|
|
The Exterior Gateway Protocol (EGP) is an interdomain reachability protocol used in the Internet, a large, international network connecting research institutions, government agencies, universities, and private commercial businesses. EGP is documented in Request For Comments (RFC) 904, published in April 1984.
As the first exterior gateway protocol to gain widespread acceptance in the Internet, EGP served a valuable purpose. Unfortunately, the weaknesses of EGP have become more apparent as the Internet has grown and matured. Because of these weaknesses, EGP is currently being phased out of the Internet, and is being replaced by other exterior gateway protocols such as the Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) and the Interdomain Routing Protocol (IDRP). For more information about these protocols, see Chapter 27, "Border Gateway Protocol," and Chapter 28, "OSI Routing."
EGP was originally designed to communicate reachability to and from the Advanced Research Projects Agency Network (ARPANET) core routers. Information was passed from individual source nodes in distinct Internet administrative domains called autonomous systems (ASs) up to the core routers, which passed the information through the backbone until it could be passed down to the destination network within another AS. This relationship between EGP and other ARPANET components is shown in Figure 26-1.
Figure 26-1 : EGP and the ARPANET
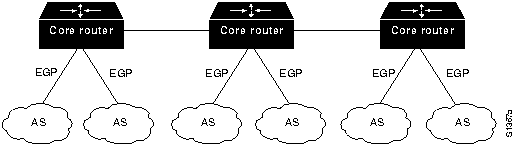
Although EGP is a dynamic routing protocol, it uses a very simple design. It does not use metrics and therefore cannot make intelligent routing decisions. EGP routing updates contain network reachability information. In other words, they specify that certain networks are reachable through certain routers.
EGP has three primary functions. First, routers running EGP establish a set of neighbors. These neighbors are simply routers with which an EGP router wishes to share reachability information; there is no implication of geographic proximity. Second, EGP routers poll their neighbors to see if they are alive. Third, EGP routers send update messages containing information about the reachability of networks within their ASs.
An EGP packet is shown in Figure 26-2.
Figure 26-2 : EGP Packet Format
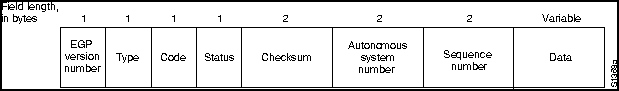
The fields of the EGP packet are as follows:
Table 26-1 : EGP Message Types
| Message | Function |
|---|---|
| Neighbor acquisition | Establishes/de-establishes neighbors |
| Neighbor reachability | Determines if neighbors are alive |
| Poll | Determines reachability of a particular network |
| Routing update | Provides routing updates |
| Error | Indicates error conditions |
Additional fields follow the EGP header. The contents of these fields vary depending on the message type (as specified by the type field).
The neighbor acquisition message includes a hello interval field and a poll interval field. The hello interval field specifies the interval period for testing whether neighbors are alive. The poll interval field specifies the routing update frequency.
The neighbor reachability message adds no extra fields to the EGP header. These messages use the code field to indicate whether the message is a hello message or a response to a hello message. Separating the reachability assessment function from the routing update function reduces network traffic because network reachability changes usually occur more often than routing parameter changes. Only after a specified percentage of reachability messages have not been received does an EGP node declare a neighbor to be down.
To provide correct routing between ASs, EGP must know the relative location of remote hosts. The poll message allows EGP routers to acquire reachability information about the networks on which these hosts reside. These messages only have one field beyond the common header---the IP source network field. This field specifies the network to be used as a reference point for the request.
Routing update messages provide a way for EGP routers to indicate the locations of various networks within their ASs. In addition to the common header, these messages include many additional fields. The number of interior gateways field indicates the number of interior gateways appearing in the message. The number of exterior gateways field indicates the number of exterior gateways appearing in the message. The IP source network field provides the IP address of the network from which reachability is measured. Following this field is a series of gateway blocks. Each gateway block provides the IP address of a gateway and a list of networks and distances associated with reaching those networks.
Within the gateway block, EGP lists networks by distances. In other words, at distance three, there may be four networks. These networks are then listed by address. The next group of networks may be those that are distance four away, and so on.
EGP does not interpret the distance metrics that are contained within the routing update messages. In essence, EGP uses the distance field to indicate whether a path exists; the distance value can only be used to compare paths if those paths exist wholly within a particular AS. For this reason, EGP is more of a reachability protocol than a routing protocol. This restriction also places topology limitations on the structure of the Internet. Specifically, an EGP portion of the Internet must be a tree structure in which a core gateway is the root, and there are no loops among other ASs within the tree. This restriction is a primary limitation of EGP, and provides an impetus for its gradual replacement by other, more capable exterior gateway protocols.
Error messages identify various EGP error conditions. In addition to the common EGP header, EGP error messages provide a reason field, followed by an error message header. Typical EGP errors (reasons) include bad EGP header format, bad EGP data field format, excessive polling rate, and the unavailability of reachability information. The error message header consists of the first three 32-bit words of the EGP header.
|
|
Copyright 1988-1996 © Cisco Systems Inc.