Cisco Connection Online (CCO), formerly Cisco Information Online (CIO), is Cisco Systems' primary, real-time support channel. Maintenance customers and partners can self-register on CCO to obtain additional content and services." at the end of this publication for lists of supported interfaces.
The following feature sets are available for the AS5200. Refer to "Feature Sets" at the end of this publication for a complete list of the features provided in these sets.
The AS5200 requires boot ROMs of level 11.1(473) or higher.
The memory requirements for feature sets available for the AS5200 are shown in Table 1.
Table 1 : Release 11.1(474) Memory Requirements
| AS5200 | Required Code Memory | Required Main Memory | Release 11.1 Runs from |
|---|---|---|---|
| IP/Managed Modems Set | 8 MB Flash | 8 MB RAM | Flash |
| Desktop/Managed Modems Set | 8 MB Flash | 8 MB RAM | Flash |
| Enterprise/RMON/
Managed Modems Set |
8 MB Flash | 8 MB RAM | Flash |
LAN and WAN Interfaces Supported
Table 2 summarizes the LAN interfaces supported on the AS5200.
Table 3 summarizes the WAN data rates and interfaces supported on the AS5200.
Table 2 : LAN Interfaces Supported
| Interface | AS5200 |
|---|---|
| Ethernet (AUI) | Yes |
| Ethernet (10BaseT) | --- |
| Fast Ethernet (100BaseT) | --- |
| 4-Mbps Token Ring | --- |
| 16-Mbps Token Ring | --- |
| FDDI DAS | --- |
| FDDI SAS | --- |
| FDDI multimode | --- |
| FDDI single-mode | --- |
| ATM Interface (AIP) | --- |
| Channel Interface (CIP) | --- |
| Parallel Channel Adapter (PCA) | --- |
| ESCON Channel Adapter (ECA) | --- |
| Versatile Interface (VIP) | --- |
| Channelized E1/T1 | Yes |
| Synchronous Serial | Yes |
Table 3 : WAN Data Rates and Interfaces Supported
| AS5200 | |
|---|---|
| Data Rate | |
| 48/56/64 kbps | Yes |
| 1.544/2.048 Mbps | Yes |
| 34/45/52 Mbps | --- |
| Interface | |
| EIA/TIA -232 | Yes |
| X.21 | Yes |
| V.35 | Yes |
| EIA/TIA-449 | Yes |
| EIA-530 | Yes |
| EIA/TIA-613 (HSSI) | --- |
| ISDN BRI | --- |
| ISDN PRI | Yes |
| E1-G.703/G.704 | Yes |
Table 4 lists the feature sets for the AS5200.
Table 4 : Cisco AS5200 Software Feature Sets
|
Feature |
Feature Set | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| IP/Managed Modems | Desktop/
Managed Modems |
Enterprise/RMON/
Managed Modems |
|
| SNMP | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| RMON1 | --- | --- | Yes |
| Asynchronous support (SLIP) | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| CSLIP | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| ARA Protocol | --- | Yes | Yes |
| Frame Relay | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| SMDS | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| X.25 | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| ISDN | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| PPP | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| CPPP | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| HDLC | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| IP | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| RIP | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| RIPv2 | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| IGRP | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Enhanced IGRP | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| OSPF | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| BGP | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| EGP | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| PIM | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| NHRP | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| ES-IS | --- | --- | Yes |
| IS-IS | --- | --- | Yes |
| Snapshot routing | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| NTP | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Bridging (transparent and translational) | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Multiring | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| LAN extension host | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| IPX | --- | Yes | Yes |
| NLSP | --- | Yes | Yes |
| IPXWAN 2.0 | --- | Yes | Yes |
| RTMP | --- | Yes | Yes |
| SMRP | --- | Yes | Yes |
| SRTP | --- | --- | Yes |
| AppleTalk Versions 1 and 2 | --- | Yes | Yes |
| AURP | --- | Yes | Yes |
| DECnet IV | --- | Yes | Yes |
| DECnet V | --- | --- | Yes |
| Apollo Domain | --- | --- | Yes |
| Banyan VINES | --- | --- | Yes |
| ISO CLNS | --- | --- | Yes |
| XNS | --- | --- | Yes |
| Lock-and-Key | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| MD5 routing authentication | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Kerberized login | --- | --- | Yes |
| V.120 | --- | --- | Yes |
| SRB | --- | --- | Yes |
| RSRB | --- | --- | Yes |
| APPN | --- | --- | --- |
| FRAS BAN | --- | --- | Yes |
| DLSw (RFC 1795) | --- | --- | Yes |
| DLSw+ | --- | --- | Yes |
| SDLC | --- | --- | Yes |
| SDLLC | --- | --- | Yes |
| STUN | --- | --- | Yes |
| TG/COS | --- | --- | Yes |
| QLLC | --- | --- | Yes |
| Bisync | --- | --- | Yes |
| DSPU | --- | --- | Yes |
| NetView Native Service Point | --- | --- | Yes |
| Protocol translation | --- | --- | Yes |
| TN3270 | --- | --- | Yes |
| LAT | --- | --- | Yes |
| SRT bridging | --- | --- | Yes |
| XRemote | --- | --- | Yes |
| Telnet | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| PAD | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| AutoInstall | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Modem autoconfiguring | --- | --- | Yes |
| Router monitoring | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| DHCP | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| NASI | --- | --- | --- |
| NetBEUI over PPP | --- | --- | --- |
| RADIUS | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Modem Management | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Update to Configuration Guides
The documentation in the sections below supplements the Configuration Fundamentals Configuration Guide and the Access Services Configuration Guide. Pointers to chapter titles and sections are shown in italic typeface.
Add the "Enable Digital and Analog Users to Access Network Resources" section and the "Configure Integrated Modems" section to the "Configuring Terminal Lines and Modem Support" chapter of the Access Services Configuration Guide.
Enable Digital and Analog Users to Access Network Resources
The Cisco AS5200 supports the needs of the following users:
Figure 1 shows how the AS5200 services these types of users.
Figure 1 : Cisco AS5200 Topology
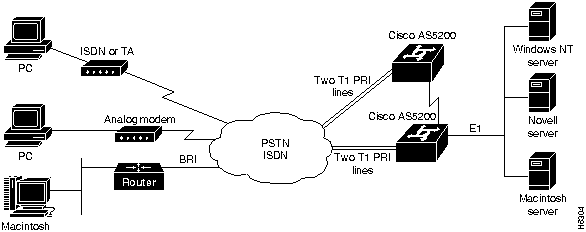
You can configure asynchronous services with the Cisco AS5200 using the Cisco IOS software. To access, monitor, test, and manage integrated modems, perform the tasks in the following sections:
Understand and Locate Integrated Modems
The Cisco AS5200 contains integrated V.34 modems that are manageable (also known as select) or nonmanageable (also known as reliable). Each manageable modem has one out-of-band port, which is used for polling modem statistics and creating a directly connected session for transmitting attention (AT) commands. Nonmanageable modems do not have out-of-band ports. As you use this document, note which commands apply to manageable versus nonmanageable modems.
Incoming ISDN and analog calls access the AS5200 through the dual T1 PRI interfaces. Unlike digital calls, incoming analog calls are first terminated and then converted to digital data at the modem card.
Each TTY line is directly mapped to an integrated AS5200 modem as shown in Table 5. The TTY lines 1 through 24 directly connect to modems 1/0 through 1/23, which are installed in the first chassis slot. The TTY lines 25 through 48 directly connect to modems 2/0 through 2/23, which are installed in the second chassis slot.
Table 5 : TTY Lines Associated to Integrated AS5200 Modems
| TTY Line | Slot/
Modem Port Number |
TTY Line | Slot/
Modem Port Number |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1/0 | 25 | 2/0 |
| 2 | 1/1 | 26 | 2/1 |
| 3 | 1/2 | 27 | 2/2 |
| 4 | 1/3 | 28 | 2/3 |
| 5 | 1/4 | 29 | 2/4 |
| 6 | 1/5 | 30 | 2/5 |
| 7 | 1/6 | 31 | 2/6 |
| 8 | 1/7 | 32 | 2/7 |
| 9 | 1/8 | 33 | 2/8 |
| 10 | 1/9 | 34 | 2/9 |
| 11 | 1/10 | 35 | 2/10 |
| 12 | 1/11 | 36 | 2/11 |
| 13 | 1/12 | 37 | 2/12 |
| 14 | 1/13 | 38 | 2/13 |
| 15 | 1/14 | 39 | 2/14 |
| 16 | 1/15 | 40 | 2/15 |
| 17 | 1/16 | 41 | 2/16 |
| 18 | 1/17 | 42 | 2/17 |
| 19 | 1/18 | 43 | 2/18 |
| 20 | 1/19 | 44 | 2/19 |
| 21 | 1/20 | 45 | 2/20 |
| 22 | 1/21 | 46 | 2/21 |
| 23 | 1/22 | 47 | 2/22 |
| 24 | 1/23 | 48 | 2/23 |
The following example shows TTY line 3 directly connected to modem 1/2, which is the third modem port in the first chassis slot:
AS5200# show modem 1/2
Mdm Typ Status Tx/Rx G Duration TX RX RTS CTS DSR DCD DTR
1/2 VFC Bad* 19200/19200 0 00:17:11 x x x x x x x
Modem 1/2, AS5200 Manageable Modem, TTY3
Firmware (Boot) Rev: 1.0.23(1.0.5)
Modem config: Incoming and Outgoing
Protocol: Normal, Compression: None
Management config: status and AT session polling
TX signals: -17 dBm, RX signals: -33 dBm
0 incoming completes, 0 incoming failures,
0 outgoing completes, 0 outgoing failures,
0 failed dial attempts, 0 ring no answers, 0 busied outs
0 no dial tones, 0 dial timeouts, 0 watchdog timeouts
0 no carriers, 0 link failures, 1 resets
0 protocol timeouts, 0 protocol errors, 0 lost events
2400- 2400-14400 14400+
# of connections 0 0 0
Mdm Typ Status Tx/Rx G Duration TX RX RTS CTS DSR DCD DTR
Monitor Modems and Enable Modem Events
You can view various modem statistics and configure modem events using the Cisco IOS software with the Cisco AS5200.
To show modem performance statistics, perform the following tasks in EXEC mode:
| Task | Command |
|---|---|
| Show various performance statistics for a modem or group of modems. | show modem [slot/modem-port | group number] |
| Show the call switching module status for a modem or group of modems. | show modem csm [slot/modem-port | group number] |
| Show the event log status for a modem or group of modems. | show modem log [slot/modem-port | group number]1 |
| Display the cumulative system statistics for all modems installed in the access server. | show modem summary1 |
| Display all directly connected AT sessions active on the access server. | show modem at-mode1 |
To create an asynchronous interface and use it as a group interface associated with a group of modems, refer to the "Configuring Interfaces" chapter in the Configuration Fundamentals Configuration Guide.
Enable Incoming and Outgoing Voice Calls
To enable incoming ISDN voice calls to access the AS5200 call switch module and integrated modems, perform the following task in interface configuration mode:
| Task | Command |
|---|---|
| Enable ISDN voice calls to dial into and dial out of the AS5200. | isdn incoming-voice modem1 |
Incoming ISDN digital calls are unaffected by this command.
See the "AS5200 Configuration Examples" section for the "ISDN Voice Calls Example" and the "Allocating Channels for Channelized T1."
To set the maximum amount of time the call switching module waits for a local modem to respond to a request before it is considered locked in a suspended state, perform the following task in global configuration mode:
| Task | Command |
|---|---|
| Set maximum time local modems will wait for a response. The default is 5 minutes. | modem recovery-time minutes |
This command does not apply to nonmanageable modems.
After the call switching module resets a suspended modem, the module recovers to a default call switching module state.
To configure the size of the history event queue buffer for manageable modems in the access server, perform the following task in global configuration mode:
| Task | Command |
|---|---|
| Define the number of modem events that each modem is able to store. The default is 100 events for each modem. | modem buffer-size number |
This command does not apply to nonmanageable modems.
Use the show modem log command to view modem events.
Troubleshoot and Manage Modems
This section describes how to troubleshoot the integrated modems and remove them from dial-up connection services.
To perform diagnostic testing on all the installed modems during the system's initial power-up or rebooting process, perform the following task in global configuration mode:
| Task | Command |
|---|---|
| Perform diagnostic testing for all modems. | modem startup-test |
The results of the modem startup test are displayed in the Status column of the show modem command's output. Modems that pass the diagnostic test are marked as Idle, Busy, Downloading, and Reset. Modems that fail the diagnostic test are marked as Bad*. These modems cannot be used for call connections. Depending on how many modems are installed, this diagnostic test may take from 5 to 15 minutes to complete.
Perform additional testing on an inoperative modem by executing the test modem back-to-back command. The no modem startup-test command disables startup testing.
See the "AS5200 Configuration Examples" section for the "Modem Startup Test Example."
Perform additional testing on a modem suspected of being inoperable by conducting a series of internal back-to-back connections and data transfers between two modems. All modem test connections occur inside the access server. For example, if mobile users cannot dial into modem 2/5, which is the sixth modem port on the modem board in the second chassis slot, attempt a back-to-back test with modem 2/5 and a known functioning modem such as modem 2/6.
Use the following command in EXEC mode to perform internal back-to-back modem tests between two modems:
| Task | Command |
|---|---|
| Perform internal back-to-back modem tests between two modems. | test modem back-to-back first-slot/modem-number second-slot/modem-number |
You might need to enable this command on several different combinations of modems to determine which one is not functioning properly. A pair of operable modems successfully connect and complete transmitting data in both directions. An operable modem and an inoperable modem do not successfully connect with each other.
See the "AS5200 Configuration Examples" section for the "Back-to-Back Modem Test Example."
