|
|
Overview of the Cisco 4000 Series Routers
The Cisco 4000 series consists of the Cisco 4000-M, the Cisco 4500-M, and the Cisco 4700-M. All models provide a configurable modular router platform using network processor modules---individual modules that when installed in the router are ready for external network connections. Performance is the key distinction between the Cisco 4000M, Cisco 4500-M, and Cisco 4700-M.
For maximum performance in the Cisco 4000 series, the Cisco 4700-M contains a 133MHz RISC microprocessor, 16 to 64 MB main memory, and a 512-KB secondary cache. The faster speed of the Cisco 4700-M allows higher throughput for high-speed interfaces. The 512-KB secondary cache is useful for process switching applications such as compression and encryption.
The Cisco 4500-M contains a 100MHz RISC microprocessor and 8 to 32 MB of main memory. The Cisco 4000-M contains a 40MHz CISC microprocessor and 4 to 32 MB of main memory.
All Cisco 4000 series routers provide flexibility, allowing network managers to easily reconfigure the router when needs change.
The Cisco 4000 series routers support up to three network processor modules at a time. The network processor modules supported on the Cisco 4000 series are as follows:
Figure 1-1 shows the front panel of a Cisco 4000 series router.
Figure 1-1 : Cisco 4000 Series Chassis---Front Panel
Design specifications for the Cisco 4000 series are as follows:
The BRI four-port and eight-port network interface modules can not be used in the same chassis with the channelized T1/ISDN PRI network interface module or the channelized E1/ISDN PRI network interface module.
The Cisco 4000-M does not support the ATM or six-port Ethernet network processor modules.The Cisco 4000-M can support only one FDDI network processor module in combination with any two other types of network processor modules.
The Cisco 4500-M and Cisco 4700-M can support two FDDI network processor modules. If you are only using one FDDI module, install it in the center slot for optimum heat dissipation.
The Cisco 4500-M and Cisco 4700-M can support one ATM network processor module or up to three six-port Ethernet network processor modules. The single-port Ethernet module is not supported on the Cisco 4500-M or the Cisco 4700-M.
Table 1-1 lists the network processor module interface options available for the Cisco 4000 series.
Table 1-1 : Network Processor Module Interface Options
| Interface Options | Port Options | Part Numbers |
|---|---|---|
| Ethernet | Single port, dual port, or six port | NP-1E=, NP-2E=, NP-6E= |
| Synchronous serial | Dual port or four port | NP-2T=, NP-4T= |
| Token Ring | Dual port or single port | NP-1RV2=, NP-2R= |
| Multimode FDDI | Single attachment or dual attachment | NP-1F-D-MM=, NP-1F-S-M= |
| Single-mode FDDI | Dual attachment | NP-1F-D-SS= |
| BRI | Four port or eight port | NP-4B=, NP-8B= |
| G.703 | Four port (balanced or unbalanced)1 | NP-4GB=, NP-4GU= |
| Channelized T1/ISDN PRI | Single channelized T1/PRI port | NP-CT1= |
| Channelized E1/ISDN PRI | Single channelized E1/PRI port | NP-CE1= |
| ATM | Single ATM port | NP-1A-SM=, NP-1A-MM=, NP-1A-DS3=, NP-1A-E3= |
Table 1-2 lists the specifications of the Cisco 4000 series routers.
Table 1-2 : System Specifications
| Description | Specification |
|---|---|
| Dimensions (H x W x D) | 3.4 x 17.6 x 17.7" (8.6 x 44.7 x 45 cm) |
| Weight | 24 lb (10.9 kg) (including the chassis and network processor modules) |
| Power | 100--240 VAC, 50--60 Hz, 3.0--1.5A or 40--72 VDC, 5--2.8A |
| Wire gauge for DC-input power connections | 14 AWG1 |
| Network interface options | Ethernet, serial, Token Ring, FDDI, BRI, G.703, channelized T1/PRI, channelized E1/PRI, ATM |
| Serial interfaces | EIA/TIA-232, EIA/TIA-449, V.35, X.21, NRZ/NRZI, DTE/DCE, EIA-530 DTE |
| Console port | EIA/TIA-232 DB-25 female connector |
| Auxiliary port | EIA/TIA-232 DB-25 male connector |
| Nonoperating temperature | -- 40--185°F (-- 40--85°C) |
| Operating humidity | 5--95%, noncondensing |
| Operating temperature | 32--104°F (0--40°C) |
| Regulatory compliance | FCC Class A, FCC Part 68, Canadian DOC Class A, CS-03, UL 1950 2nd edition, CAN/CSA 950-M93, EN60950 with Amendments 1 and 2, AN/NZS 3260, NOM 019 Additional regulatory compliance is in the Cisco 4000 Series Public Network Certification document that shipped with your router.) |
Network processor modules must be supported by the appropriate level of system software. The minimum system software version for the original Cisco 4000 was Software Release 9.1; for the Cisco 4000M, Software Release 9.14; for the Cisco 4500, and Cisco 4500-M, Cisco Internetwork Operating System (Cisco IOS) Release 10.2; for the Cisco 4700M, Cisco IOS Release 10.3(10). Table 1-3 lists the minimum system software versions for network processor modules.
