|
|

This chapter briefly describes some CiscoWorks applications and provides instructions on how to use them. It also contains an overview of how CiscoWorks functions with your HP OpenView network management platform. The chapter includes the following sections:
For detailed CiscoWorks application information, refer to the CiscoWorks online help system.
CiscoWorks now includes a new form of online help based on help systems supplied with Windows-based platforms.
Once you start the CiscoWorks online help system, you can jump to any topic within the system. For information on how to use the Help viewer, select Help>How to Use Help when the first help window appears.
Online help is available from several parts of CiscoWorks and its network management platforms:
CiscoWorks online help includes a Find button that allows you to do full-text searches within the help system. For information on how to do a search, select Help>How to Use Help when the first Help window appears.
The online system includes help descriptions for all CiscoWorks menus and windows, including windows that do not have help menus. You can view the online help system in the following ways:
CiscoWorks applications appear on your HP OpenView menus. To use CiscoWorks features and your HP OpenView software to the fullest, you must understand how to start the applications and complete some basic tasks. This section describes the location of the CiscoWorks applications on the HP OpenView menus and provides an overview of the post-installation tasks to complete before you begin to use CiscoWorks.
Table 5-1 lists the CiscoWorks applications and their menu locations, and explains the tasks they perform. The CiscoWorks applications are listed in alphabetical order.
In HP OpenView, start the CiscoWorks applications through any of the standard menu options (Administer, Monitor, Diagnose, or Misc)
| HP OpenView Menu Location | Tasks |
|---|---|
| Help>CW - Application Help | CiscoWorks online help system that allows you to investigate different levels of details within the online help system by selecting highlighted text to open additional windows. The online help system provides overview, related information, procedures, and glossary data on the CiscoWorks applications and features. It allows both keyword and full-text searches to enable users to search for specific text. |
| Administer>CW - Devices>CW - AutoInstall Mgr | Remotely deploy a new router using a neighbor router. Perform AutoInstall tasks remotely by running CiscoWorks instead of a Telnet session. |
| Administer>CW - Devices>CW - Configuration Mgr | Access configuration files of local and remote Cisco Systems devices to analyze or edit them as necessary. Compare the contents of two configuration files in the database, or compare the configuration currently running on a device with the configuration that represents the last Database to Device command you performed. |
| Administer>CW - Devices>CW - Configuration Snap-In Mgr | Create and execute selected or custom UNIX commands on a device or group of devices at any time with Global Command Scheduler. |
| Monitor>Description>CW - Contacts | Obtain information about the contact for a specific device, including the complete name, phone number, e-mail address, title, location, and address of the person responsible for the operation of the device. |
| Administer>CW - Devices>CW - Device Mgmt | Create and maintain a database that holds a complete inventory of your network--hardware, software, release levels of operation components, individuals responsible for maintaining the devices, and associated locations. Enter or change data in the database tables for network devices, networks, interfaces, contacts, vendors, and so on. |
| Monitor>CW - Device Polling | Probe and extract information about the condition of your networks using a polling feature. The information acquired is stored in the database for further evaluation and analysis. Compare the relative performance and status of devices and interfaces on the network. |
| Administer>CW - Software Images>CW - Device Software Mgr | Automate the upgrade of a system software or microcode image on a Cisco device. |
| Administer>CW - Security>CW - Domain Mgr | Create groups of devices (called domains) that CiscoWorks applications can use to accomplish network management tasks such as security, configuration, and device polling. |
| Monitor>CW - Environmental Monitor | View the environmental status of Cisco AGS+ and Cisco 7000 routers including temperature and voltage statistics. This function is available on AGS+ routers running System Software Release 9.0 or later with an environmental monitor card running ENVM Microcode Version 2.0 or later. |
| Administer>CW - System>CW - Global Command Mgr | Create, store, and execute system commands on a device or group of devices at any time with Global Command Scheduler. |
| Administer>CW - System>CW - Global Command Scheduler | Schedule commands or other jobs at regularly scheduled times using the crontab utility. |
| Monitor>CW - Health Monitor | View information about the status of a device, including buffers, CPU load, available memory, and protocols and interfaces being used. Enables you to display the Show Commands and Real-Time Graphs windows from the Health Monitor window. |
| Misc>CW - Login | Perform a generic login for all CiscoWorks applications that require user authentication so that you do not have to log in to each application separately. |
| Misc>CW - Logout | Log out of secured CiscoWorks applications to ensure security for those applications with authority checking turned on. |