Remove Inoperable Modems from Service
To remove modems from service and indicate them as suspected or proven to be inoperable, perform the following task in line configuration mode:
| Task | Command |
|---|---|
| Specify a modem as inoperable. | modem bad |
If you mark a single modem as inoperable using this command, it appears as Bad---without the asterisk (*)---in the Status column of the show modem command's output for that particular modem. A modem marked inoperable by the modem startup-test command appears as Bad* in the show modem command output for that particular modem. Use the no modem bad command to unmark a modem as Bad* or Bad and restore it for dial-up connection services.
See the "AS5200 Configuration Examples" section for the "Inoperable Modem Example."
To reset and isolate the modem hardware for extensive troubleshooting, perform the following task in line configuration mode:
| Task | Command |
|---|---|
| Reset and isolate the modem hardware. | modem hold-reset |
Use this command if you are experiencing extreme modem behavior (for example, if the modem is uncontrollably dialing into the network). This command prevents the modem from establishing software relationships such as those created by the test back-to-back modem command and the modem startup-test command. The modem is unusable while the modem hold-reset command is configured.
This command is also used to reset a modem that is frozen in a suspended state. Disable the suspended modem with the modem hold-reset command, and then restart hardware initialization with the no modem hold-reset command.
A modem decommissioned by the modem hold-reset command does not accept modem firmware upgrades using the copy modem command.
See the "AS5200 Configuration Examples" section for the "Hold and Reset Modem Example."
Disable a Modem from Dial-Up Services
To disable modems from dialing or answering calls, perform one of the following tasks in line configuration mode:
| Task | Command |
|---|---|
| Gracefully disable a modem from dial-up services. | modem busyout |
| Abruptly shut down a modem from dial-up services. | modem shutdown |
The modem busyout command is not executed until the active modem is idle. No active connections are interrupted when you use this command. In contrast, the modem shutdown command immediately terminates all active connections on the specified modem. The resulting modem status for both these commands is the same.
Enable the no form of these commands to restore a modem for dial-up services.
You can still configure the following commands on a disabled modem:
See the "AS5200 Configuration Examples" section for the "Disable Modem Examples."
To debug a modem or group of modems, perform the following tasks in EXEC mode:
| Task | Command |
|---|---|
| Debug a modem's out-of-band port, which is used to poll modem events. | debug modem oob [slot/modem-port | group group-number] |
| Debug a call switching module, which is used to connect calls. | debug modem csm [slot/modem-port | group group-number] |
| Debug the call trace, which determines why calls are terminated. Use this keyword only with manageable modems. Upload the call trace on normal, abnormal, or all call terminations. | debug modem trace [normal | abnormal | all] [slot/modem-port | group group-number] |
Use the debug modem command to do the following:
To create an asynchronous interface and use it as a group interface associated with a group of modems, refer to the "Configuring Interfaces" chapter in the Configuration Fundamentals Configuration Guide.
See the "AS5200 Configuration Examples" section for the "Debug Modem Example."
Send AT Commands to Manageable Modems
Each AS5200 manageable modem has one out-of-band port, which is used to poll modem statistics and transmit AT commands. The Cisco IOS software uses a directly connected session to transfer information to an out-of-band port. To transfer AT commands, you must permit a directly connected session on a modem, open a directly connected session and send AT commands to a modem, and clear a directly connected session from a modem.
Permit a Directly Connected Session
To permit a manageable modem to accept a directly connected session, which is enabled by default on all modems, perform the following task in line configuration mode:
| Task | Command |
|---|---|
| Permit a modem to accept a directly connected session. | modem at-mode-permit |
The no modem at-mode-permit command disables a modem from accepting a direct connection, which is useful for ensuring modem security.
See the "AS5200 Configuration Examples" section for the "Directly Connected Session Example."
Open a Directly Connected Session and Transmit AT Commands
To open a directly connected session and enable AT command mode, which is needed to transmit to a manageable modem, perform the following command in EXEC mode:
| Task | Command |
|---|---|
| Open a directly connected session and enter AT command mode. | modem at-mode slot/modem-port |
Once you enable this command, you can transmit AT commands directly from your terminal session. Most incoming or outgoing calls on the modem are not interrupted when you open a directly connected session and transmit AT commands. However, some AT commands interrupt a call---for example, the ATH AT command, which hangs up a call.
Open and close one directly connected session at a time. Multiple open directly connect sessions slow down modem performance.
Refer to the 12-Port Modem AT Command Set and Register Summary publication (part of the AS5200 documentation set) for a complete list of AT commands that you can transmit.
See the "AS5200 Configuration Examples" section for the "Transmit AT Command Example."
Clear a Directly Connected Session
You can clear or terminate an active directly connected session in two ways:
See the "AS5200 Configuration Examples" section for the "Clear Session from a Second Telnet Session Example."
Each manageable modem has one out-of-band port, which is used for polling modem statistics.
Set Time Interval between Polls
To set the time interval between the polls that are sent to the local modems for reporting modem status and statistics, perform the following task in global configuration mode:
| Task | Command |
|---|---|
| Specify the number of seconds between polls. The default is 12 seconds.The configuration range is 2 to 120 seconds. | modem poll time seconds |
See the "AS5200 Configuration Examples" section for the "Time Interval Example."
To poll for a modem's status and statistics through its out-of-band port, perform the following task in line configuration mode:
| Task | Command |
|---|---|
| Poll for a modem's status and statistics. | modem status-poll |
The no modem status-poll command disables status polling through the out-of-band port for a specified modem.
See the "AS5200 Configuration Examples" section for the "Modem Polling Example."
To set the maximum number of polling attempts used to retrieve a local modem's status or statistics, perform the following task in global configuration mode:
| Task | Command |
|---|---|
| Set maximum number of polling attempts. The default is three polling attempts. The configuration range is from 0 to 10 attempts. | modem poll retry number |
If the number of attempts to retrieve modem status or statistics exceeds the number you define, the out-of-band port is removed from operation. In this case, you must reset the modem hardware using the clear modem command.
See the "AS5200 Configuration Examples" section for the "Polling Attempts Example."
To download firmware to modems in the access server, perform one of the following tasks in EXEC mode:
| Task | Command |
|---|---|
| Copy modem firmware from Flash memory to a modem. | copy flash modem |
| Copy modem firmware from a TFTP server to a modem. | copy tftp modem |
| Copy modem firmware remotely from a network server to a modem. | copy rcp modem |
After you enter a command, you are prompted for the download destination, the remote host name, and the path leading to the source modem firmware as requested by the system software.
If a modem that you wish to upgrade is busy with a call when the copy modem command is enabled, the upgrade for that modem yields until the active call is dropped. All other idle modems in the upgrade range proceed with the downloading operation.
See the "AS5200 Configuration Examples" section for the "Download Firmware Examples."
Add the "Display an AS5200 Time Division Multiplexer" section to the "Configuring Interfaces" chapter of the Configuration Fundamentals Configuration Guide.
Display an AS5200 Time Division Multiplexer
The time division multiplexer (TDM) bus receives incoming digital data and digitized analog calls and redirects them to the PRI board and integrated modems. This section describes how to view a snapshot of the incoming TDM data and the internal TDM connections.
Each TDM bus device in the Cisco AS5200 contains two types of memory: connection memory and data memory. The TDM data memory holds the inbound and outbound frames. Each frame has 32 channels to be processed. The TDM connection memory determines the internal hardware connections for each channel held in data memory.
To display a snapshot of the TDM bus connection memory's output, perform the following task in EXEC mode:
| Task | Command |
|---|---|
| Display connection memory for the TDM. | show tdm connections [motherboard | slot number]1 |
Each TDM device has eight inputs and eight outputs. Each input and output is a serial stream of frames that has 32 channels (also known as timeslots) of data. The channel destinations held in connection memory are displayed in hexadecimal numbers. The five least significant bits represent the source channel. The three most significant bits represent the source stream (also known as the source frame). Up to eight streams and 32 possible channels per stream can be switched by each TDM device.
When an inbound modem call is received, the call switching module notifies the TDM driver to connect the inbound channel to a given modem. The call switching module is responsible for managing which modem gets chosen from the modem pool.
The show tdm connections command shows the connection memory for all TDM connections in the access server if you do not limit the display to the motherboard or a slot.
See the "AS5200 Configuration Examples" section for the "TDM Connection Memory Example."
To display a snapshot of the TDM bus data memory, which receives and processes incoming frames and channels from the network, perform the following task in EXEC mode:
| Task | Command |
|---|---|
| Display a snapshot of the TDM data memory. | show tdm data [motherboard | slot number]1 |
See the "AS5200 Configuration Examples" section for the "TDM Data Memory Example."
To display TDM bus connection information each time a connection is made, such as between the PRI card and a modem card, perform the following task in EXEC mode:
| Task | Command |
|---|---|
| Display source and destination connection information. One TDM device exists on the PRI board, on the motherboard, and on each modem board. | debug tdm |
Expect up to 256 TDM connections to be displayed on your terminal when this command is enabled.
Add the "Configure Channelized T1 on the Cisco AS5200" section to the "Configuring Terminal Lines and Modem Support" chapter of the Access Services Configuration Guide.
Configure Channelized T1 on the Cisco AS5200
The Cisco AS5200 Universal Access Server is an ISDN-capable access server that can make and receive ISDN and analog calls from remote clients needing access to network resources. The Cisco AS5200 has two T1 controllers, which can be configured individually.
On a Cisco AS5200, you can allocate the 24 available channels for channelized T1 in the following four ways:
To configure the T1 controllers in the Cisco AS5200, perform the tasks in the following sections:
Configure the T1 Controllers to Make and Receive Calls
Set parameters for a T1 controller to make and receive calls. To do so, perform the following steps beginning in global configuration mode:
| Task | Command |
|---|---|
| |
controller t1 0 |
| |
cablelength long dbgain-value dbloss-value |
| |
framing esf |
| |
linecode b8zs |
| |
clock source line primary 1 |
| or If you are not running ISDN, configure channels to accept voice calls. or If you are not running ISDN, configure channels for synchronous serial communications. This step creates interfaces that you can configure. |
pri-group timeslots 1-24
cas-group 1 timeslots 1-24 channel-group 1 timeslots 1-24 |
| |
fdl {att | ansi} |
Repeat Steps 1 through 7 to configure T1 controller 1, making sure in Step 5 to select T1 controller 1's line as the secondary clock source. You do not have to configure the timeslots in the same way on the two T1 controllers. You can configure the timeslots on this second controller as needed, no matter how you configured the timeslots in T1 controller 0.
Configure the ISDN D-Channel Serial Interfaces
Once you create the interfaces,two corresponding D channel serial interfaces are automatically created. Serial interface 0:23 is the D channel for T1 controller 0, and serial interface 1:23 is the D channel for T1 controller 1. You must configure each serial interface to receive and make calls.
To configure an ISDN D-Channel serial interface, perform the following steps beginning in global configuration mode:
| Task | Command |
|---|---|
| |
interface serial 0:23 |
| |
isdn incoming-voice modem 1, 2 |
| |
dialer rotary-group number 3 |
Repeat Steps 1 through 3 for serial interface 1:23, which is the D channel on the second T1 controller.
Add the "Configure RMON for the AS5200" section to the "Managing the System" chapter in the Configuration Fundamentals Configuration Guide.
To set a Remote Monitoring (RMON) alarm or event, perform one of the following tasks in global configuration mode:
| Task | Command |
|---|---|
| Set an alarm on a MIB object. | rmon alarm number variable interval {delta | absolute} rising-threshold value [event-number] falling-threshold value [event-number] [owner string] |
| Add or remove an event in the RMON event table. | rmon event number [log] [trap community] [description string] [owner string] |
You can set an alarm on any MIB object in the access server. To disable an alarm, you must enable the no form of this command on each alarm you configure. You cannot disable all the alarms you configure at once. Refer to RFC 1757 to learn more about alarms and events and how they interact with each other.
See the "AS5200 Configuration Examples" section for the "RMON Alarm and Event Examples."
Add the "AS5200 Configuration Examples" section to the "Configuring Terminal Lines and Modem Support" chapter of the Access Services Configuration Guide.
The following section provides example AS5200 configurations, including a sample startup configuration:
Sample Startup Configuration for the Cisco AS5200
This section includes a complete start up configuration for the Cisco AS5200. This configuration includes a comprehensive setup for dialing in to IP, IPX, and AppleTalk networks.
Configuring Security
The following configuration establishes a base security and local database:
aaa new-model aaa authentication login default local aaa authentication login console none aaa authentication ppp default if-needed local username jojackso password 7 kjfow34899347xkccx username wmays password 7 dfl;fd45065rgkv;lhnk username bruth password 7 kldte40095565rgh89r9834 username hwilliam password 7 tyiewzl04540o3498c !