Table 1-3 : Minimum Software Release Version
| Network Processor Module Type | Minimum Software Release Version |
|---|---|
| Multimode FDDI | Software Release 9.14(1) |
| Dual Ethernet | Software Release 9.14(2) |
| Six-port Ethernet | Cisco IOS Release 10.3(6) |
| Single-mode FDDI | Software Release 9.14(3) |
| Dual and Version 2 Token Ring | Software Release 9.14(5) |
| Four-port serial | Software Release 9.14(6) |
| ISDN BRI | Cisco IOS Release 10.2 |
| G.703 | Cisco IOS Release 10.2(7) |
| Channelized T1/ISDN PRI | Cisco IOS Release 10.3(4) |
| Channelized E1/ISDN PRI | Cisco IOS Release 10.3(4) |
| ATM OC-3C | Cisco IOS Release 10.3(4) |
| ATM DS-3 and E3 | Cisco IOS Release 11.0(5) |
Table 1-4 lists the processor and memory specifications of the Cisco 4000 series routers.
Table 1-4 : Cisco 4000 Series Processor and Memory Specifications
| Description | Cisco 4000-M | Cisco 4500-M | Cisco 4700-M |
|---|---|---|---|
| Processor | 40-MHz Motorola 68EC030 | 100-MHz IDT Orion RISC1 | 133-MHz IDT Orion RISC |
| Main memory (DRAM)2 | 4, 8, 16, or 32 MB | 8, 16, or 32 MB | 16, 32, or 64 MB |
| Secondary cache memory | None | None | 512 KB |
| Shared memory (DRAM) | 4 or 16 MB | 4, 8, or 16 MB | 4, 8, or 16 MB |
| Flash memory | 4 or 8 MB | 4, 8, 16, 32, or 64 MB | 4, 8, 16, 32, or 64 MB |
| NVRAM3 | 128 KB | 128 KB | 128 KB |
| Boot ROM | 128 KB--8 MB | 128--512 KB | 128--512 KB |
| Boot Flash | Not available | 4--16 MB | 4--16 MB |
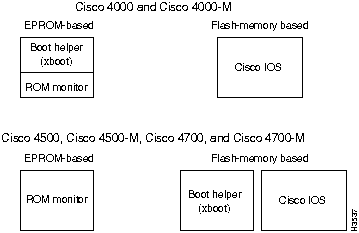
The Cisco 4000 series memory systems (see Figure 1-2) have the following functions:
The differences between the memory systems in the Cisco 4000 series allows enhanced software upgradability in the Cisco 4500-M and Cisco 4700-M.
Figure 1-2 : Cisco 4000 Series Memory Systems and Software Images
Each module in the Cisco 4000 series can change memory configurations to accommodate internetworking demands. The memory requirements are affected by the following factors:
The standard configuration for shared memory is 4 MB for the Cisco 4000 series. 4 MB of memory is enough for most configurations with fewer than 24 physical or virtual interfaces. Routers with multiple ISDN BRI network processor modules or with 24 or more physical and virtual interfaces require 8 to 16 MB of shared memory.
Table 1-5 : Cisco 4000-M Shared Memory Requirements
| Network Processor Module | Per-Module Shared Memory Requirements |
| Single-port Ethernet | 0.1 MB |
| Dual-port Ethernet and dual-port serial | 0.2 MB |
| Dual-port Token Ring, four-port serial, and G.703/G.704 serial | 0.4 MB |
| Eight-port BRI, CT1/PRI, and CE1/PRI | 1.0 MB |
| FDDI | 2.0 MB |
Table 1-6 : Cisco 4500-M and Cisco 4700-M Shared Memory Requirements
| Network Processor Module | Per-Module Shared Memory Requirements |
| Dual-port Ethernet and dual-port serial | 0.4 MB |
| Dual-port Token Ring, four-port serial, and G.703/G.704 serial | 0.6 MB |
| Six-port Ethernet, Eight-port BRI, CT1/PRI, and CE1/PRI | 1.2 MB |
| ATM and one FDDI1 | 2.0 MB |
| Two FDDI2 | 3.0 MB |
The amount of main memory required by a Cisco 4000 series router is affected by the size of the network and by the access list configurations. However, it is difficult to quantify the exact main memory requirements based only on network size. Use the following guidelines to determine approximate main memory requirements.
Main memory requirement guidelines for Cisco 4000 series routers are as follows:
|
|
Copyright 1988-1996 © Cisco Systems Inc.