| Diagnose>Network Connectivity>CW - Path Tool | View and analyze the path between two devices. Perform analysis on the path to collect utilization and error data. Display the devices encountered between the source and the destination device, the link speeds connecting these SNMP devices, and the interface names. |
| Monitor>CW - Polling Summary | Summarize the polling setup completed within Device Polling. Browse data, and stop and start polling. |
| Administer>CW - System>CW - Process Mgr | Start, stop, and view status of CiscoWorks-related processes including Polling (nmpolld), CiscoConnect (httpd), System Log (syslogd), Sybase Server (dataserver), and TACACS (xtacacsd) daemons. |
| Monitor>CW - Real-Time Graphs | View device information such as the router health (buffer space, CPU load, environment, free memory, and security); interface health (bits per second, bytes, errors, packets per second, packets, and queues); and protocol traffic (IP, ICMP, SNMP, TCP, UDP, AppleTalk, DECnet IV, Novell, VINES, and XNS) using a grapher utility. |
| Administer>CW - Security>CW - SA Password | Log in to the Sybase database account so you can perform system administrator tasks. |
| Administer>CW - Security>CW - Security Mgr | Create authority checking procedures to protect selected CiscoWorks applications and network devices from unauthorized individuals by requiring a login to use protected applications. This protection ensures that only users with a valid account and password can perform tasks such as configuring a router, deleting database device information, or defining polling procedures. |
| Diagnose>CW - Show Commands | View device data about any SNMP device, including Cisco routers and communication servers. This data includes the software version, buffers, selected device interfaces, traffic mix, IP accounting checkpoint, ARP, and IP route. Emulates the EXEC show commands for Cisco routers. |
| Administer>CW - Software Images>CW - Software Inventory Mgr | Update the Sybase database to include current device software and hardware status. Sort device information according to platform and software image, and invoke Device Software Manager to update specific devices. |
| Administer>CW - Software Images>CW - Software Library Mgr | Maintains a master storage area that contains a list of all available Cisco system software. These Cisco IOS software images are retrieved by the user with a variety of methods. |
| Misc>CW - Sync w/Sybase | Synchronize the HP OpenView and Sybase databases. CiscoWorks maintains data in the Sybase database, whereas HP OpenView maintains its own database. Sync w/Sybase ensures that device data from the HP OpenView database is in the Sybase database (Sync w/Platform) and vice versa. Generally, synchronize the databases whenever new devices are added to your network. Use Sync Selected to add individual devices. |
| Misc>Sybase ESQR | Use Sybase ESQR utilities to run and print reports on any table created with the Device Polling application. |
| Administer>CW - Security>CW - TACACS Mgr | Maintain the TACACS password file on UNIX hosts that act as TACACS servers. Create and update TACACS accounts and computer-generated passwords. |
| Misc>CW - Toolbox | Allows you to start CiscoWorks applications directly, without using the menus on your network management platform. Click on an application's icon in the Toolbox window to start the application. You can also display help for each application from the Toolbox. |
Perform the following tasks before using any CiscoWorks application on HP OpenView:
Before performing any of these tasks, you must become familiar with the HP OpenView Console window and learn how to access its menu items.
CiscoWorks is integrated with HP OpenView network management platform.
During installation and configuration, CiscoWorks adds customized schema files with Cisco-specific device types (such as the Cisco AGS+) to the platform's schema files directory. CiscoWorks also adds its applications to the HP OpenView menus.
It is important to understand the HP OpenView environment and how to use your platform software in conjunction with CiscoWorks. To answer your network management questions, refer to HP OpenView documentation.
The following sections provide detailed information on HP OpenView post-installation tasks, and an overview of how CiscoWorks functions on the HP OpenView network management platform:
This section briefly explains two ways to start the HP OpenView Console to run CiscoWorks. You can use several commands to start the HP OpenView Console. However, you must be running an X windows manager, such as Motif.
Perform the following tasks to start CiscoWorks when there is no database present:
Step 1 To start the HP OpenView Console initially (when no database is present) or when you want to bring up the last map file, enter the following:
ovw
If problems occur, your PATH environment variable might not include a path to the HP OpenView executables. You can enter a fully qualified path. In the following example, /opt/OV/bin is the path to the executables:
/opt/OV/bin/ovw
If you don't want to start HP OpenView with a network map, or you want to load a specific map with the startup command, skip to the following section, "Starting CiscoWorks with the Database."
Step 2 Select File>Open/List Maps to load a database map file into the HP OpenView Console.
To start CiscoWorks when the database is present:
%ovw -mapmap_name
For more information on starting the HP OpenView Console or troubleshooting startup problems, refer to the HP OpenView 3.3 User's Guide or the HP OpenView 4.0 User's Guide.
CiscoWorks is fully integrated with HP OpenView, so you can access CiscoWorks applications directly from the main window of the HP OpenView platform. (See Figure 5-1 and Figure 5-2.)
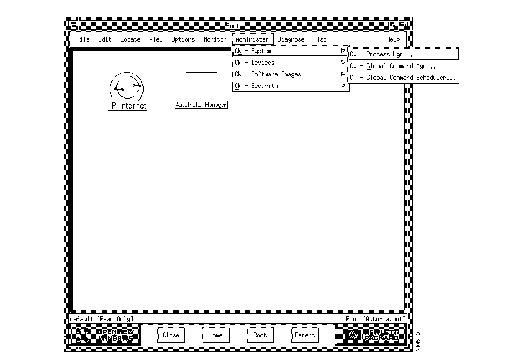