Setting the ISDN Switch Type
The following global configuration command sets the ISDN switch type:
isdn switch-type primary-5ess
Configuring IP Dialin
The following commands configure the appropriate interfaces for IP dialin:
controller T1 0 framing esf linecode b8zs clock source line primary pri-group timeslots 1-24 ! controller T1 1 framing esf linecode b8zs clock source line secondary pri-group timeslots 1-24 ! interface Serial0:23 isdn incoming-voice modem dialer rotary-group 1 ! interface Serial1:23 isdn incoming-voice modem dialer rotary-group 1 ! interface Loopback0 ip address 172.16.254.254 255.255.255.0 ! interface Ethernet0 ip address 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.0 ! interface Group-Async1 ip unnumbered Loopback0 ip tcp header-compression passive encapsulation ppp async mode interactive peer default ip address pool default dialer-group 1 dialer idle-timeout 3600 ppp authentication pap chap default group-range 1 48 ! interface Dialer1 ip unnumbered Loopback0 encapsulation ppp peer default ip address pool default ip local pool default 172.16.254.1 172.16.254.48 dialer in-band dialer-group 1 dialer idle-timeout 3600 ppp multilink ppp authentication chap pap default
Configuring Modem Lines
The following example configures modem lines 1 to 48:
line 1 48 autoselect during-login autoselect pppmodem InOut modem autoconfigure type microcom_hdms transport input all stopbits 1 rxspeed 57600 txspeed 57600 flowcontrol hardware login local
Assigning a Routing Protocol
The following commands configure enhanced IGRP:
router eigrp 202 network 172.16.0.0
Configuring a Dialin Pool, Domain Name, DNS Server, and NBNS Server
The following commands configure a range of IP addresses in an IP address pool, a domain name, and name servers:
ip domain-name cisco.com ip name-server 172.16.99.99 ! async-bootp dns-server 172.16.10.100 172.16.39.67 async-bootp nbns-server 172.16.200.200 172.16.201.200
Enabling IPX Dialin
The following commands enable IPX dialin:
dialer-list 1 protocol ip permit ipx routing 0060.3ef1.6f74 interface Loopback0 ipx network FEFEFE interface Ethernet 0 ipx network 123ABCD encapsulation SAP interface Group-Async1 group-range 1 48 ipx ppp-client Loopback0 interface Dialer1 ipx unnumbered loopback 0 dialer map ipx FEFEFE.0000.0c00.1234 name stock dialer map ipx FEFEFE.0000.0c00.4567 name john dialer map ipx FEFEFE.0000.0c00.89AB name cisco dialer-list 1 protocol ipx permit
Configuring AppleTalk Dialin
The following commands enable users running PPP applications to dial in to an AppleTalk network:
appletalk routing appletalk virtual-net 2 ATCP Zone appletalk cable-range 1-1 1.120 appletalk zone Ethernet appletalk client-mode
Allocating Channels for Channelized T1
You can configure the 24 channels of a channelized T1 to support ISDN PRI, robbed bit signaling, channel grouping, or a combination of all three.
Allocating all Channels for ISDN PRI
The following example shows you how to configure all 24 channels to support ISDN PRI on a Cisco AS5200:
AS5200(config)# controller T1 0 AS5200(config-controller)# pri-group timeslots 1-24 AS5200(config-controller)# %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Serial1:0, changed state to down %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Serial1:1, changed state to down %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Serial1:2, changed state to down %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Serial1:3, changed state to down %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Serial1:4, changed state to down %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Serial1:5, changed state to down %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Serial1:6, changed state to down %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Serial1:7, changed state to down %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Serial1:8, changed state to down %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Serial1:9, changed state to down %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Serial1:10, changed state to down %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Serial1:11, changed state to down %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Serial1:12, changed state to down %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Serial1:13, changed state to down %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Serial1:14, changed state to down %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Serial1:15, changed state to down %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Serial1:16, changed state to down %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Serial1:17, changed state to down %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Serial1:18, changed state to down %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Serial1:19, changed state to down %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Serial1:20, changed state to down %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Serial1:21, changed state to down %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Serial1:22, changed state to down %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Serial1:23, changed state to up %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface Serial1:23, changed state to up
Allocating all Channels for Robbed Bit Signaling
The following example shows you how to configure all 24 channels to support robbed bit signaling on a Cisco AS5200:
AS5200(config)# controller T1 0 AS5200(config-controller)# cas-group 1 timeslots 1-24 AS5200(config-controller)# %DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 1 timeslot 1 is up %DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 1 timeslot 2 is up %DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 1 timeslot 3 is up %DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 1 timeslot 4 is up %DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 1 timeslot 5 is up %DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 1 timeslot 6 is up %DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 1 timeslot 7 is up %DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 1 timeslot 8 is up %DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 1 timeslot 9 is up %DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 1 timeslot 10 is up %DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 1 timeslot 11 is up %DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 1 timeslot 12 is up %DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 1 timeslot 13 is up %DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 1 timeslot 14 is up %DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 1 timeslot 15 is up %DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 1 timeslot 16 is up %DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 1 timeslot 17 is up %DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 1 timeslot 18 is up %DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 1 timeslot 19 is up %DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 1 timeslot 20 is up %DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 1 timeslot 21 is up %DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 1 timeslot 22 is up %DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 1 timeslot 23 is up %DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 1 timeslot 24 is up
Allocating all Channels to Server as One Channel Group
The following example shows you how to configure all 24 channels as one channel group on a Cisco AS5200:
AS5200(config)# controller T1 0 AS5200(config-controller)# channel-group 1 timeslots 1-24 AS5200(config-controller)# %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Serial1:1, changed state to down %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface Serial1:1, changed state to up %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Serial1:1, changed state to up
Mixing and Matching Channels
The following example shows you how to configure all 24 channels to support a combination of ISDN PRI, robbed bit signaling, and channel grouping. The range of timeslots that you allocate must match the timeslot allocations that your central office chooses to use. This is a rare configuration due to the complexity of aligning the correct range of timeslots on both ends of the connection.
The following configuration creates serial interfaces 0 to 9, which correspond to ISDN PRI timeslots 1 to 10 (shown as serial 1:0 through serial 1:9). The serial line 1:23 is the D channel, which carries the analog signal bits that dial a modem's phone number and determine if a modem is busy or available. The D channel is automatically created and assigned to timeslot 24.
AS5200(config)# controller T1 0 AS5200(config-controller)# pri-group timeslots 1-10 AS5200(config-controller)# %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Serial1:0, changed state to down %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Serial1:1, changed state to down %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Serial1:2, changed state to down %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Serial1:3, changed state to down %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Serial1:4, changed state to down %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Serial1:5, changed state to down %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Serial1:6, changed state to down %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Serial1:7, changed state to down %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Serial1:8, changed state to down %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Serial1:9, changed state to down %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Serial1:23, changed state to up %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface Serial1:23, changed state to up
Channelized T1 data is transmitted over timeslots 11 through 16, which are assigned to serial interface 1 and virtual channel group 11 (shown as serial 1:11) in the next configuration example. However, notice how the earlier attempt to configure channel group 1 is denied because timeslot 1 is used by the previous ISDN PRI group configuration:
AS5200(config-controller)# channel-group 1 timeslots 11-16 %Channel-group 1 is already an isdn channel AS5200(config-controller)# channel-group 11 timeslots 11-16 AS5200(config-controller)# %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Serial1:11, changed state to down AS5200(config-controller)# %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface Serial1:11, changed state to up %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Serial1:11, changed state to up
The channel associated signal E&M is configured on virtual signal group 17 for the remaining 17 to 23 timeslots, which are used for incoming and outgoing analog calls. There is no specific interface, such as the serial interface show in the earlier examples, that corresponds to the timeslot range. Notice how channel number 12 can not be used to configure these timeslots, because it is used in the previously configured channel group range, which is timeslots 11 to 16.
AS5200(config-controller)# cas-group 12 timeslots 17-23 The channel has been assigned to pri or channel-group AS5200(config-controller)# cas-group 17 timeslots 17-23 AS5200(config-controller)#
Back-to-Back Modem Test Example
The first part of the following example shows a successful connection between modem 2/1 and modem 2/0, which verifies normal operating conditions between these two modems. However, when modem 2/1 is tested against modem 2/3, the back-to-back modem test fails. Therefore, modem 2/3 is suspected or proven to be inoperable. Modem 2/3 is removed from dial-up services through the use of the modem bad command on line 28.
AS5200# test modem back-to-back 2/1 2/0 Repetitions (of 10-byte packets) [1]: 10 AS5200# %MODEM-5-B2BCONNECT: Modems (2/1) and (2/0) connected in back-to-back test: CONN ECT9600/REL-MNP %MODEM-5-B2BMODEMS: Modems (2/0) and (2/1) completed back-to-back test: success/ packets = 20/20 AS5200# test modem back-to-back 2/1 2/3 Repetitions (of 10-byte packets) [1]: 10 AS5200# %MODEM-5-BADMODEMS: Modems (2/3) and (2/1) failed back-to-back test: NOCARRIER AS5200# configure terminal AS5200(config)# line 28 AS5200(config-line)# modem bad AS5200(config-line)# end
Once you enter the test modem back-to-back command, you must define the number of packets transmitted between modems at the Repetitions prompt. The ideal range of packets to transmit and receive is from 1 to 100. The default is 1 packet. The response message (for example, "success/packets = 2/2") tells you how many packets were successfully sent in both directions compared to the total number of packets attempted to be sent in both directions. Because the software reports the packet total in both directions, the reported numbers are two times the number you originally specify.
Clear Session from a Second Telnet Session Example
The following example shows how to execute the modem at-mode command from a Telnet session:
AS5200# modem at-mode 1/1
The following example shows how to execute the clear modem at-mode command from a second Telnet session while the first Telnet session is connected to the modem:
AS5200# clear modem at-mode 1/1 clear "modem at-mode" for modem 1/1 [confirm] AS5200#
The following output is displayed in the first Telnet session once the modem is cleared by the second Telnet session:
Direct connect session cleared by vty0 (171.69.1.164)
The following example configures the Cisco AS5200 to use the T0 controller for the primary clocking source and the T1 controller as the secondary clocking source:
AS5200(config)# controller t1 0 AS5200(config-if)# clock source line primary AS5200(config)# AS5200(config)# controller t1 1 AS5200(config-if)# clock source line secondary
The following example is sample output from the debug modem trace abnormal command:
AS5200# debug modem trace abnormal 1/14
Modem 1/14 Abnormal End of Connection Trace. Caller 123-4567
Start-up Response: AS5200 Modem, Firmware 1.0
Control Reply: 0x7C01
DC session response: brasil firmware 1.0
RS232 event:
DSR=On, DCD=On, RI=Off, TST=Off
changes: RTS=No change, DTR=No change, CTS=No change
changes: DSR=No change, DCD=No change, RI=No change, TST=No change
Modem State event: Connected
Connection event: Speed = 19200, Modulation = VFC
Direction = Originate, Protocol = reliable/LAPM, Compression = V42bis
DTR event: DTR On
Modem Activity event: Data Active
Modem Analog signal event: TX = -10, RX = -24, Signal to noise = -32
End connection event: Duration = 10:34-11:43,
Number of xmit char = 67, Number of rcvd char = 88, Reason: Watchdog Time-out.
Directly Connected Session Example
The following example permits modem 1/1 on TTY line 1 to accept a directly connected session using the modem at-mode-permit command:
configure terminal line 1 modem at-mode-permit
The following example gracefully disables the modem associated with line 1 from dialing and answering calls. The modem is disabled only after all active calls on the modem are dropped.
configure terminal line 1 modem busyout
The following example abruptly shuts down the modem associated with line 2. All active calls on the modem are dropped immediately.
configure terminal line 2 modem shutdown
The following example shows how to copy the modem firmware file called modem_upgrade from the TFTP server called Modem_Server to modem 2/0, which is installed in the Cisco AS5200:
AS5200# copy tftp modem Modem Firmware Download Modem Numbers? 2/0 Address or name of remote host [UNKNOWN]? Modem_Server Source file name? dirt/elem/modem_upgrade Accessing file 'dirt/elem/modem_upgrade on Modem_Server... Loading dirt/elem/modem_upgrade .from 223.255.254.254 (via Ethernet0): ! [OK] Loading dirt/elem/modem_upgrade from 223.255.254.254 (via Ethernet0): !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! [OK - 237503/278528 bytes] AS5200# %MODEM-5-DL_START: Modem (2/0) started firmware download %MODEM-5-DL_GOOD: Modem (2/0) completed firmware download: MNPClass10V.34/V.FCModemRev1.0.23/85.23/85
Once the modem firmware successfully downloads, a response message reports the new version number of the installed modem firmware---for example Rev1.0.23/85.23/85---as shown the last line of this example.
The next time you use the copy tftp modem command, the interactive display shows the name of the previously accessed remote server as the default setting. For example, Modem_Server replaces UNKNOWN as shown in this example.
You might want to copy the file to one modem first for testing before copying the file to all the modems in the access server.