CiscoWorks applications are available from HP OpenView main menus. For example, to open the Process Manager application, select Administer>CW - System>CW - Process Mgr.
HP OpenView does not use glyphs or a Glyph menu. To access device-dependent applications, perform the following steps:
Step 1 Select a device in your network map or submap.
Step 2 Select the specified CiscoWorks application from the appropriate menu.
This section briefly outlines the steps you must complete on HP OpenView before continuing with CiscoWorks tasks. For instructions on using specific CiscoWorks applications, refer to the appropriate sections in this section, or to the CiscoWorks online help system.
Follow these steps to learn about CiscoWorks applications that use the Sybase database:
Step 1 HP OpenView.
Refer to the sections "Starting CiscoWorks on HP OpenView," earlier in this chapter, to learn how to start HP OpenView.
Step 2 Access Security Manager to turn on authentication checking and provide users and groups access privileges to CiscoWorks applications.
For more information, refer to the CiscoWorks online help section on setting up domains and securing applications in Security Manager.
Step 3 Set up your database using the utilities provided with HP OpenView software.
For information on the HP OpenView Manage Objects command, refer to the section "HP OpenView Processes That Affect CiscoWorks," or to the HP OpenView documentation.
Step 4 Use Sync w/Sybase to synchronize your HP OpenView database devices with the CiscoWorks Sybase database.
If you are adding individual devices, use the Device Management, AutoInstall Manager, or Sync w/Sybase applications to add device data to the Sybase database. For information on AutoInstall Manager, Sync w/Sybase, and Device Management, refer to the appropriate CiscoWorks online help sections.
Step 5 Use the CiscoWorks applications and HP OpenView utilities to help you monitor and manage your network activity.
Table 5-2 lists the general network management tasks and their responsible software applications. Use this table to determine which documentation set (CiscoWorks or
HP OpenView) to use if you have questions or need information. The X indicates that this information is located in the HP OpenView manual set for the utility or application.
CiscoWorks uses one HP OpenView application, xnmgraph, which presents real-time or logged network data in graphical format. The xnmgraph application is used in the Health Monitor and Real-Time Graphs applications to display data in graphical format. You can change the graph properties either with the popup menu on the graph window or by editing the X resources in the /usr/OV/app-defaults/XNm file for HPOV 3.3 and $APP_DEFS/XNm for HPOV 4.0.
For more detailed information on xnmgraph, refer to your HP OpenView documentation.
Some HP OpenView processes affect how CiscoWorks runs, depending on their configuration in OpenView. As you continue to work with OpenView processes and CiscoWorks, consider the following conditions in which the two environments coexist:
CiscoWorks applications require a database of network devices and a network map that contains these devices. HP OpenView automatically displays a default map, called IP Map, which shows all the IP devices connected to the local HP OpenView system. The Manage Objects command enables you to find the devices in the primary network to which your system is attached. Use this command to view your network and a run-time database for HP OpenView.
To run the Manage Objects command, perform the following steps:
Step 1 Display the HP OpenView Console by entering the following command:
ovw
The HP OpenView Console window appears.
Step 2 Click on the IP Internet default map to open it.
Step 3 Click on a device symbol to select it.
Step 4 Select Options>Manage Objects.
Manage Objects begins to construct views of the network. When the process is complete, you see a representation of the subnetwork joined to the selected device. Subnetworks appear in the form of lines connecting the selected device symbol to other device symbols.
Step 5 Select File>Save Map As to save the database of devices that you created.
For detailed information on how to run the Manage Objects command, refer to the HP OpenView User's Guide. To add devices to a network map after CiscoWorks installation, you can use the Device Management, AutoInstall Manager, or Sync w/Sybase applications. For more information on adding devices after CiscoWorks installation, refer to the next section, "Adding Cisco Devices to Your HP OpenView Network Map."
To add a Cisco device to your new network map, perform the following steps:
Step 1 Display your network map.
Refer to your HP OpenView documentation for instructions on how to use your network map.
Step 2 Select Edit>Add Object.
The Add Object Palette appears.
Step 3 Click on the Cisco router icon to display the Symbol Subclasses for Cisco Routers.
Step 4 Using the left mouse button or its equivalent, click on a Cisco device symbol; then move your mouse to the network map and click the left mouse button again.
The Cisco device symbol is copied into the map and the Add Object window appears.
Step 5 Complete the Add Object window; then click on OK to record information about the object you just added.
Network devices that are discovered by the Manage Objects command may exist as generic devices. You must identify them as Cisco devices to take advantage of CiscoWorks functionality.
To change device status from generic to that of a Cisco device, perform the following steps:
Step 1 Use the mouse to point to a Cisco device in the HP OpenView Console window.
Step 2 Press the right mouse button or its equivalent.
The symbol popup menu for the device appears, as shown in Figure 5-3.