The following example shows how to download the same modem firmware file from the TFTP server Modem_Server to all the modems in the Cisco AS5200:
AS5200# copy tftp modem Modem Firmware Download Modem Numbers? all Address or name of remote host [UNKNOWN]? Modem_Server Source file name? dirt/elem/modem_upgrade Accessing file 'dirt/elem/modem_upgrade on Modem_Server... Loading dirt/elem/modem_upgrade .from 223.255.254.254 (via Ethernet0): ! [OK] Loading dirt/elem/modem_upgrade from 223.255.254.254 (via Ethernet0): !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! [OK - 237503/278528 bytes] AS5200# %MODEM-5-DL_START: Modem (2/0) started firmware download %MODEM-5-DL_START: Modem (2/1) started firmware download %MODEM-5-DL_START: Modem (2/2) started firmware download %MODEM-5-DL_START: Modem (2/3) started firmware download %MODEM-5-DL_START: Modem (2/4) started firmware download %MODEM-5-DL_START: Modem (2/5) started firmware download %MODEM-5-DL_START: Modem (2/6) started firmware download %MODEM-5-DL_START: Modem (2/7) started firmware download %MODEM-5-DL_START: Modem (2/8) started firmware download %MODEM-5-DL_START: Modem (2/9) started firmware download %MODEM-5-DL_START: Modem (2/10) started firmware download %MODEM-5-DL_START: Modem (2/11) started firmware download %MODEM-5-DL_START: Modem (2/12) started firmware download %MODEM-5-DL_START: Modem (2/13) started firmware download %MODEM-5-DL_START: Modem (2/14) started firmware download %MODEM-5-DL_START: Modem (2/15) started firmware download %MODEM-5-DL_START: Modem (2/16) started firmware download %MODEM-5-DL_START: Modem (2/17) started firmware download %MODEM-5-DL_START: Modem (2/18) started firmware download %MODEM-5-DL_START: Modem (2/19) started firmware download %MODEM-5-DL_START: Modem (2/20) started firmware download %MODEM-5-DL_START: Modem (2/21) started firmware download %MODEM-5-DL_START: Modem (2/22) started firmware download %MODEM-5-DL_START: Modem (2/23) started firmware download %MODEM-5-DL_GOOD: Modem (2/2) completed firmware download: MNPClass10V.34/V.FCModemRev1.0.23/85.23/85 %MODEM-5-DL_GOOD: Modem (2/10) completed firmware download: MNPClass10V.34/V.FCModemRev1.0.23/85.23/85 %MODEM-5-DL_GOOD: Modem (2/4) completed firmware download: MNPClass10V.34/V.FCModemRev1.0.23/85.23/85 %MODEM-5-DL_GOOD: Modem (2/6) completed firmware download: MNPClass10V.34/V.FCModemRev1.0.23/85.23/85 %MODEM-5-DL_GOOD: Modem (2/7) completed firmware download: MNPClass10V.34/V.FCModemRev1.0.23/85.23/85 %MODEM-5-DL_GOOD: Modem (2/12) completed firmware download: MNPClass10V.34/V.FCModemRev1.0.23/85.23/85 %MODEM-5-DL_GOOD: Modem (2/11) completed firmware download: MNPClass10V.34/V.FCModemRev1.0.23/85.23/85 %MODEM-5-DL_GOOD: Modem (2/13) completed firmware download: MNPClass10V.34/V.FCModemRev1.0.23/85.23/85 %MODEM-5-DL_GOOD: Modem (2/1) completed firmware download: MNPClass10V.34/V.FCModemRev1.0.23/85.23/85 %MODEM-5-DL_GOOD: Modem (2/14) completed firmware download: MNPClass10V.34/V.FCModemRev1.0.23/85.23/85 %MODEM-5-DL_GOOD: Modem (2/19) completed firmware download: MNPClass10V.34/V.FCModemRev1.0.23/85.23/85 %MODEM-5-DL_GOOD: Modem (2/22) completed firmware download: MNPClass10V.34/V.FCModemRev1.0.23/85.23/85 %MODEM-5-DL_GOOD: Modem (2/5) completed firmware download: MNPClass10V.34/V.FCModemRev1.0.23/85.23/85 %MODEM-5-DL_GOOD: Modem (2/8) completed firmware download: MNPClass10V.34/V.FCModemRev1.0.23/85.23/85 %MODEM-5-DL_GOOD: Modem (2/9) completed firmware download: MNPClass10V.34/V.FCModemRev1.0.23/85.23/85 %MODEM-5-DL_GOOD: Modem (2/17) completed firmware download: MNPClass10V.34/V.FCModemRev1.0.23/85.23/85 %MODEM-5-DL_GOOD: Modem (2/0) completed firmware download: MNPClass10V.34/V.FCModemRev1.0.23/85.23/85 %MODEM-5-DL_GOOD: Modem (2/3) completed firmware download: MNPClass10V.34/V.FCModemRev1.0.23/85.23/85 %MODEM-5-DL_GOOD: Modem (2/21) completed firmware download: MNPClass10V.34/V.FCModemRev1.0.23/85.23/85 %MODEM-5-DL_GOOD: Modem (2/16) completed firmware download: MNPClass10V.34/V.FCModemRev1.0.23/85.23/85 %MODEM-5-DL_GOOD: Modem (2/15) completed firmware download: MNPClass10V.34/V.FCModemRev1.0.23/85.23/85 %MODEM-5-DL_GOOD: Modem (2/18) completed firmware download: MNPClass10V.34/V.FCModemRev1.0.23/85.23/85 %MODEM-5-DL_GOOD: Modem (2/20) completed firmware download: MNPClass10V.34/V.FCModemRev1.0.23/85.23/85 %MODEM-5-DL_GOOD: Modem (2/23) completed firmware download: MNPClass10V.34/V.FCModemRev1.0.23/85.23/85
The first part of the following example shows a successful connection between modem 2/1 and modem 2/0, which verifies normal operating conditions between these two modems. However, when modem 2/1 is tested against modem 2/3, the back-to-back modem test fails. Therefore, modem 2/3 is suspected or proven to be inoperable. Modem 2/3 is removed from dial-up services through the use of the modem bad command on line 28 (see Table 5).
AS5200# test modem back-to-back 2/1 2/0 Repetitions (of 10-byte packets) [1]: 10 AS5200# %MODEM-5-B2BCONNECT: Modems (2/1) and (2/0) connected in back-to-back test: CONN ECT9600/REL-MNP %MODEM-5-B2BMODEMS: Modems (2/0) and (2/1) completed back-to-back test: success/ packets = 20/20 AS5200# test modem back-to-back 2/1 2/3 Repetitions (of 10-byte packets) [1]: 10 AS5200# %MODEM-5-BADMODEMS: Modems (2/3) and (2/1) failed back-to-back test: NOCARRIER AS5200# configure terminal AS5200(config)# line 28 AS5200(config-line)# modem bad AS5200(config-line)# end
The following example configures incoming and outgoing ISDN analog calls at the D channel serial interface:
AS5200(config)# interface serial 0:23 AS5200(config-if)# isdn incoming-voice modem AS5200(config-if)#
The following example disables a suspended modem and resets its hardware initialization:
configure terminal line 4 modem hold-reset no modem hold-reset
The following example enables modem status polling through the out-of-band port connected to line 1:
configure terminal line 1 modem status-poll
The following example shows how to perform a startup test on the integrated AS5200 modems:
configure terminal modem startup-test
Display the results of the modem-startup test after you reboot the system by enabling the show modem command as shown in the following example:
AS5200# show modem 2/3 Mdm Typ Status Tx/Rx G Duration TX RX RTS CTS DSR DCD DTR 2/3 VFC Bad* 19200/19200 0 00:17:11 x x x x x x x Modem 2/3, AS5200 Manageable Modem, TTY4 Firmware (Boot) Rev: 1.0.23(1.0.5) Modem config: Incoming and Outgoing Protocol: Normal, Compression: None Management config: status and AT session polling TX signals: -17 dBm, RX signals: -33 dBm
The following example configures the server to attempt to retrieve statistics from a local modem up to five times before discontinuing the polling effort.
configure terminal modem poll retry 5
The following example increases the receiver gain by 26 decibels and decreases the transmitting pulse by 7.5 decibels:
AS5200(config)# controller t1 0 AS5200(config-controller)# cablelength long gain26 -7.5db
The following example enables the rmon event command:
rmon event 1 log trap eventtrap description "High ifOutErrors" owner sdurham
This example creates RMON event number 1, which is defined as High ifOutErrors, and generates a log entry when the event is triggered by an alarm. The user sdurham owns the row that is created in the event table by this command. This example also generates a Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) trap when the event is triggered.
The following example configures an RMON alarm using the rmon alarm command:
rmon alarm 10 ifOutErrors.1 20 delta rising-threshold 15 1 falling-threshold 0 owner jjohnson
This example configures RMON alarm number 10. The alarm monitors the MIB variable ifOutErrors.1 once every 20 seconds until the alarm is disabled, and checks the change in the variable's rise or fall. If the ifOutErrors.1 value shows a MIB counter increase of 15 or more, such as from 100000 to 100015, the alarm is triggered. The alarm in turn triggers event number 1, which is configured with the rmon event command. Possible events include a log entry or a SNMP trap. If the ifOutErrors.1 value changes by 0, the alarm is reset and can be triggered again.
The following example sets the time interval between polls to 10 seconds using the modem poll time configuration command:
configure terminal modem poll time 10
The following example shows source stream 3 (ST3) channel 2 switched out of stream 6 (ST6) channel 2:
AS5200# show tdm connections motherboard MT8980 motherboard unit 0, Control Register = 0x1F, ODE Register = 0x06 Connection Memory for ST6: Ch0: 0x62, Ch1: 0x00, Ch2: 0x00, Ch3: 0x00 Ch4: 0x00, Ch5: 0x00, Ch6: 0x00, Ch7: 0x00 Ch8: 0x00, Ch9: 0x00, Ch10: 0x00, Ch11: 0x00 Ch12: 0x00, Ch13: 0x00, Ch14: 0x00, Ch15: 0x00 Ch16: 0x00, Ch17: 0x00, Ch18: 0x00, Ch19: 0x00 Ch20: 0x00, Ch21: 0x00, Ch22: 0x00, Ch23: 0x00 Ch24: 0x00, Ch25: 0x00, Ch26: 0x00, Ch27: 0x00 Ch28: 0x00, Ch29: 0x00, Ch30: 0x00, Ch31: 0x00
To interpret the hexadecimal number 0x62 into meaningful information, you must translate it into binary code. These two hexadecimal numbers represent a connection from any stream and a channel on any stream. The number 6 translates into the binary code 0110, which represents the third-source stream. The number 2 translates into the binary code 0010, which represents the second-source channel.
Stream 6 (ST6) channel 0 is the destination for source stream 3 (ST3) channel 2 in this example.
The following example shows a snapshot of TDM bus memory where the normal ISDN idle pattern (0x7E) is present on all channels of the TDM device resident on the motherboard:
AS5200# show tdm data motherboard MT8980 motherboard unit 0, Control Register = 0x1F, ODE Register = 0x06 Data Memory for ST0: Ch0: 0x7E, Ch1: 0x7E, Ch2: 0x7E, Ch3: 0x7E Ch4: 0x7E, Ch5: 0x7E, Ch6: 0x7E, Ch7: 0x7E Ch8: 0x7E, Ch9: 0x7E, Ch10: 0x7E, Ch11: 0x7E Ch12: 0x7E, Ch13: 0x7E, Ch14: 0x7E, Ch15: 0x7E Ch16: 0x7E, Ch17: 0x7E, Ch18: 0x7E, Ch19: 0x7E Ch20: 0x7E, Ch21: 0x7E, Ch22: 0x7E, Ch23: 0x7E Ch24: 0x7E, Ch25: 0x7E, Ch26: 0x7E, Ch27: 0x7E Ch28: 0x7E, Ch29: 0x7E, Ch30: 0x7E, Ch31: 0x7E Data Memory for ST1: Ch0: 0x7E, Ch1: 0x7E, Ch2: 0x7E, Ch3: 0x7E Ch4: 0x7E, Ch5: 0x7E, Ch6: 0x7E, Ch7: 0x7E Ch8: 0x7E, Ch9: 0x7E, Ch10: 0x7E, Ch11: 0x7E Ch12: 0x7E, Ch13: 0x7E, Ch14: 0x7E, Ch15: 0x7E Ch16: 0x7E, Ch17: 0x7E, Ch18: 0x7E, Ch19: 0x7E Ch20: 0x7E, Ch21: 0x7E, Ch22: 0x7E, Ch23: 0x7E Ch24: 0x7E, Ch25: 0x7E, Ch26: 0x7E, Ch27: 0x7E Ch28: 0x7E, Ch29: 0x7E, Ch30: 0x7E, Ch31: 0x7E
The following example opens a directly connected session on modem 1/1, enters AT command mode on modem 1/1, and transmits the ATH AT command through modem 1/1's out-of-band port:
AS5200# modem at-mode 1/1 You are now entering AT command mode on modem (slot 1 / port 1). Please type CTRL-C to exit AT command mode. at%v MNP Class 10 V.34/V.FC Modem Rev 1.0/85 OK at\s IDLE 000:00:00 LAST DIAL NET ADDR: FFFFFFFFFFFF MODEM HW: SA 2W United States 4 RTS 5 CTS 6 DSR - CD 20 DTR - RI MODULATION IDLE MODEM BPS 28800 AT%G0 MODEM FLOW OFF AT\G0 MODEM MODE AUT AT\N3 V.23 OPR. OFF AT%F0 AUTO ANS. ON ATS0=1 SERIAL BPS 115200 AT%U0 BPS ADJUST OFF AT\J0 SPT BPS ADJ. 0 AT\W0 ANSWER MESSGS ON ATQ0 SERIAL FLOW BHW AT`3 PASS XON/XOFF OFF AT\X0 PARITY 8N AT
The manageable modem returns "OK" if the AT command you transmit is successfully enabled.
The following example configures the ANSI T1.403 standard for the T1 controllers:
AS5200(config)# controller t1 0 AS5200(config-controller)# fdl ansi AS5200(config-controller)# exit AS5200(config)# controller t1 1 AS5200(config-controller)# fdl ansi
Commands in the Configuration Fundamentals Command Reference and the Access Services Command Reference publications have been added or changed. Use the following new or changed commands to configure the AS5200. Refer to the Cisco IOS Release 11.1 configuration guide and command reference publications for additional commands.
All commands are presented alphabetically in this document, although they are summarized by the chapter to which they belong as follows:
To increase the pulse of a signal at the receiver and decrease the pulse from the transmitter using pulse equalization and line build-out for a T1 cable on an AS5200, use the cablelength controller configuration command. To return the pulse equalization and line build-out values to their default settings, use the no form of this command.
Syntax Description
| long | Specifies a long cable length for channel service unit (CSU) connections. |
| dbgain-value | Number of decibels by which the receiver signal is increased. Use the keyword gain26 or gain36 to specify this value. |
| dbloss-value | Number of decibels by which the receiver signal is decreased. Use one of the following keywords to specify this value:
|
Default
Long cable length, receiver gain of 36 dB, and transmitter loss of 0 dB.
Command Mode
Controller configuration
Usage Guidelines
Use this command for configuring the controller T1 interface on the AS5200 access server.
A pulse equalizer regenerates a signal that has been attenuated and filtered by a cable loss. Pulse equalization does not produce a simple gain, but it filters the signal to compensate for complex cable loss. A gain26 receiver gain compensates for a long cable length equivalent to 26 dB of loss, while a gain36 compensates for 36 dB of loss.
The lengthening or building out of a line is used to control far-end crosstalk. Line build-out attenuates the stronger signal from the customer installation transmitter so that the transmitting and receiving signals have similar amplitudes. A signal difference of less than 7.5 dB is ideal. Line build-out does not produce simple flat loss (also known as resistive flat loss). Instead, it simulates a cable loss of 7.5 dB, 15 dB, or 22.5 dB so that the resulting signal is handled properly by the receiving equalizer at the other end.
Example
The following example increases the receiver gain by 26 decibels and decreases the transmitting pulse by 7.5 decibels for a long cable:
AS5200(config)# controller t1 0 AS5200(config-controller)# cablelength long gain26 -7.5db
To configure channelized T1 timeslots with channel associated signaling (also known as robbed bit signaling), which enables an AS5200 modem to answer and send an analog call, use the cas-group controller configuration command. Use the no form of this command to disable channel associated signaling for one or more timeslots.
Syntax Description
| channel-number | Specifies a single channel group number. The channel number can be between 0 and 23. |
| timeslots range | (Optional) Specifies a timeslot range of values from 1 to 24. The default value configures 24 timeslots with the channel associated signal called E&M (Ear and Mouth), which is the default signal type. |
Default
Disabled
Command Mode
Controller configuration
Usage Guidelines
Use this command to enable an AS5200 modem to receive and send incoming and outgoing analog calls through each T1 controller that is configured for a channelized T1 line, which has 24 possible channels.
Switched 56 digital calls are not supported under this new feature.
Example
The following example shows you how to configure all 24 channels to support robbed bit signaling on a Cisco AS5200:
AS5200(config)# controller T1 0 AS5200(config-controller)# cas-group 1 timeslots 1-24 AS5200(config-controller)# %DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 1 timeslot 1 is up %DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 1 timeslot 2 is up %DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 1 timeslot 3 is up %DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 1 timeslot 4 is up %DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 1 timeslot 5 is up %DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 1 timeslot 6 is up %DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 1 timeslot 7 is up %DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 1 timeslot 8 is up %DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 1 timeslot 9 is up %DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 1 timeslot 10 is up %DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 1 timeslot 11 is up %DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 1 timeslot 12 is up %DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 1 timeslot 13 is up %DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 1 timeslot 14 is up %DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 1 timeslot 15 is up %DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 1 timeslot 16 is up %DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 1 timeslot 17 is up %DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 1 timeslot 18 is up %DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 1 timeslot 19 is up %DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 1 timeslot 20 is up %DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 1 timeslot 21 is up %DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 1 timeslot 22 is up %DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 1 timeslot 23 is up %DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 1 timeslot 24 is up
To reset a manageable modem's hardware on an Cisco AS5200, use the clear modem EXEC command.
Syntax Description
| slot/modem-port | Slot and modem port number. Remember to include the forward slash (/) when entering this variable. |
| group group-number | Modem group. |
Default
Disabled
Command Mode
EXEC
Usage Guidelines
This command resets the specified modem or group of modems, or all the modems in the system. The modem hardware is reset for modems that are idle or busied out for log periods of time.
You can construct a logical modem group using the interface group-async command.
Example
The following example resets the hardware for manageable modem 1/1:
clear modem 1/1
To clear an attention (AT) directly connected session to a manageable modem from a second Telnet session into the AS5200, use the clear modem at-mode EXEC command.
Syntax Description
| at-mode | An AT directly connected session. |
| slot/modem-port | Slot and modem port number. Remember to include the forward slash (/) when entering this variable. |
Default
Disabled
Command Mode
EXEC
Usage Guidelines
This command applies only to the Cisco AS5200.
An AT directly connected session is usually initiated and closed from the same Telnet session by means of the modem at-mode command and Ctrl-C. However, you can clear an AT directly connected session that was mistakenly left open, by enabling the clear modem at-mode command from a second Telnet session into the access server.
Examples
The following example shows how to execute the modem at-mode command from a Telnet session:
modem at-mode 1/1
The following example shows how to execute the clear modem at-mode command from a second Telnet session while the first Telnet session is connected to the modem:
AS5200# clear modem at-mode 1/1 clear "modem at-mode" for modem 1/1 [confirm] AS5200#
The following output is displayed in the first Telnet session once the modem is cleared by the second Telnet session:
Direct connect session cleared by vty0 (171.69.1.164)
Related Command
modem at-mode
To clear the statistical counters on a manageable modem installed in an Cisco AS5200, use the clear modem counters EXEC command.
Syntax Description
| slot/modem-port | (Optional) Slot and modem port number. Remember to include the forward slash (/) when entering this variable. |
| group group-number | (Optional) Modem group. |
Default
Disabled
Command Mode
EXEC
Usage Guidelines
Entering the clear modem counters command without specifying an optional keyword or argument resets the modem statistics on each AS5200 modem and the summary statistics displayed in the show modem summary command.
You can create a logical modem group using the interface group-async command.
Example
The following example shows how clear the statistical counters on manageable modem 1/1:
clear modem counters 1/1
To select the clock source for the time division multiplexer (TDM) bus in a Cisco AS5200, use the clock source interface configuration command. The no form of this command configures the clock source to its default setting.
Syntax Description
| line | Clock source on the active line. |
| primary | Primary TDM clock source. |
| secondary | Secondary TDM clock source. |
| internal | Selects the free running clock (also known as internal clock) as the clock source. |
Defaults
Primary TDM clock source from the T0 controller
Secondary TDM clock source from the T1 controller
Command Mode
Interface configuration
Usage Guidelines
To use the clocking coming in from a T1 line, configure the clock source line primary command on the controller that has the most reliable clocking. Configure the clock source line secondary command on the controller that has the next best known clocking. With this configuration, the primary line clocking is backed up to the secondary line if the primary clocking shuts down.
Example
The following example configures the Cisco AS5200 to use the T0 controller as the primary clocking source and the T1 controller as the secondary clocking source:
AS5200(config)# controller t1 0 AS5200(config-if)# clock source line primary AS5200(config-if)# exit AS5200(config)# controller t1 1 AS5200(config-if)# clock source line secondary
To download firmware to modems in the Cisco AS5200, use the copy modem EXEC command.
Syntax Description
| flash | Copies firmware from Flash memory to the modem. |
| tftp | Copies firmware from the TFTP server to the modem. |
| rcp | Downloads a remote copy of the firmware from a network server to the modem. |
Default
Disabled
Command Mode
EXEC
Usage Guidelines
After you enable this command, you are asked to provide the download destination (a slot/modem-port or all), the remote host name, and the path leading to the source modem firmware.
If a modem that you wish to upgrade is busy with a call when the copy modem command is enabled, the upgrade for that modem yields until the active call is dropped. All other idle modems in the upgrade range proceed with the downloading operation.
Examples
The following example shows how to copy the modem firmware file called modem_upgrade from the TFTP server called Modem_Server to modem 2/0, which is installed in the Cisco AS5200:
AS5200# copy tftp modem Modem Firmware Download Modem Numbers? 2/0 Address or name of remote host [UNKNOWN]? Modem_Server Source file name? dirt/elem/modem_upgrade Accessing file 'dirt/elem/modem_upgrade on Modem_Server... Loading dirt/elem/modem_upgrade .from 223.255.254.254 (via Ethernet0): ! [OK] Loading dirt/elem/modem_upgrade from 223.255.254.254 (via Ethernet0): !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! [OK - 237503/278528 bytes] AS5200# %MODEM-5-DL_START: Modem (2/0) started firmware download %MODEM-5-DL_GOOD: Modem (2/0) completed firmware download: MNPClass10V.34/V.FCModemRev1.0.23/85.23/85
As shown in this example, you might want to upgrade and test one modem's firmware before upgrading all the modems' firmware on the access server, as shown in the next example.
This example shows how to download the same modem firmware file from the TFTP server to all the modems in the Cisco AS5200:
AS5200# copy tftp modem Modem Firmware Download Modem Numbers? all Address or name of remote host [UNKNOWN]? Modem_Server Source file name? dirt/elem/modem_upgrade Accessing file 'dirt/elem/modem_upgrade on Modem_Server... Loading dirt/elem/modem_upgrade .from 223.255.254.254 (via Ethernet0): ! [OK] Loading dirt/elem/modem_upgrade from 223.255.254.254 (via Ethernet0): !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! [OK - 237503/278528 bytes] AS5200# %MODEM-5-DL_START: Modem (2/0) started firmware download %MODEM-5-DL_START: Modem (2/1) started firmware download %MODEM-5-DL_START: Modem (2/2) started firmware download %MODEM-5-DL_START: Modem (2/3) started firmware download %MODEM-5-DL_START: Modem (2/4) started firmware download %MODEM-5-DL_START: Modem (2/5) started firmware download %MODEM-5-DL_START: Modem (2/6) started firmware download %MODEM-5-DL_START: Modem (2/7) started firmware download %MODEM-5-DL_START: Modem (2/8) started firmware download %MODEM-5-DL_START: Modem (2/9) started firmware download %MODEM-5-DL_START: Modem (2/10) started firmware download %MODEM-5-DL_START: Modem (2/11) started firmware download %MODEM-5-DL_START: Modem (2/12) started firmware download %MODEM-5-DL_START: Modem (2/13) started firmware download %MODEM-5-DL_START: Modem (2/14) started firmware download %MODEM-5-DL_START: Modem (2/15) started firmware download %MODEM-5-DL_START: Modem (2/16) started firmware download %MODEM-5-DL_START: Modem (2/17) started firmware download %MODEM-5-DL_START: Modem (2/18) started firmware download %MODEM-5-DL_START: Modem (2/19) started firmware download %MODEM-5-DL_START: Modem (2/20) started firmware download %MODEM-5-DL_START: Modem (2/21) started firmware download %MODEM-5-DL_START: Modem (2/22) started firmware download %MODEM-5-DL_START: Modem (2/23) started firmware download %MODEM-5-DL_GOOD: Modem (2/2) completed firmware download: MNPClass10V.34/V.FCModemRev1.0.23/85.23/85 %MODEM-5-DL_GOOD: Modem (2/10) completed firmware download: MNPClass10V.34/V.FCModemRev1.0.23/85.23/85 %MODEM-5-DL_GOOD: Modem (2/4) completed firmware download: MNPClass10V.34/V.FCModemRev1.0.23/85.23/85 %MODEM-5-DL_GOOD: Modem (2/6) completed firmware download: MNPClass10V.34/V.FCModemRev1.0.23/85.23/85 %MODEM-5-DL_GOOD: Modem (2/7) completed firmware download: MNPClass10V.34/V.FCModemRev1.0.23/85.23/85 %MODEM-5-DL_GOOD: Modem (2/12) completed firmware download: MNPClass10V.34/V.FCModemRev1.0.23/85.23/85 %MODEM-5-DL_GOOD: Modem (2/11) completed firmware download: MNPClass10V.34/V.FCModemRev1.0.23/85.23/85 %MODEM-5-DL_GOOD: Modem (2/13) completed firmware download: MNPClass10V.34/V.FCModemRev1.0.23/85.23/85 %MODEM-5-DL_GOOD: Modem (2/1) completed firmware download: MNPClass10V.34/V.FCModemRev1.0.23/85.23/85 %MODEM-5-DL_GOOD: Modem (2/14) completed firmware download: MNPClass10V.34/V.FCModemRev1.0.23/85.23/85 %MODEM-5-DL_GOOD: Modem (2/19) completed firmware download: MNPClass10V.34/V.FCModemRev1.0.23/85.23/85 %MODEM-5-DL_GOOD: Modem (2/22) completed firmware download: MNPClass10V.34/V.FCModemRev1.0.23/85.23/85 %MODEM-5-DL_GOOD: Modem (2/5) completed firmware download: MNPClass10V.34/V.FCModemRev1.0.23/85.23/85 %MODEM-5-DL_GOOD: Modem (2/8) completed firmware download: MNPClass10V.34/V.FCModemRev1.0.23/85.23/85 %MODEM-5-DL_GOOD: Modem (2/9) completed firmware download: MNPClass10V.34/V.FCModemRev1.0.23/85.23/85 %MODEM-5-DL_GOOD: Modem (2/17) completed firmware download: MNPClass10V.34/V.FCModemRev1.0.23/85.23/85 %MODEM-5-DL_GOOD: Modem (2/0) completed firmware download: MNPClass10V.34/V.FCModemRev1.0.23/85.23/85 %MODEM-5-DL_GOOD: Modem (2/3) completed firmware download: MNPClass10V.34/V.FCModemRev1.0.23/85.23/85 %MODEM-5-DL_GOOD: Modem (2/21) completed firmware download: MNPClass10V.34/V.FCModemRev1.0.23/85.23/85 %MODEM-5-DL_GOOD: Modem (2/16) completed firmware download: MNPClass10V.34/V.FCModemRev1.0.23/85.23/85 %MODEM-5-DL_GOOD: Modem (2/15) completed firmware download: MNPClass10V.34/V.FCModemRev1.0.23/85.23/85 %MODEM-5-DL_GOOD: Modem (2/18) completed firmware download: MNPClass10V.34/V.FCModemRev1.0.23/85.23/85 %MODEM-5-DL_GOOD: Modem (2/20) completed firmware download: MNPClass10V.34/V.FCModemRev1.0.23/85.23/85 %MODEM-5-DL_GOOD: Modem (2/23) completed firmware download: MNPClass10V.34/V.FCModemRev1.0.23/85.23/85
The following example shows how to copy the modem firmware file called STAR.M from Flash memory to the integrated modem 1/2:
AS5200# copy flash modem Modem Numbers (<slot>/<port> | group <number> | all)? 1/2 System flash directory: File Length Name/status 1 3539820 as5200-i-m.allcookies 2 239203 STAR.M 3 23072 BOOT.105 [3802288 bytes used, 4586320 available, 8388608 total] Source file name? STAR.M AS5200# %MODEM-5-DL_START: Modem (1/2) started firmware download %MODEM-5-DL_GOOD: Modem (1/2) completed firmware download: MNPClass10V.34/V.FCModemRev1.0.23/85.23/85 AS5200#
To set the facilities data link exchange standard for the CSU on the AS5200's T1 controllers, enter the fdl controller configuration command. The no form of this command disables this facilities data-link support.