Step 3 Select Change Symbol Type from the Symbol Popup menu.
The Change Symbol Type window appears, as shown in Figure 5-4.

Step 4 Select a symbol class that corresponds to the device selected in the map. For example, if the selected device in your network map is a Cisco 7000, select Cisco Router (because Cisco 7000 is a class of Cisco Router).
The Change Symbol Type window expands to display the Symbol Subclasses for Class Cisco Router.
Step 5 Select a symbol subclass for the specified symbol. For example, if the selected device in your network map is a Cisco 7000, select the 7000 symbol.
Step 6 Repeat Steps 1 through 5 to identify other devices in the network map.
Step 7 Confirm that the selected devices have the correct SNMP community strings by viewing the SNMP Configuration window. Select Options>SNMP Configuration from the HP OpenView menu bar.
CiscoWorks uses two separate databases:
The HP OpenView run-time database is a third database that interacts with the CiscoWorks databases. This platform database stores information about the network. By synchronizing the Sybase database with the HP OpenView database of the network platform, you build a complete resource of information.
Your HP OpenView platform maintains a run-time database of devices that you create using HP OpenView utilities. In order to use CiscoWorks applications, you must list devices in the Sybase database. Sync w/Sybase performs the following functions to enable you to use CiscoWorks applications:
Use Sync w/Sybase to synchronize database information. The Sync w/Sybase application appears in the CiscoWorks menu and device popup menus. Run Sync w/Sybase if you just initialized
HP OpenView and want to fully synchronize both databases. Run Sync w/Sybase from the device menu if you want to synchronize one or more specific devices. In both cases, the Sync w/Sybase window, from which you can select other options, displays. (See Figure 5-5.)