Syntax Description
| att | Selects AT&T technical reference 54016 for extended superframe facilities data link exchange support. |
| ansi | Selects ANSI T1.403 for extended superframe facilities data link exchange support. |
Default
Disabled
Command Mode
Controller configuration
Usage Guidelines
You must configure this command on both T1 controllers if you want to support the CSU function on each T1 line. However, you must use the same facilities data link exchange standard as your service provider. You can have a different standard configured on each T1 controller.
Example
The following example configures the ANSI T1.403 standard for both T1 controllers:
AS5200(config)# controller t1 0 AS5200(config-controller)# fdl ansi AS5200(config-controller)# exit AS5200(config)# controller t1 1 AS5200(config-controller)# fdl ansi
To enable incoming ISDN voice calls to access the Cisco AS5200 call switch module and integrated modems, use the isdn incoming-voice modem interface configuration command. The no form of this command stops all incoming ISDN voice calls from routing to the modems.
Default
Disabled
Command Mode
Interface configuration
Usage Guidelines
Incoming ISDN digital calls are unaffected by this command. ISDN digital calls directly connect to network resources even when the no isdn incoming-voice modem command is configured.
Example
The following example enables incoming and outgoing ISDN calls to route to the modems using the D channel serial interface:
AS5200(config)# interface serial 0:23 AS5200(config-if)# isdn incoming-voice modem AS5200(config-if)#
To open a directly connected session and enter AT command mode on an Cisco AS5200, which is used for sending AT commands to a manageable modem, use the modem at-mode EXEC command.
Syntax Description
| slot/modem-port | Slot and modem port number. Remember to include the forward slash (/) when entering this variable. |
Default
Disabled
Command Mode
EXEC
Usage Guidelines
Manageable modems return "OK" if the AT command you transmit is successfully enabled. Press Ctrl-C after transmitting an AT command to close the directly connected session.
Example
The following example opens a directly connected session on modem 1/1, enters AT command mode on modem 1/1, and transmits the ATH AT command through modem 1/1's out-of-band port:
AS5200# modem at-mode 1/1 You are now entering AT command mode on modem (slot 1 / port 1). Please type CTRL-C to exit AT command mode. at%v MNP Class 10 V.34/V.FC Modem Rev 1.0/85 OK at\s IDLE 000:00:00 LAST DIAL NET ADDR: FFFFFFFFFFFF MODEM HW: SA 2W United States 4 RTS 5 CTS 6 DSR - CD 20 DTR - RI MODULATION IDLE MODEM BPS 28800 AT%G0 MODEM FLOW OFF AT\G0 MODEM MODE AUT AT\N3 V.23 OPR. OFF AT%F0 AUTO ANS. ON ATS0=1 SERIAL BPS 115200 AT%U0 BPS ADJUST OFF AT\J0 SPT BPS ADJ. 0 AT\W0 ANSWER MESSGS ON ATQ0 SERIAL FLOW BHW AT`3 PASS XON/XOFF OFF AT\X0 PARITY 8N AT
Related Command
clear modem at-mode
To permit a manageable modem installed in the Cisco AS5200 to accept a directly connected session, which is required to send AT commands, use the modem at-mode-permit line configuration command. The no form of this command disables permission for modems to accept a direct connection.
Syntax Description
This command has no keywords or arguments.
Default
Enabled
Command Mode
Line configuration
Usage Guidelines
After you enter this command, enter the modem at-mode command to enable a directly connected session on the modem. From AT command mode, you can enter AT commands directly from your terminal session.
Refer to the 12-Port Modem AT Command Set and Register Summary publication (part of the AS5200 documentation set) for a complete list and description of AT commands.
The no modem at-mode-permit command disables a modem from accepting a direct connection, which is useful for ensuring modem security.
Example
The following example permits the modem connected to TTY line 1 to accept a directly connected session:
line 1 modem at-mode-permit
Related Commands
clear modem at-mode
modem at-mode
To remove a modem, which is installed on a Cisco AS5200, from service and indicate it as suspected or proven to be inoperable, use the modem bad line configuration command. The no form of this command restores a modem to service.
Syntax Description
This command has no keywords or arguments.
Default
Disabled
Command Mode
Line configuration
Usage Guidelines
If you mark a modem as inoperable, it appears as Bad---without the asterisk (*)---in the Status column of the show modem command output. A modem marked inoperable by the modem startup-test command appears as Bad* in the show modem command output. Use the no modem bad command to unmark a modem as Bad* or Bad and restore it for dial-up connection services.
Example
The first part of the following example shows a successful connection between modem 2/1 and modem 2/0, which verifies normal operating conditions between these two modems. However, when modem 2/1 is tested against modem 2/3, the back-to-back modem test fails. Therefore, modem 2/3 is suspected or proven to be inoperable. Modem 2/3 is removed from dial-up services through the use of the modem bad command on line 28 (see Table 5).
AS5200# test modem back-to-back 2/1 2/0 Repetitions (of 10-byte packets) [1]: 10 AS5200# %MODEM-5-B2BCONNECT: Modems (2/1) and (2/0) connected in back-to-back test: CONN ECT9600/REL-MNP %MODEM-5-B2BMODEMS: Modems (2/0) and (2/1) completed back-to-back test: success/ packets = 20/20 AS5200# test modem back-to-back 2/1 2/3 Repetitions (of 10-byte packets) [1]: 10 AS5200# %MODEM-5-BADMODEMS: Modems (2/3) and (2/1) failed back-to-back test: NOCARRIER AS5200# configure terminal AS5200(config)# line 28 AS5200(config-line)# modem bad AS5200(config-line)# end
Related Commands
modem startup-test
show modem
test modem back-to-back
To configure the size of the history event queue buffer for manageable modems installed in a Cisco AS5200, use the modem buffer-size command.
Syntax Description
| number | Defined number of modem events that each manageable modem is able to store. |
Default
100 modem events
Command Mode
Global configuration
Usage Guidelines
A large buffer size uses significant amounts of processing memory. If the processing memory is running low, reduce the modem buffer size.
To view modem events, use the show modem log command.
Example
The following example enables each modem in the access server to store 150 modem events:
modem buffer-size 150
Related Command
show modem log
To gracefully disable a modem, which is installed in a Cisco AS5200, from dialing or answering calls, use the modem busyout line configuration command. The no form of this command reenables a modem.
Syntax Description
This command has no keywords or arguments.
Default
Disabled
Command Mode
Line configuration
Usage Guidelines
The disabling action is not executed until the active modem returns to an idle state. No active connections are interrupted when you use this command.
Example
The following example disables the modem associated with line 1 from dialing and answering calls. You do not specify a slot/modem-port number with this command:
line 1 modem busyout
Related Command
modem shutdown
To reset and isolate integrated modems for extensive troubleshooting, which are installed in a Cisco AS5200, use the modem hold-reset line configuration command. The no form of this command restarts a modem.
Syntax Description
This command has no keywords or arguments.
Default
Disabled
Command Mode
Line configuration
Usage Guidelines
This command is also used to reset a modem that is frozen in a suspended state. Disable the suspended modem with the modem hold-reset command, and then restart initialization with the no modem hold-reset command.
Example
The following example disables a suspended modem and resets its initialization:
configure terminal line 4 modem hold-reset no modem hold-reset
To set the maximum number of polling attempts used to retrieve performance statistics from a manageable modem installed on a Cisco AS5200, use the modem poll retry global configuration command.
Syntax Description
| number | Maximum number of polling attempts. The configuration range is from 0 to 10 attempts. |
Default
Three polling attempts
Command Mode
Global configuration
Usage Guidelines
Higher settings cause the software to keep polling one modem for status and to avoid polling other modems, which decreases the amount of statistics that are gathered.
Example
The following example configures the server to attempt to retrieve statistics from a local modem up to five times before discontinuing the polling effort:
modem poll retry 5
Related Commands
clear modem
modem poll time
modem status-poll
To set the time interval between modem polls, which report modem statistics on a Cisco AS5200, use the modem poll time global configuration command. To restore the default setting of the poll time, use the no form of this command.
Syntax Description
| seconds | Number of seconds between polls. The configuration range is 2 to 120 seconds. |
Default
Twelve seconds elapse between each modem poll.
Command Mode
Global configuration
Usage Guidelines
This command does not apply to nonmanageable modems.
Example
The following example sets the time interval between polls to 10 seconds:
modem poll time 10
Related Commands
modem poll retry
modem status-poll
To set the maximum amount of time the call switching module waits for a local modem to respond to a request before it is considered locked in a suspended state, use the modem recovery-time global configuration command. The no form of this command sets a 5-minute response time, which is the default setting.
Syntax Description
| minutes | Maximum amount of time local modems wait for a response. |
Default
5 minutes
Command Mode
Global configuration
Usage Guidelines
This command applies only to the Cisco AS5200.
After the call switching module resets a suspended modem, it recovers to a default call switching module state.
Example
The following example configures the call switching module to wait for 8 minutes:
modem recovery-time 8
To abruptly shut down an active or idle modem installed on an Cisco AS5200, use the modem shutdown line configuration command. The no form of this command takes the modem out of a shutdown state and places it back in service.
Syntax Description
This command has no keywords or arguments.
Default
Disabled
Command Mode
Line configuration
Usage Guidelines
Enable the no modem shutdown command to restore a shutdown modem for service.
Example
The following example abruptly shuts down the modem associated with line 2. All active calls on the modem are dropped immediately.
configure terminal line 2 modem shutdown
Related Command
modem busyout
To perform diagnostic testing on each modem during the Cisco AS5200's initial power-up or rebooting process, use the modem startup-test global configuration command. The no form of this command disables startup testing.
Syntax Description
This command has no keywords or arguments.
Default
Enabled
Command Mode
Global configuration
Example
The following example shows how to perform a startup test on the integrated AS5200 modems:
configure terminal modem startup-test
Display the results of the modem startup test after you reboot the system by enabling the show modem command.
Related Commands
show modem
test modem back-to-back
To poll for modem statistics through an out-of-band port in a Cisco AS5200, use the modem status-poll line configuration command. The no form of this command disables status polling through the out-of-band port for a specified modem.
Syntax Description
This command has no keywords or arguments.
Default
Enabled
Command Mode
Line configuration
Usage Guidelines
This command applies only to manageable modems that have out-of-band ports.
Example
The following example enables modem status polling through the out-of-band port through
TTY line 1:
configure terminal line 1 modem status-poll
Related Commands
modem poll retry
modem poll time
To set an alarm on any MIB object in the Cisco AS5200, use the rmon alarm configuration command. Use the no form of this command to disable the alarm.
Syntax Description
| number | Alarm number, which is identical to the alarmIndex in the alarmTable in the Remote Network Monitoring (RMON) MIB. |
| variable | MIB object to monitor, which translates into the alarmVariable used in the alarmTable of the RMON MIB. |
| interval | Time in seconds the alarm monitors the MIB variable, which is identical to the alarmValue used in the alarm table of the RMON MIB. |
| delta | Tests the change between MIB variables, which affects the alarmSampleType in the alarmTable of the RMON MIB. |
| absolute | Tests each MIB variable directly, which affects the alarmSampleType in the alarmTable of the RMON MIB. |
| rising-threshold value | Value at which the alarm is triggered. |
| event-number | (Optional) Event number to trigger when the rising or falling threshold exceeds its limit. This value is identical to the alarmRisiongEventIndex or the alarmFallingEventIndex in the alarm Table of the RMON MIB. |
| falling-threshold value | Value at which the alarm is reset. |
| owner string | (Optional) Specifies an owner for the alarm, which is identical to the alarm owner in the alarmTable of the RMON MIB. |
Default
No alarms configured
Command Mode
Global configuration
Usage Guidelines
To disable the RMON alarms, you must use the no form of the command on each configured alarm. For example, enter no rmon alarm 1, where the 1 identifies which alarm is to be removed.
See RFC 1757 for more information about the RMON alarm group.
Example
The following example configures an RMON alarm using the rmon alarm command:
rmon alarm 10 ifOutErrors.1 20 delta rising-threshold 15 1 falling-threshold 0 owner jjohnson
This example configures RMON alarm number 10. The alarm monitors the MIB variable ifOutErrors.1 once every 20 seconds until the alarm is disabled, and checks the change in the variable's rise or fall. If the ifOutErrors.1 value shows a MIB counter increase of 15 or more, such as from 100000 to 100015, the alarm is triggered. The alarm in turn triggers event number 1, which is configured with the rmon event command. Possible events include a log entry or a SNMP trap. If the ifOutErrors.1 value changes by 0, the alarm is reset and can be triggered again.
Related Commands
rmon event
show rmon
To add or remove an event in the RMON event table that is associated with an RMON event number, use the rmon event global configuration command. Use the no form of this command to disable RMON on the interface.
Syntax Description
| number | Assigned event number, which is identical to the eventIndex in the eventTable in the RMON MIB. |
| log | (Optional) Generates an RMON log entry when the event is triggered and sets the eventType in the RMON MIB to log or log-and-trap. |
| trap community | (Optional) SNMP community string used for this trap. Configures the setting of the eventType in the RMON MIB for this row as either snmp-trap or log-and-trap. This value is identical to the eventCommunityValue in the eventTable in the RMON MIB. |
| description string | (Optional) Specifies a description of the event, which is identical to the event description in the eventTable of the RMON MIB. |
| owner string | (Optional) Owner of this event, which is identical to the eventDescription in the eventTable of the RMON MIB. |
Default
No events configured
Command Mode
Global configuration
Usage Guidelines
This command applies only to the Cisco AS5200.
Example
The following example enables the rmon event command:
rmon event 1 log trap eventtrap description "High ifOutErrors" owner sdurham
This example configuration creates RMON event number 1, which is defined as High ifOutErrors, and generates a log entry when the event is triggered by an alarm. The user sdurham owns the row that is created in the event table by this command. This configuration also generates a Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) trap when the event is triggered.
See RFC 1757 for more information about the RMON MIB.
To show modem performance statistics on an Cisco AS5200, enable the show modem EXEC command.
Syntax Description
| csm | (Optional) Shows the internal status of the call switching module. |
| log | (Optional) Shows the modem history event status performed on a manageable modem or group of modems. |
| slot/modem-port | (Optional) Specifies the location of a slot and modem port. If this number is not specified, statistics for all connected modems are displayed. Remember to include the forward slash (/) when entering this variable. |
| group number | (Optional) Specifies the location of a specific group of modems. If this number is not specified, statistics for all modems in the access server are displayed. |
| summary | (Optional) Displays a cumulative statistics report for all manageable modems dialing into and out of the network. |
| at-mode | (Optional) Displays all AT sessions connected to manageable modems. |
Command Mode
EXEC
Usage Guidelines
The keywords log, summary, and at-mode apply only to manageable modems.
The number of events that you can record and view with the show modem log command is defined using the modem buffer-size command. The events stored in the buffer wrap around the event queue. You cannot clear the modem event queue.
Use the clear modem counters command to reset modem counters and clear the modem summary report of modem statistics.
Sample Displays
The following display shows output information for the show modem command:
AS5200# show modem
Inc calls Out calls Busied Failed No Succ
Mdm Usage Succ Fail Succ Fail Out Dial Answer Pct.
1/0 0% 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0%
1/1 0% 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0%
1/2 0% 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0%
1/3 0% 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0%
Table 6 describes the fields in the previous display
Table 6 : Show Modem Field Descriptions
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Mdm | Slot and modem port number. The following modem states can appear to the left of a slot/modem port number:
b---Modem was removed from service with the modem shutdown command or the modem busyout command. R---Modem is held and isolated in a suspended state by the modem hold-reset command. B---Modem is Bad*, Bad, or the downloaded firmware has failed. D---Modem is currently downloading firmware. T---Modem is conducting a back-to-back modem test. *---Modem is connected or dialing. |
| Usage | Percentage of the total system uptime that all modems are in use. |
| Inc calls | Number of incoming calls that successfully and unsuccessfully connected to an available AS5200 integrated modem. |
| Out calls | Number of outgoing calls that successfully and unsuccessfully dialed out from an available AS5200 integrated modem. |
| Busied Out | Number of modems that have been manually removed from service. |
| Failed Dial | Number of modems that attempted to dial into the network but failed to make a connection. |
| No Answer | Number of modems that detected an incoming ring but failed to answer the call. |
| Succ Pct. | Successful connection percentage of total available modems. |
The following example shows the statistics and current configurations for the manageable modem 1/1. A dash (-) indicates a field that is not available on nonmanageable modems. An x indicates a field that is available and active on manageable modems.
AS5200# show modem 1/1
Mdm Typ Status Tx/Rx G Duration TX RX RTS CTS DSR DCD DTR
1/1 V34 Idle 1200/1200 0 01:39:59 x x x x x x x
Modem 1/1, AS5200 Manageable Modem
Firmware (Boot) Rev: 1.0.1 (0.0.2)
Modem config: Incoming and Outgoing
Protocol: Normal, Compression: None
Management config: status and AT session polling
TX signals: -17 dBm, RX signals: -33 dBm
Last clearing of "show modem" counters 00:11:34
0 incoming completes, 0 incoming failures,
0 outgoing completes, 0 outgoing failures,
0 failed dial attempts, 0 ring no answers, 0 busied outs
0 no dial tones, 0 dial timeouts, 0 watchdog timeouts
0 no carriers, 0 link failures, 0 resets
0 protocol timeouts, 0 protocol errors, 0 lost events
2400- 2400-14400 14400+
# of connections 0 0 0
Table 7 describes the fields in the previous display.
Table 7 : Show Modem Slot/Modem Field Descriptions
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Mdm | Slot and modem number. |
| Typ | Modulation type. |
| Status | Current status of the modem. Possible values include
Conn---Modem is connected to a remote host. Bad---Inoperable state, which is configured by the modem bad command. Bad*---Inoperable state, which is configured by the modem startup-test command during initial power-up testing. Reset---Modem is in reset mode. D/L---Modem is downloading firmware. Bad FW---Downloaded modem firmware is not operational. Busy---Modem is out of service and not available for calls. Idle---Modem is ready for incoming and outgoing calls. |
| Tx/Rx | Transmission and receiving speed for the most recently connected call. |
| G | Modem group number assigned to the modem. The group number 0 means the modem is not part of any group. |
| Duration | Time duration of the current call or the last call. |
| Modem functions | The following modem functions are displayed on manageable modems. A field that is available and turned on is marked with an x. An unavailable field is marked with a dash (-).
TX---Transmit Data. The DTE transmits data to the DCE. RX---Receive Data. The DCE receives data from the DTE. RTS---Request To Send. The DTE signals to the DCE that the DTE accepts data into its buffers. CTS---Clear To Send. The DCE signals to the DTE that the DCE accepts data into its buffers. DSR---Data Set Ready. The modem is ready to start communication. DCD---Data Carrier Detect. The DCE indicates to the DTE that a call is present and established with a remote modem. Dropping the DCD function terminates the session. DTR---Data Terminal Ready. The DTE indicates to the DCE that it accepts calls. |
| Firmware | Installed modem firmware. |
| Modem config | Current modem configuration, which includes the fields Incoming, Outgoing, Incoming and Outgoing, and Unknown. |
| Protocol | Protocol the modem is running such as Normal, Direct, reliable/MNP, and reliable/LAPM (Link Access Procedure for Modems). |
| Compression | Compression algorithm running on the modem, such as None, V42bis, and MNP class 5. |
| Management config | Indicates if the modem is configured for out-of-band port polling. |
| TX signals | Analog signal levels that the modem transmits for signal-to-noise ratio. |
| RX signals | Analog signal levels that the modem receives for signal-to-noise ratio. |
| Last clearing of "show modem" counters | Last time the modem's counters were cleared using the clear modem counters command. A summary of modem events also appears.
|
| # of connections | Speed summary of the number of calls that have connected since the system has been up. Speed categories are 2400 bps, 2400--14400 bps, and 14400+ bps. |
The following example displays example output for a nonmanageable modem. Notice that unavailable fields are marked with dashes (-):
AS5200# show modem 1/1
Mdm Typ Status Tx/Rx G Duration TX RX RTS CTS DSR DCD DTR
1/1 - Idle 19200/19200 0 00:01:05 - - - - - - -
Modem 1/1, AS5200 Non-Manageable Modem
Firmware (Boot) Rev: Unknown
Modem config: Unknown
Management config: Not Manageable Modem
Last clearing of "show modem" counters never
- incoming completes, - incoming failures
- outgoing completes, - outgoing failures,
0 failed dial attempts, 0 ring no answers, 0 busied outs
0 no dial tones, 0 dial timeouts, 0 watchdog timeouts
- no carriers, - link failures, 0 resets
- protocol timeouts, - protocol errors, - lost events
2400- 2400-14400 14400+
# of connections - - -
The following example displays the call switching module information for modem 1/2:
AS5200# show modem csm 1/2 MODEM_INFO: slot 1, port 2, unit 130, modem_mask=0x0004, modem_port_offset=0 tty_hwidb=0x00000000, modem_tty=0x004370A8, mgmt_tty=0x004370A8, modem_pool=0x0041D99C csm_status(0): CSM_STATUS_UNLOCKED csm_state(0x00000000)=CSM_OC_STATE, csm_event_proc=0x0005B448 invalid_event_count=0, wdt_timeout_count=0 wdt_timestamp_started is not activated wait_for_dialing:False, wait_for_bchan:False pri_chnl=TDM_ISDN_STREAM(s0, c0), modem_chnl=TDM_ISDN_STREAM(s0, c0) dchan_idb_start_index=0, dchan_idb_index=0, call_id=0x0000, bchan_num=0 csm_event=CSM_EVENT_NONE, cause=0x0000, phone_num= ring_indicator=0, oh_state=0, oh_int_enable=0, modem_reset=0 ring_no_answer=0, ic_failure=0, ic_complete=0 dial_failure=0, oc_failure=0, oc_complete=0 oc_busy=0, oc_no_dial_tone=0, oc_dial_timeout=0 remote_link_disc=0, busyout=0, modem_reset=0 call_duration_started=00:00:00, call_duration_ended=00:00:00, total_call_duration=00:00:00 The calling party phone number = 4082968388 The called party phone number = 4085267406
Table 8 describes the most useful fields in the previous display.
Table 8 : Show Modem Call Switching Module Field Descriptions
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| MODEM_INFO | Displays internal data structure information. |
| csm_status | Displays the status of the call switching module. Possible displays include unlocked, active call, busyout req, shutdown, bad modem, modem hold, back-to-back, file downloading, and reset. |
| csm_state | Displays the current state of the call switching module. Possible states include idle and connected. Incoming calls are marked IC and outgoing calls are marked OC. |
| Modem counters | Counters for different modem events. |
| The calling party phone number
The called party phone number |
Phone numbers for the dialing integrated modem and the remote modem. |
The following example shows the event log status for a manageable modem and identifies the time elapsed since each modem event was performed (for example, 01:02:41 means the modem event occurred 1 hour, 2 minutes, and 41 seconds ago):
AS5200# show modem log 1/1
Modem 1/1 Events Log:
00:02:41: Startup Response: Brasil Modem
Modem (boot) firmware = 1.0.23 (1.0.5)
00:02:41: Control Reply: 0xFE01
00:02:41: RS232 event:
RTS=On, DTR=Off, CTS=On
DSR=On, DCD=On, RI=Off, TST=Off
changes: RTS=No change, DTR=Changed, CTS=Changed
changes: DSR=Changed, DCD=Changed, RI=No change, TST=No change
00:02:41: Modem Activity event: Data Active
00:02:41: RS232 event:
RTS=On, DTR=Off, CTS=On
DSR=On, DCD=On, RI=Off, TST=Off
changes: RTS=No change, DTR=No change, CTS=No change
changes: DSR=No change, DCD=No change, RI=No change, TST=No change
00:02:42: Modem State event: Idle
00:02:42: End connection event: Retransmits for MNP block (TX/RX) = 0/0
Duration = 0:00:00, Number of TX/RX char = 0/0
Local Disc Reason = Unknown, Remote Disc Reason = Unknown
00:02:29: DTR event: DTR On
00:02:29: RS232 event:
RTS=On, DTR=On, CTS=On
DSR=On, DCD=On, RI=Off, TST=Off
changes: RTS=No change, DTR=Changed, CTS=No change
changes: DSR=No change, DCD=No change, RI=No change, TST=No change
00:02:34: ISDN outgoing called number: 16664200
00:02:34: Modem State event: Dialing/Answering
00:02:22: Modem State event: Waiting for Carrier
00:01:58: Modem State event: Connected
00:01:58: Connection event: TX/RX Speed = 26400/26400, Modulation = V34
Direction = Originate, Protocol = reliable/MNP, Compression = V42bis
00:01:58: Modem Analog signal event: TX = -13, RX = -14, Signal to noise = -40
00:01:58: RS232 event:
RTS=On, DTR=On, CTS=On
DSR=On, DCD=Off, RI=Off, TST=Off
changes: RTS=No change, DTR=No change, CTS=No change
changes: DSR=No change, DCD=Changed, RI=No change, TST=No change
00:00:57: Modem State event: Disconnecting
00:00:57: Modem Activity event: Data Active
00:00:57: End connection event: Retransmits for MNP block (TX/RX) = 0/0
Duration = 0:00:59, Number of TX/RX char = 30/2061
Local Disc Reason = Remote Link Disc, Remote Disc Reason = DTR Drop
00:00:57: Modem State event: Idle
The following example shows the cumulative system statistics for all manageable modems on the access server:
AS5200# show modem summary
Incoming calls Outgoing calls Busied Failed No Succ
Usage Succ Fail Avail Succ Fail Avail Out Dial Ans Pct.
5% 2 0 12 0 0 0 0 0 0 100%
Table 9 describes the fields in the previous display.
Table 9 : Show Modem Summary Field Descriptions
| Fields | Descriptions |
|---|---|
| Incoming and Outgoing calls | Calls dialing into and out of the modem.
|
| Busied Out | Total number of times the modems were taken out of service with the modem busy command or the modem shutdown command. |
| Failed Dial | Total number of attempts the modems did not hang up or there was no dial tone. |
| No Ans | Total number of times call ringing was detected, but the calls were not answered by a modem. |
| Succ Pct. | Successful connection percentage of total available modems. |
The following example shows the sample display for modem group 1, which is composed of modem 1/0 through modem 1/23:
AS5200# show modem group 1
Incoming calls Outgoing calls Busied Failed No Succ
Grp Usage Succ Fail Avail Succ Fail Avail Out Dial Ans Pct.