Depending on the number of database records and the information contained in each, database synchronization can be time-consuming.
 | Time Saver First-time CiscoWorks users should run the Device (Network>Sybase) option to synchronize all device information. If you are a first-time user and want the quickest method of synchronizing, use Quick Sync, which synchronizes all the devices, with the warning that device information will not be complete. If you use Quick Sync, you may want to return to Sync w/Sybase when you have more time to use the Device (Network>Sybase) option to fill in the incomplete device information. |
To adjust for synchronization time and to meet special needs, select one of the following commands from the Options menu of the Sync w/Sybase window:
Figure 5-6 illustrates the relationship between the HP OpenView and CiscoWorks databases. Although you can add device names directly to either database, you must run Sync w/Sybase to confirm that the information about a particular device is correct in both places.
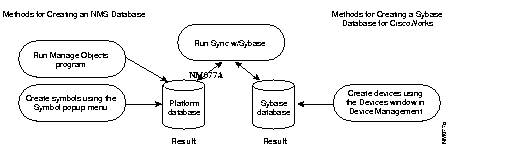
For more detailed information about the database and the Sync w/Sybase and Sync with
HP OpenView applications, refer to the CiscoWorks online help on "Sync w/Sybase." For more information about the AutoInstall Manager application, refer to the CiscoWorks online help on "AutoInstall Manager."
When you have finished creating a run-time database with network devices, follow these steps to run the Sync w/Sybase application:
Step 1 Select Misc>Sync w/Sybase.
The Sync w/Sybase window appears. (See Figure 5-7.)
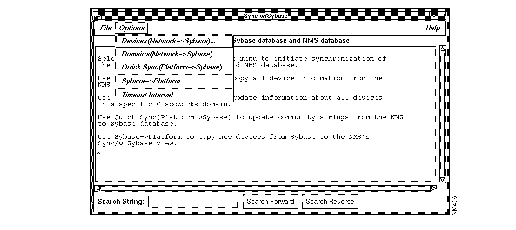
The synchronization process takes from 3 minutes to over an hour, depending on the size of your network and the number of devices you are synchronizing.
Select File>Exit to stop the synchronization process at any time. The devices synchronized up to this point are saved in the Sybase database.
Step 2 Select File>Exit to exit this window.
To use HP OpenView and CiscoWorks, you must make sure that the environment variables explained in are set correctly. Refer to the section "Verifying Changes to the .cshrc File," in the "Validating CiscoWorks Installation" chapter.
Normally, these environment variables are set during the CiscoWorks installation process.
This section provides an overview of how to use a CiscoWorks application. It uses the Path Tool application as an example. For a detailed explanation of all CiscoWorks applications, refer to the CiscoWorks online help.
To use the Path Tool application, you must have at least two network devices in the Sybase database. Use Sync w/Sybase to add network devices to the Sybase database.
The Path Tool application enables you to display the routing path between a source device and a destination device.
To graphically display the path between two devices, perform the following steps:
Step 1 In the HP OpenView Console window, click on an SNMP device and select Diagnose>Network Connectivity>CW - Path Tool.
A window similar to that in Figure 5-8 appears. The information about the source device is completed.

Step 2 To select the destination device, click on Select next to the Path Destination field or enter the complete device name in the Path Destination field.
If you click on Select, the Device Selection window appears listing the devices in the HP OpenView database. It is similar to the window shown in Figure 5-9.

Step 3 Click on the device that you want to specify as the destination and click on OK.
After the connection has been established, the device name appears in the Path Destination field in the Path Tool window.
Step 4 Click on OK in the Path Tool window to display the Path Tool Hops window.
A browser window appears (similar to the window shown in Figure 5-10), displaying the progress of the Path Tool as it makes each network hop from the source to the destination device.

After the connection is established, another Path Tool window appears (similar to the window shown in Figure 5-11), graphically displaying the path between the source and destination devices you specified.

Step 5 Select File>Exit to close the window.
For more information on how to use the Path Tool, refer to the online help for Path Tool.
If you use the Security Manager application to protect specific applications, all users must enter a valid username and password to access applications. For a detailed description of which CiscoWorks applications you can protect, refer to the CiscoWorks online help section on setting up domains and securing applications.
Each CiscoWorks application has varying levels of access privileges. Users are granted inherent privileges to certain applications (such as the ability to display devices) based solely on their group-domain associations. The CiscoWorks administrator governing Security Manager can grant further levels of "application-specific" privileges (such as add or change database information) to selected groups.
When security is enabled, if you previously used the Login command to log in to CiscoWorks, a user identification window does not appear. If you do not use the Login command, CiscoWorks prompts you for a username and password each time you run a secured application. This login controls access to the application.
If you use Security Manager to secure your CiscoWorks applications, you can use Login and Logout. For more information on logging in and out, refer to the CiscoWorks online help section on Login and Logout.
|
|