1 0% 0 0 24 0 0 24 0 0 0 0%
Modem Group 1: 1/0, 1/1, 1/2, 1/3, 1/4, 1/5, 1/6, 1/7, 1/8, 1/9, 1/10, 1/11, 1/12, 1/13,
1/14, 1/15, 1/16, 1/17, 1/18, 1/19, 1/20, 1/21, 1/22, 1/23
The following example shows all the directly connected sessions currently using the internal out-of-band ports on the integrated manageable modems:
AS5200# show modem at-mode Active AT-MODE management sessions: Modem User's Terminal 1/1 0 cty 0
To display a snapshot of the time division multiplexer (TDM) bus connection memory in an Cisco AS5200, use the show tdm connections EXEC command.
Syntax Description
| motherboard | (Optional) Motherboard in the Cisco AS5200. |
| slot number | (Optional) Slot number. |
Command Mode
EXEC
Usage Guidelines
The show tdm connections command shows the connection memory for all TDM bus connections in the access server if you do not limit the display to the motherboard or a slot.
Sample Display
The following example shows source stream 3 (ST3) channel 2 switched out of stream 6 (ST6) channel 2:
AS5200# show tdm connections motherboard MT8980 motherboard unit 0, Control Register = 0x1F, ODE Register = 0x06 Connection Memory for ST6: Ch0: 0x62, Ch1: 0x00, Ch2: 0x00, Ch3: 0x00 Ch4: 0x00, Ch5: 0x00, Ch6: 0x00, Ch7: 0x00 Ch8: 0x00, Ch9: 0x00, Ch10: 0x00, Ch11: 0x00 Ch12: 0x00, Ch13: 0x00, Ch14: 0x00, Ch15: 0x00 Ch16: 0x00, Ch17: 0x00, Ch18: 0x00, Ch19: 0x00 Ch20: 0x00, Ch21: 0x00, Ch22: 0x00, Ch23: 0x00 Ch24: 0x00, Ch25: 0x00, Ch26: 0x00, Ch27: 0x00 Ch28: 0x00, Ch29: 0x00, Ch30: 0x00, Ch31: 0x00
To interpret the hexadecimal number 0x62 into meaningful information, you must translate it into binary code. These two hexadecimal numbers represent a connection from any stream and a channel on any stream. The number 6 translates into the binary code 0110, which represents the third-source stream. The number 2 translates into the binary code 0010, which represents the second-source channel.
Stream 6 (ST6) channel 0 is the destination for source stream 3 (ST3) channel 2 in this example.
To display a snapshot of the time division multiplexer (TDM) bus data memory in an Cisco AS5200, use the show tdm connections EXEC command.
Syntax Description
| motherboard | (Optional) Motherboard in the Cisco AS5200. |
| slot number | (Optional) Slot number. |
Command Mode
EXEC
Usage Guidelines
The data memory for all TDM bus connections in the access server is displayed if you do not specify a motherboard or slot.
Sample Display
The following example shows a snapshot of TDM memory where the normal ISDN idle pattern (0x7E) is present on all channels of the TDM device resident on the motherboard:
AS5200# show tdm data motherboard MT8980 motherboard unit 0, Control Register = 0x1F, ODE Register = 0x06 Data Memory for ST0: Ch0: 0x7E, Ch1: 0x7E, Ch2: 0x7E, Ch3: 0x7E Ch4: 0x7E, Ch5: 0x7E, Ch6: 0x7E, Ch7: 0x7E Ch8: 0x7E, Ch9: 0x7E, Ch10: 0x7E, Ch11: 0x7E Ch12: 0x7E, Ch13: 0x7E, Ch14: 0x7E, Ch15: 0x7E Ch16: 0x7E, Ch17: 0x7E, Ch18: 0x7E, Ch19: 0x7E Ch20: 0x7E, Ch21: 0x7E, Ch22: 0x7E, Ch23: 0x7E Ch24: 0x7E, Ch25: 0x7E, Ch26: 0x7E, Ch27: 0x7E Ch28: 0x7E, Ch29: 0x7E, Ch30: 0x7E, Ch31: 0x7E Data Memory for ST1: Ch0: 0x7E, Ch1: 0x7E, Ch2: 0x7E, Ch3: 0x7E Ch4: 0x7E, Ch5: 0x7E, Ch6: 0x7E, Ch7: 0x7E Ch8: 0x7E, Ch9: 0x7E, Ch10: 0x7E, Ch11: 0x7E Ch12: 0x7E, Ch13: 0x7E, Ch14: 0x7E, Ch15: 0x7E Ch16: 0x7E, Ch17: 0x7E, Ch18: 0x7E, Ch19: 0x7E Ch20: 0x7E, Ch21: 0x7E, Ch22: 0x7E, Ch23: 0x7E Ch24: 0x7E, Ch25: 0x7E, Ch26: 0x7E, Ch27: 0x7E Ch28: 0x7E, Ch29: 0x7E, Ch30: 0x7E, Ch31: 0x7E
To diagnose a modem that may not be functioning properly in an Cisco AS5200, use the test modem back-to-back EXEC command.
Syntax Description
| first-slot/modem-number | Slot and modem number of the first test modem. Remember to include the forward slash (/) when entering this variable. |
| second-slot/modem-number | Slot and modem number of the second test modem. Remember to include the forward slash (/) when entering this variable. |
Default
Disabled
Command Mode
EXEC
Usage Guidelines
Use this command to perform back-to-back testing of two modems. You might need to enable this command on several different combinations of modems to determine which one is not functioning properly.
Example
The following example shows how to perform a back-to-back modem test between modem 2/0 and modem 2/1 and removes modem 2/1, which is associated with TTY line 26, from all dial-in and dial-out services:
AS5200# test modem back-to-back 2/0 2/1 back2back 2/0 2/1 Repetitions (of 10-byte packets) [1]: AS5200# %MODEM-5-B2BCONNECT: Modems (2/0) and (2/1) connected in back-to-back test: CONNECT9600/REL-MNPM %MODEM-5-B2BMODEMS: Modems (2/0) and (2/1) completed back-to-back test: success/packets = 2/2
Related Command
modem bad
Update to Debug Command Reference
Add the following commands to the Cisco IOS Release 11.1 Debug Command Reference:
To debug an AS5200 modem's call switching module, use the debug modem csm EXEC command. Use the no form of this command to disable debug output.
Syntax Description
| slot/modem-port | (Optional) Slot and modem port number. Remember to include the forward slash (/) when entering this variable. |
| group group-number | (Optional) Modem group. |
Command Mode
EXEC
Usage Guidelines
Use the debug modem csm command to troubleshoot call switching problems. Once you enable this command, the whole sequence of switching of incoming calls and outgoing calls can be traced on the screen.
Sample Displays
The following example shows call switching module (csm) trace output when the debug modem csm is configured and an incoming call enters the modem:
AS5200(config)# service timestamps debug uptime AS5200(config)# end AS5200# debug modem csm Modem Management Call Switching Module debugging is on AS5200# 00:04:09: ccpri_ratetoteup bear rate is 10 00:04:09: CSM_MODEM_ALLOCATE: slot 1 and port 0 is allocated. 00:04:09: MODEM_REPORT(0001): DEV_INCALL at slot 1 and port 0 00:04:09: CSM_PROC_IDLE: CSM_EVENT_ISDN_CALL at slot 1, port 0 00:04:11: CSM_RING_INDICATION_PROC: RI is on 00:04:13: CSM_RING_INDICATION_PROC: RI is off 00:04:15: CSM_PROC_IC1_RING: CSM_EVENT_MODEM_OFFHOOK at slot 1, port 0
The following example shows csm trace output when the debug modem csm command is configured and an outgoing call is dialed from modem 1/2 into the network:
atdt16665202 00:11:21: CSM_PROC_IDLE: CSM_EVENT_MODEM_OFFHOOK at slot 1, port 2 00:11:21: T1_MAIL_FROM_NEAT: DC_READY_RSP: mid = 1, slot = 0, unit = 0 00:11:21: CSM_PROC_OC1_REQUEST_DIGIT: CSM_EVENT_DIGIT_COLLECT_READY at slot 1, port 2 00:11:24: T1_MAIL_FROM_NEAT: DC_FIRST_DIGIT_RSP: mid = 1, slot = 0, unit = 0 00:11:24: CSM_PROC_OC2_COLLECT_1ST_DIGIT: CSM_EVENT_GET_1ST_DIGIT at slot 1, port 2 00:11:27: T1_MAIL_FROM_NEAT: DC_ALL_DIGIT_RSP: mid = 1, slot = 0, unit = 0 00:11:27: CSM_PROC_OC3_COLLECT_ALL_DIGIT: CSM_EVENT_GET_ALL_DIGITS (16665202) at slot 1, port 2 00:11:27: ccpri_ratetoteup bear rate is 10 00:11:27: MODEM_REPORT(A000): DEV_CALL_PROC at slot 1 and port 2 00:11:27: CSM_PROC_OC4_DIALING: CSM_EVENT_ISDN_BCHAN_ASSIGNED at slot 1, port 2
To debug an AS5200 modem's out-of-band port, use the debug modem oob EXEC command. Use the no form of this command to disable debug output.
Syntax Description
| slot/modem-port | (Optional) Slot and modem port number. Remember to include the forward slash (/) when entering this variable. |
| group group-number | (Optional) Modem group. |
Command Mode
EXEC
Usage Guidelines
Entering the debug modem oob command without specifying a slot and modem number debugs all out-of-band ports in the AS5200, which produces an excessive amount of output information.
The message types and sequence numbers that appear in the command's output are initiated by the modem oob protocol and used by software developers for debugging purposes.
Sample Display
The following example debugs the out-of-band port on modem 2/0, which creates modem startup messages between the network management software and the modem:
AS5200# debug modem oob 2/0 MODEM(2/0): One message sent --Message type:3, Sequence number:0 MODEM(2/0): Modem DC session data reply MODEM(2/0): One mes%sage sent --Message type:83, Sequence number:1 MODEM(2/0): DC session event = MODEM(2/0): One message sent --Message type:82, Sequence number:2 MODEM(2/0): No status changes since last polled MODEM(2/0): One message sent --Message type:3, Sequence number:3 MODEM(2/0): Modem DC session data reply MODEM(2/0): One message sent --Message type:83, Sequence number:4
To debug an AS5200 modem's call trace, use the debug modem trace EXEC command. Use the no form of this command to disable debug output.
Syntax Description
| normal | (Optional) Uploads the call trace to the syslog server on normal call termination (for example, a local user hangup or a remote user hangup). |
| abnormal | (Optional) Uploads the call trace to the syslog server on abnormal call termination (for example, any call termination other than normal termination, such as a lost carrier or a watchdog timeout). |
| all | (Optional) Uploads the call trace on all normal and abnormal call termination. |
| slot/modem-port | (Optional) Slot and modem port number. Remember to include the forward slash (/) when entering this variable. |
| group group-number | (Optional) Modem group. |
Command Mode
EXEC
Usage Guidelines
The debug modem trace command applies only to manageable modems, which are modems that support modem polling and sending AT commands.
Sample Display
The following example is sample output from the debug modem trace abnormal command:
AS5200# debug modem trace abnormal 1/14
Modem 1/14 Abnormal End of Connection Trace. Caller 123-4567
Start-up Response: AS5200 Modem, Firmware 1.0
Control Reply: 0x7C01
DC session response: brasil firmware 1.0
RS232 event:
DSR=On, DCD=On, RI=Off, TST=Off
changes: RTS=No change, DTR=No change, CTS=No change
changes: DSR=No change, DCD=No change, RI=No change, TST=No change
Modem State event: Connected
Connection event: Speed = 19200, Modulation = VFC
Direction = Originate, Protocol = reliable/LAPM, Compression = V42bis
DTR event: DTR On
Modem Activity event: Data Active
Modem Analog signal event: TX = -10, RX = -24, Signal to noise = -32
End connection event: Duration = 10:34-11:43,
Number of xmit char = 67, Number of rcvd char = 88, Reason: Watchdog Time-out.
To display time division multiplexer (TDM) bus connection information each time a connection is made on the Cisco AS5200, use the debug tdm EXEC command. Use the no form of this command to disable debug output.
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Command Mode
EXEC
Usage Guidelines
If you are losing channel data between the dual T1 Primary Rate Interfaces (PRI) and any termination points, such as an Ethernet or modem point, enable the debug tdm command.
This command displays the TDM bus connection information for each TDM device installed in the access server. One TDM device exists on the PRI board, on the motherboard, and on each modem board. Expect up to 256 TDM connections to be displayed on your terminal when this command is enabled.
Example
The following example enables the debug tdm command:
debug tdm dialtone connection requested. TDM(reg: 0x2138100): Close connection to STo7, channel 1 TDM(reg: 0x2138100): Connect STi3, channel 1 to STo7, channel 1
Available 24 hours a day, 7 days a week, CCO provides a wealth of standard and value-added services to Cisco's customers and business partners. CCO services include product information, software updates, release notes, technical tips, the Bug Navigator, configuration notes, brochures, descriptions of service offerings, and download access to public and authorized files.
CCO serves a wide variety of users through two interfaces that are updated and enhanced simultaneously---a character-based version and a multimedia version that resides on the World Wide Web (WWW). The character-based CCO supports Zmodem, Kermit, Xmodem, FTP, Internet e-mail, and fax download options, and is excellent for quick access to information over lower bandwidths. The WWW version of CCO provides richly formatted documents with photographs, figures, graphics, and video, as well as hyperlinks to related information.
You can access CCO in the following ways:
http://www.cisco.com.
cco.cisco.com.
For a copy of CCO's Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ), contact
ccohelp@cisco.com.
For additional information, contact
ccoteam@cisco.com.
tac@cisco.com.
To obtain general information about Cisco Systems, Cisco products, or upgrades, contact 800 553-6387, 408 526-7208, or
csrep@cisco.com.

|
|
Copyright 1988-1996 © Cisco Systems Inc.